 In common parlance, supply means making something available or providing something. In economics, supply is used in the context of goods, it means the quantity of goods offered for sale by the producer, in the market at a given price and time. It is often contrasted with stock, which refers to the excess of goods present in the market over the goods supplied.
In common parlance, supply means making something available or providing something. In economics, supply is used in the context of goods, it means the quantity of goods offered for sale by the producer, in the market at a given price and time. It is often contrasted with stock, which refers to the excess of goods present in the market over the goods supplied.
While supply is obtained from stock, the stock is the result of production. In other words, the total quantity of finished goods present with the seller is stock whereas that part of the stock that is offered for sale is a supply.
In this write-up, we have discussed the differences between stock and supply.
Content: Stock Vs Supply
- Comparison Chart
- Definition
- Key Differences
- Example
- What is Supply Function?
- Determinants of Supply
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Supply | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Stock refers to the total quantity of goods measured at a particular point of time, that is available with the producers. | Supply implies the actual quantity of goods that the seller is ready to sell at a particular price, at a given point in time. |
| Time Dimension | No time dimension | It has a time dimension. |
| Measurement | It is measured at a certain point in time. | It is measured over a specific period of time. |
| Depends on | Production | Price |
| Interdependence | Not dependent on supply, so it can be greater than or less than supply. | Depends on stock, it is always less than the stock |
| Nature | Static | Dynamic |
| What does it do? | It helps to fulfill the sudden or unexpected rise in the market demand for the product. | It helps in the generation of revenue. |
| Increases | With the increase in production. | With the increase in stock. |
Definition of Stock
Stock refers to the total quantity of goods, which are available with the producers during a given period of time. It comprises both – the quantity of goods supplied for sale and the quantity of a commodity stored, hoarded, or withdrawn from the market, to be sold in the future. That is why a stock is also called potential supply.
The stock of a commodity is equal to the total quantity of the commodity produced, during a period minus the quantity of the commodity sold. However, all that is produced by the producers, is not offered for sale in the market as a definite part is stored in the warehouses, and released when the prices are favorable.
Hence, it is that quantity of the commodity which is present in the market and can be supplied for sale in short notice, is stock.
Stock = Unsold goods + Current Production – Current Sales
So, the quantity of stock primarily includes the stock in hand. Also, it will include the stock produced but excludes the stock sold, during the year.
Example
There are four firms operating in the market that manufactures pen. In the month of April, Firm A manufactured 5000 pens and sold 2000 pens, Firm B manufactured 6000 pens and sold 3000 pens, Firm C manufactures 2500 pens and sold 1000 pens, and Firm D manufactured 9000 pens and sold 3500 pens. The unsold stock was 10000 pens. In this way, the total stock of pens is 23000 pens.
Also Read: Difference Between Stock and Flow
Definition of Supply
In Economics, the term ‘supply’ can be defined as the various quantities of a commodity which a seller is willing and able to sell, at the different prevailing prices in the market, over a specified period of time. This means that supply does not mean the complete stock of commodity, rather it includes only that portion of goods that is brought to the market by the producers, for the purpose of selling and distribution.
- It indicates a relationship between price and quantity.
- It is one part of the market exchange, the other part is demand.
- It implies the desired quantity, which the producers are willing to sell, not the quantity they actually sell.
- It is also a flow, just like a demand.
The three aspects of supply are:
- Willingness and Ability
- Range of Prices and Quantities
- Given Time Period
The supply of goods is highly affected by the prevalent market price, as the supply of goods tends to increase with the increase in its price and vice versa. Therefore, as the price of the goods rises or falls from time to time, consequently the supply increases or decreases.
Example
A firm manufactures body lotion. In the year 2020, it produced 50000 units of body lotion and the previous stock was 12000 units, out of which 18000 units were offered for sale @ Rs. 200 per unit, 12000 units for Rs 220 and 8000 units for Rs. 235. So, the different quantities of units offered at different prices indicate supply.
Also Read: Difference Between Demand and Supply
Key Differences Between Stock and Supply
So far we have understood the concept of stock and supply, now let us understand the difference between stock and supply with explanation:
- By the term ‘stock’ we mean the total volume of goods that can be brought to the market on short notice, for the purpose of selling and distribution. As against, supply indicates the number of goods which is offered for sale in the market. It is that part of the stock which the seller has made available for sale in the market.
- When it comes to the time dimension, the stock has no time dimension, but supply is measured with reference to time, i.e. per year, per month, per week, or per day.
- The stock of a commodity is measured at a specific point in time. As against, we measure supply over a particular period of time.
- The stock of the commodity is based on production, whereas the supply of the commodity depends on price, along with other factors.
- While the stock of goods is independent of supply, so it can be more than or less than the supply of goods, the Supply of commodity depends on the stock. Therefore, it is usually less in comparison to the stock, as stock includes current as well as previous stock.
- As supply is concerned with the period of time, it is a flow concept. It keeps on changing and displays an ongoing activity that is why it is dynamic in nature. Oppositely, the stock is static in nature because the stock is calculated at a specific point in time, so it provides a record of the total quantity of a commodity on that date.
- The stock of goods facilitates in meeting the unexpected rise in the demand for the product in the market, on short notice. On the other hand, goods are supplied by the company, to offer for sale and generate revenue.
- As the production of goods increases, the stock also increases, whereas the supply of the goods increases with an increase in the stock.
Example
Zyx ltd manufactures notebooks. In the year 2021, it manufactured 10,00,000 notebooks, out of which, the firm supplied 3,00,000 notebooks for sale @ Rs. 150 per notebook, 1,50,000 notebooks for Rs. 180 and 3,00,000 notebooks for Rs. 200 and 2,50,000 for Rs. 210.
In the given case, 10,00,000 notebooks represent the stock of notebooks with the manufacturer, whereas the different quantities of notebooks available for sale at different prices are its supply.
What is Supply Function?
The functional relationship existing between the total quantity supplied of the goods and the determinants of supply is called the supply function.
Determinants of Supply
The factors influencing the supply of a commodity are discussed here: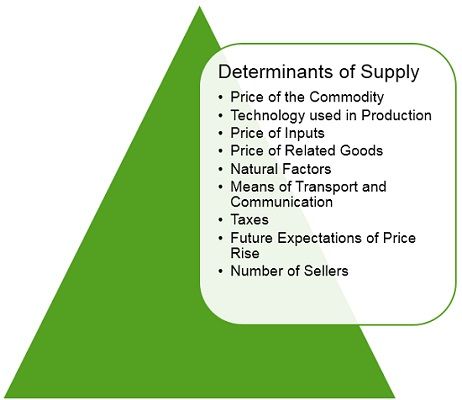
Price of the Commodity
The price of the commodity has a great influence on its supply. This is because, the producer spends a huge amount on the production of goods by arranging the required resources, like land, labor, capital, raw materials, machinery, etc. commonly known as cost of production.
The amount invested by the producer in production can be recovered by selling the product at different prices. Hence, higher price fetches higher revenue and so higher will be the supply.
Technology used in Production
The technology of production plays a crucial role in the supply of the commodity because when new and improved technology of production is used, it reduces the overall investment and increases the profit margin. And this encourages the producers to supply more quantities of commodity.
Price of Inputs
As the price of the inputs used in the production of the commodity decreases, the total cost of production tends to decrease, and there will be an increase in the profit margin. And this will increase the quantity supplied by the firm.
Conversely, when the price of the inputs increases, the overall cost of production increases, and there will be a decrease in the profit margin which discourages the firms to supply more of that commodity at the prevailing prices.
Price of Related Goods
Suppose a firm produces two gadgets mobiles and tablets, if there is a rise in the price of the mobiles, the firm will be encouraged to produce that with the given resources, as it will fetch more profit to the firm, resulting in a decrease in the supply of tablets.
Natural Factors
The supply of agricultural produce is greatly influenced by favorable or unfavorable natural conditions, like rain, sunlight, seed quality, irrigation. fertility of the land, climatic conditions, etc. Also, natural calamities like droughts, floods, etc also badly affect the crops.
Means of Transport and Communication
Modern transportation and communication facility helps in maintaining the supply of the commodity, as it can be easily moved from one location to another without any delay, thus reducing the lead time.
Taxes
When taxes are imposed at a high rate by the government on a certain commodity, this discourages the firms to produce such commodities, which also reduces their supply.
Future Expectations of Price Rise
If there is an expectation that the prices might rise in the coming time, then the present supply of the commodity expecting price rise is curtailed, with an aim of increasing the supply when the prices go up.
Number of Sellers
The total number of sellers existing in the market, often determines the quantity supplied of the commodity, as the higher the number of sellers, the higher would be the quantity supplied.
Conclusion
As we all know, prices of goods and services are determined by the market forces, i.e. demand and supply and so when the prevailing prices are low, a lesser quantity is supplied by the seller, even when he has an abundant stock of goods. Contrarily, when the prevailing prices are high, a large quantity is supplied by the seller.
So we can say that, when the prices are low, less quantity of goods is supplied.



Leave a Reply