 Reconstruction is a process of the company’s reorganization, concerning legal, operational, ownership and other structures, by revaluing assets and reassessing the liabilities. There are two methods of reconstruction which are internal reconstruction and external reconstruction. The former is the method in which the reconstruction is undertaken without winding up the company and forming a new one, while the latter, is one whereby the existing company loses its existence, and a new company is set up to take over the business of the existing company.
Reconstruction is a process of the company’s reorganization, concerning legal, operational, ownership and other structures, by revaluing assets and reassessing the liabilities. There are two methods of reconstruction which are internal reconstruction and external reconstruction. The former is the method in which the reconstruction is undertaken without winding up the company and forming a new one, while the latter, is one whereby the existing company loses its existence, and a new company is set up to take over the business of the existing company.
Reconstruction is required when the company is incurring losses for many years, and the statement of account does not reflect the true and fair position of the business, as a higher net worth is depicted, than that of the real one. Here, in the given article, we are going to talk about all the important differences between internal and external reconstruction.
Content: Internal Reconstruction Vs External Reconstruction
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Internal Reconstruction | External Reconstruction |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Internal reconstruction refers to the method of corporate restructuring wherein existing company is not liquidated to form a new one. | External reconstruction is one in which the company undergoing reconstruction is liquidated to take over the business of existing company. |
| New company | No new company is formed. | New company is formed. |
| Use of specific terms in Balance Sheet | Balance Sheet of the company contains "And Reduced". | No specific terms are used in the Balance sheet. |
| Capital reduction | Capital is reduced and the external liability holders waive their claims. | No reduction in the capital |
| Approval of court | Approval of court is must. | No approval of court is required. |
| Transfer of Assets and Liabilities | No such transfer takes place. | Assets and liabilities of existing company are transferred to the new company. |
Definition of Internal Reconstruction
A recourse undertook by the enterprise, in which substantial changes are made in the company’s capital structure, without resorting to the liquidation of the existing company, is called internal reconstruction. In finer terms, it is the inner rearrangement of the company’s financial structure, in which the company undergoing reconstruction continues to exist.
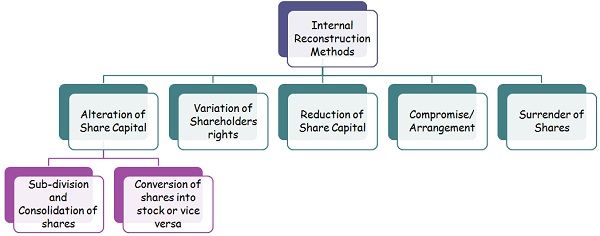
Internal Reconstruction focuses on relieving the company from debts and losses by negotiating with the creditors and reducing the outstanding amount towards them, so as to reach a favorable position. The methods given below are generally employed to effect the internal reconstruction process:
- Alteration of Share Capital
- Sub-division and Consolidation of Shares
- Conversion of shares into stock or stock into shares.
- Variation of Shareholder’s rights
- Reduction of Share Capital
- Compromise/Arrangement
- Surrender of Shares.
In this process, the assets are restated, to represent fair values, and liabilities are restated to show the settable amount, and thus the balance sheet shows a true picture. In this scheme, trading losses and fictitious assets are written off, against the claim sacrificed by the debenture holders, creditors, etc.
Definition of External Reconstruction
External Reconstruction is a process in which the company’s financial affairs are wound up, and a new company is formed to take over the assets and liabilities of the existing company, after the reorganization of the financial position. It requires the approval of shareholders, creditors and National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT).
In external reconstruction, the undertaking is being continued by the company but is in substance transferred to a company which is not an external one, but another entity that comprises of almost same shareholders, to be carried on by the transferee company. The accounting treatment of external reconstruction is same as the amalgamation in the nature of the purchase.
Key Differences Between Internal and External Reconstruction
The following points are relevant on account of the differences between internal and external reconstruction:
- Internal reconstruction can be defined as the reorganization of the company, without liquidating the existing company and forming a new one. On the other hand, an external reconstruction is a form of corporate restructuring wherein the existing company is liquidated to give birth to a new company, for continuing the business of the existing one.
- No new company is formed in internal reconstruction. Conversely, the new company is formed in the external reconstruction, to take over the business of the existing company.
- In internal reconstruction, the capital of the company is reduced, and external liabilities such as debenture holders and creditors waive their claims by giving a discount. On the other hand, in external reconstruction, there is no reduction in the capital of the company.
- In internal reconstruction, court’s approval is mandatory, because the reduction in capital may affect the rights of the shareholders, which requires confirmation from the court. As against, in external reconstruction, there is no such approval required.
- When the company undergoes internal reconstruction process, the Balance sheet prepared after the process contains the terms, “And Reduced.” On the contrary, there are no specific terms used in the Balance Sheet in the case of external reconstruction.
- In internal reconstruction, since there is no new company is formed, there is no transfer of assets and liabilities. Unlike, external reconstruction, assets, and liabilities of the old company are transferred to the new company.
Conclusion
The primary objective of reconstruction of an entity is the reorganization of its capital which can be done by canceling unrepresentative value of the assets of the business, settling creditors claim by taking the discount and achieving economies in operations.





mark natili says
what an article. Thank you
genesis tweek says
thank you for making this site, during my exam, I visited u guys millions of times.