 Programmed Decisions can be understood as, those decisions which can be taken with the help of customary or routine approach. On the other hand, Non-programmed Decisions are the ones that are taken when there is a rare or unexpected problem faced by organizations.
Programmed Decisions can be understood as, those decisions which can be taken with the help of customary or routine approach. On the other hand, Non-programmed Decisions are the ones that are taken when there is a rare or unexpected problem faced by organizations.
Decision making is a tough task wherein a person has to weigh all the pros and cons of each alternative, in order to logically choose one course of action out of the various alternatives available. While making any decisions, one must consider the values, preferences and beliefs associated with the choice.
Decision making is one of the managerial function, which is divided into two types, programmed decisions and non-programmed decisions. So, now we are going to tell you the difference between these two types of decisions, have a look.
Content: Programmed Vs Non-programmed Decisions
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Programmed Decisions | Non-programmed Decisions |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Programmed decisions are the everyday decisions, which are taken within the periphery of the organization's rules and policies. | Non-programmed decisions are known for dealing with rare or unusual problems, which do not have predefined alternatives. |
| Problem | Well-structured and repetitive | Ill-structured and non-repetitive |
| Decision made by | Middle or Low-level managers | Top-level managers |
| How to take decisions? | Predefined rules, policies and standards | Logical and creative thinking |
| Impact | Short term | Long term |
| Problem-related information | Readily available | Unavailable or available to some extent only |
| Judgement | Objective judgement | Subjective judgement |
Definition of Programmed Decisions
Programmed Decisions are those decisions which are taken at various stages during the operational process. These are regular or recurring in nature and so there is an existing set of rules, guidelines and procedures available to consider while taking the decisions. This is due to the reason that the problem occurs frequently and so the solution is readily available. These are alternately called as routine decisions or low-involvement decisions.
The decision is based on significant factors that are measurable and observable, and that is why, the decision can be taken quickly without a lot of discussions, as well as consistency is maintained in decision making.
While taking a programmed decision, the manager need not look for alternative solutions, rather a structure and non-creative pattern is followed to deal with it. Further, the decision is simple or sometimes relatively complex, but the criteria are clearly laid out, which the supervisors, managers or department heads have to consider while taking such decisions.
Definition of Non-programmed Decisions
Non-programmed Decision refers to the novel decisions made by the top-level executives to resolve an unexpected issue, which may or may not occur in future. These are also referred to as non-routine or high-involvement decisions.
These are rational and comprehensive decisions, for which any criteria is not specified, because of unavailability of the required or complete information. They are taken when a new and unique problem or situation arises before the management, mainly because of the dynamic business environment.
The criteria for taking non-programmed decisions are not clearly defined or sometimes not defined at all. So, a number of factors are considered and the situation is discussed with the panel of top executives or managers, so as to identify various possibilities, that may take place as a result of the decisions and a final solution to the problem or situation is chosen, to cope with the situation.
Therefore, the decision-maker needs to think creatively, rationally, independently and tactfully, with the company’s future in mind, so as to make a sound decision. Further, a considerable degree of risk and uncertainty is always there because the consequences are unknown.
Key Differences Between Programmed and Non-programmed Decisions
The points given below are substantial so far as the difference between programmed and non-programmed decisions:
- Programmed Decisions are those decisions which are concerned with well-defined situations or circumstances and are made considering standard operating procedures. On the other hand, Non-programmed decisions are new and undefined, for which subjective judgement is needed to be taken by the company’s highest level of management.
- Programmed Decisions are usually taken in the normal course of operations, as they occur on a daily basis. Non-programmed decisions are taken when there is a sudden, unexpected issue or situation arises before the company.
- Programmed Decisions are taken by middle or low-level management, whereas non-programmed decisions are taken by top-level management of the company.
- When it comes to the nature of decisions, the programmed ones are structured and repetitive. As against, the unprogrammed ones are unstructured and non-repetitive.
- One can handle programmed decisions through pre-defined standards, rules, procedures and business patterns. On the other hand, scientific analysis, creative thinking and logical reasoning are required to handle non-programmed decisions.
- The impact of programmed decisions is for the short term only, because they take place very often. Conversely, non-programmed decisions have a far-reaching impact, as they are taken for exceptional issues, which do not occur in general.
- Programmed decisions rely on objective judgement wherein previous experiences and past records are considered. As against, non-programmed decisions rely on subjective judgement, wherein the situation or problem is thoroughly assessed to find out alternative solutions.
Examples
Programmed Decisions:
- Reorder of material and supplies.
- Employees request for leaves.
- Development of a weekly work schedule.
- Recruitment and training of new employees.
Non-programmed Decisions:
- Increase in distribution expenses.
- Adoption of a new technique of production.
- Business Process Reengineering decision
- Change in government policies, in which the company deals.
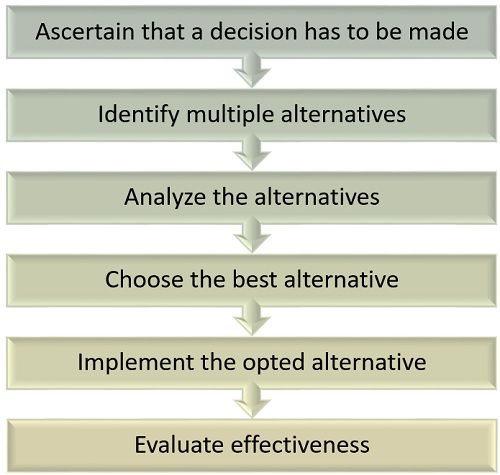
Decision-making Process
Conclusion
To sum up, decision making is the process of identifying and choosing from various alternatives, the best course of action to solve the problem at hand.
Programmed Decisions help managers to make a similar decision for the same situation, rather than making a new decision every time.
On the flip side, non-programmed decisions are difficult because no or incomplete information is available to the management concerning the problem. So the decision-maker needs to think wisely and creatively to deal with the same.






Leave a Reply