 Management Audit refers to an independent examination of the managerial activities undertaken at different levels of the management so as to determine its functions, efficiency and achievement. On the other hand, Cost Audit refers to the process of authenticating the cost of production, based on the accounts, concerning the use of material, labour and overheads, which a company maintains.
Management Audit refers to an independent examination of the managerial activities undertaken at different levels of the management so as to determine its functions, efficiency and achievement. On the other hand, Cost Audit refers to the process of authenticating the cost of production, based on the accounts, concerning the use of material, labour and overheads, which a company maintains.
What does the word ‘Independent’ mean in Auditing?
‘Independent’ means the opinion which an auditor expresses is not subordinate to the wishes of the party who have appointed him. So, he does not follow the instructions of any such party while giving his opinion on the examination performed.
In this content, we will enlighten you with all the points of difference between cost audit and management audit.
Content: Cost Audit Vs Management Audit
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Cost Audit | Management Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Cost Audit refers to the comprehensive checking and examination of the correctness of the cost statements, data, records and systems. | Management Audit implies a complete examination of the company to appraise its policies, plans and structure of the management, to ascertain its effectiveness. |
| Is it mandatory? | Yes, for certain classes of companies, it is mandatory to perform a cost audit. | No, it is not mandatory for companies to perform management audit. |
| Auditor's Qualification | The person must be a practicing CMA. | Any independent expert or management consultant or internal auditor of the company. |
| Periodicity | It is conducted for every financial year. | It is conducted for more than one financial year. |
| Audit Report Submission | There is a prescribed time limit within which the report should be submitted. | No time limit for submission of the management audit report. |
| Accountability | The auditor is accountable to the shareholders and central government. | The auditor is accountable to the company's management. |
| Objective | To determine the reliability of cost information. | To review management's efficiency, so as to improve it. |
| Base | Cost statements | Managerial Activities |
| Audit Techniques | Examines and analyses data of material, labor and overheads. | Identifies the adequacy and reliability of procedures and internal control systems in operation. |
| Focuses on | Accuracy of costing system and ascertainment of the actual cost of production. | Appraisal of management policies and activities. |
Definition of Cost Audit
Cost Audit implies an independent evaluation of the cost books, statements, records and various documents, so as to ascertain that costs of production are presented in a true and fair manner. It involves the determination of the aptness of the cost accounting system. It involves:
- Evaluation of adherence to the relevant cost account records rules, which applies to the product under review.
- Examination of the costing system to check whether it is appropriate to ascertain the cost of the product under review.
- Assessment of the organization’s operational and other efficiencies, with regard to the product under review.
- Submission of the audit report to the relevant authority in the prescribed format.
For this purpose, Standards on Cost Auditing serves as a guide to the auditor, at every single stage of the audit process with regard to the procedure followed responsibilities of the auditor and cost reporting. The cost audit report is submitted to the Board of Directors and also to the Central Government.
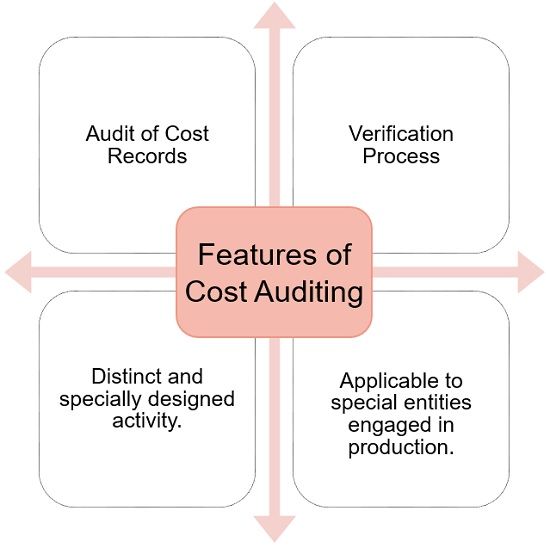
Salient Features of Cost Audit
- Audit of Cost Records: Audit of cost records of an organization, which includes an audit of statements, accounts and other documents.
- Verification Process: It is a process of verification of the cost involved in the production or manufacture of any item.
- Distinct and specially designed activity: It is a unique activity conducted additionally.
- Applicable to special entities: Directed to those firms which conduct production, manufacture, processing or mining operations.
Who performs Cost Audit?
A practising Cost Accountant who is appointed by the Board of Directors is eligible to perform a Cost Audit. Further, the cost auditor is required to comply with the Standards on Cost Auditing (SCA). He/She checks whether or not:
- Cost records are correct.
- The cost accounting system, records and procedures are adequate.
- Cost accounts adhere to the cost accounting plan.
- Cost records are kept and maintained as prescribed by law.
- Cost records reflect a true and fair view of the cost of production, processing and marketing.
Also Read: Difference Between Cost Audit and Financial Audit
Definition of Management Audit
Management Audit refers to the process of a systematic and independent appraisal of the performance of managerial functions. In this process, critical examination of the policies, procedures, operations and programmes that are inherent to the internal control system. It is a part or extended version of the internal audit.
Note: It was T.G Rose, who introduced the concept of Management Audit, as a logical system to assess the quality of management.
To be precise, a management audit is the assessment of systems that a company’s management adopts and implements. It looks for the shortcomings in the company’s internal control and ways to improve the performance.
It is to determine the effectiveness of the management, in an attempt to regulate the activities of the concern, which facilitates the achievement of organizational objectives in a timely manner. It aims to improve the efficiency of the management. 
You must be wondering – Why a management audit is conducted?
Well, the ownership of a company is spread among a large group of shareholders and the company’s operations are handled by a few people who own a small share of its equity. Therefore, dispersed ownership and fixed management are the two main reasons to conduct management audits, by an independent authority.
It is undertaken with an aim of:
- Appraising the performance of management at various levels.
- Outlining the decision or activities, which are not in line with the objectives of the organization.
- Determining that different levels of the management are aware of the objectives.
- Ascertaining that adequate and effective controls are implemented at different levels.
- Evaluating plans devised to meet organizational objectives.
- Reviewing the organizational structure of the company.
Who performs Management audits?
Management Audit is not legally mandatory for the company. Hence, statutorily no such specific qualifications of the auditor are prescribed by law. Hence, it is at the decretion of the company’s board as to who is to be appointed as a management auditor.
So, any independent expert or management consultant can be appointed by the Board of Directors to carry out a management audit. However, internal auditors of the company can also perform management audits.
Management Auditor is required to submit the report to the company’s owners or management. There is no prescribed format in which the report is to be submitted. The auditor can present the report in the form and includes the contents, as he thinks fit. The report encompasses the auditor’s opinion on matters whether:
- The internal control system in use is suitable and infallible.
- Position of the operating cost involved in production in comparison to its competitors.
- Overall performance of the company is satisfactory, if not then what can be done to improve it.
- The relationship between management and workers and staff is harmonious.
- Return on investment is satisfactory and reasonable
Also Read: Difference Between Internal Audit and External Audit
Key Differences Between Cost Audit and Management Audit
So far we have understood the meaning of the two types of audit and the person who performs these audits. Now we will look into the differences between cost audit and management audit.
- Management audit is a type of appraisal in which the overall performance of the management is examined through an objective and comprehensive assessment by an independent authority. Conversely, a Cost Audit is the independent examination of the accuracy of the cost accounts and the compliance to the cost accounting plan.
- There is no statutory requirement for companies, to perform management audits. It is optional for companies. As against, for certain classes of companies, it is compulsory to conduct cost audit.
- As said above, management audit is not statutorily required, so there are no prescribed qualifications of a management auditor. However, any independent expert or management consultant or internal auditor of the company can conduct a management audit. Conversely, a cost accountant firm or a practising Cost and Management Accountant (CMA) can perform a cost audit.
- There is no time frame for conducting a management audit, as it can be conducted whenever the need arises, be it less than one year or more than one year. In contrast, a cost audit is required to be undertaken year after year, and so it is performed for every financial year.
- There is no time limit for the submission of the management audit report. However, there is a prescribed time limit within which the cost audit report must be submitted.
- The management audit report is to be submitted to the company’s owners or management. Oppositely, the Cost audit report is to be submitted to the company’s board and central government.
- Management Audit aims to analyse the management’s effectiveness in utilizing the resources of the company. As against, cost audit is performed to ascertain the reliability of cost information depicted by the cost records of the company.
- The basis for conducting a management audit is the managerial functions and activities of the enterprise. In contrast, cost statements form the basis for carrying out cost audits.
- The audit techniques used in management audit tends to identify the adequacy and reliability of procedures and internal control system in operation. Conversely, the audit techniques used to perform cost audit aims to examine and analyses data of material, labour and overheads.
- Management Audit is the audit of a company’s management, in which various policies, operations and functions of management are examined, reviewed and appraised. In contrast, a cost audit focuses on the accuracy of the costing system and the determination of the actual cost of production.
Objectives of Cost Audit
- To verify cost accounts of the company so as to determine, that they are maintained in a proper manner and all the relevant standards and principles are duly complied with.
- To detect frauds and errors.
- To check the cost of each cost unit and cost centre, to make certain that they are ascertained appropriately.
- To facilitate price fixation of the goods and services.
- To identify and correct abnormal loss of material and time.
- To advise the company’s management based on the interfirm comparison of the cost records, the areas where improvement in performance is required.
- To make periodical reconciliation of cost accounts and final accounts.
Objectives of Management Audit
- To make certain that there is the effective utilization of the firm’s resources including, men, money, materials, machines and methods.
- To put forward suggestions for improvement in methods of operations.
- To determine weaknesses in the structure of the organization, as well as in the system and recommend necessary improvements.
- To point out organizational efficiency in planning, policies, and objectives,
- To predict problems and recommend preventive measures, to resolve them.
Also Read: Difference Between Internal Control and Internal Audit
Conclusion
To sum up, we could say, cost audit is to check the correctness of the cost accounting data presented, whereas a management audit is to review the functions of management.






Leave a Reply