 Generally, a company gives two kinds of dividends to its shareholders – cash dividends and stock dividends. A cash dividend is one in which the company distributes a definite amount of money to each shareholder for each share owned. On the other hand, a stock dividend is obtained from distributable equity in the form of stock.
Generally, a company gives two kinds of dividends to its shareholders – cash dividends and stock dividends. A cash dividend is one in which the company distributes a definite amount of money to each shareholder for each share owned. On the other hand, a stock dividend is obtained from distributable equity in the form of stock.
Oppositely, Stock Split is another action which the company takes, in which the number of shares held by a shareholder gets multiplied. In this, what exactly happens is that the company does not issue any shares, rather the outstanding shares are split or divided into a definite ratio.
So, the difference between stock dividend and stock split is that a stock dividend is distributed among the shareholders as equity stocks whereas stock split is nothing but the division of equity stocks.
Content: Stock Dividend Vs Stock Split
- Comparison Chart
- What is Stock Dividend?
- What is Stock Split?
- Key Differences
- Similarities
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Stock Dividend | Stock Split |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Stock Dividend is nothing but pro-rata distribution of the own stock of the company to the shareholders. | Stock Split implies the process of dividing the existing outstanding shares into a number of smaller shares. |
| Increase | The number of shares increases by the percentage of a stock dividend. | Number of shares increases by a fraction. |
| Objective | To distribute accumulated earnings without paying dividends in order to increase the creditworthiness of the company. | To increase the affordability of the stock for small retail investors, to increase market liquidity. In this way, it can attract new investors. |
| Reason | Reward existing shareholders for this investment. | Make the shares marketable. |
| Face Value and Market Value | Face Value remains the same after the stock dividend and it reduces the market value of the shares. | Reduces in proportion to split ratio. |
| Future Dividend per share | Remains the same since the face value is the same. | Decreases with the decrease in the face value. |
| Share capital and reserves | Share capital increases, but reserves get reduced proportionately. | Share capital and reserves remain the same. |
| Journal Entries | Require Journal Entries | Does not Require Journal Entries |
| Benefit | Existing Shareholders | Existing and potential shareholders |
| Company Rationale | The stock dividend is a substitute for cash dividends. | It will increase share liquidity. |
| Example | A Stock Dividend of 10% implies that for every 10 shares held by the shareholder, he is going to get one additional share. | A Stock Split of 1:2 means, the shareholder will have 2 shares for every 1 share held. |
What is Stock Dividend?
Stock Dividends are issued in place of or in addition to the cash dividend. It is when a company declares and issues additional shares of its own stock to the existing shareholder.
But here one must note that an increase in outstanding shares, it results in a dilution of the earnings per share, which will cause the share prices to fall.
In common parlance, the stock dividend can take the form of a bonus issue. Basically, a bonus issue means the issue of a bonus i.e. extra shares as a reward to the existing shareholders by the company, without any extra price. This means that the company issues them free of cost.
However, how many shares will be allotted to each shareholder will depend on the shareholder’s holding in the company. Further, the issue of bonus shares is announced in a specific ratio. The alternative term for bonus issue is capitalization issue.
For this purpose, the company makes use of free reserves.
Reasons for Stock Dividends
- It does not require the use of cash. An organization can decide to distribute stock dividends when it does not have sufficient cash to declare the dividend.
- It reduces the market price of the stock thereby increasing the marketability of the stock but decreasing the market price per share. Hence, it might look more attractive to thousands of investors.
- It does not showcase the taxable income to the recipients.
- It also satisfies the dividend expectation of the stockholders without spending cash.
Effect of Stock Dividend
- Distribution of stock dividends results in a decrease in the Earning Per Share (EPS), Price per share, and Book Value per share, with an increase in the number of shares.
- It reflects the positive indicator of the financial soundness of the enterprise.
- After the distribution of stock dividends, there may be a decline in the price of the stock but the market value of the company remains the same.
How does it affect effects shareholder’s equity?
Stock Dividend changes the composition of stockholder’s equity. This is because it results in the transfer of the part of retained earnings to paid-up capital. It actually transfers the company’s general reserves into share capital. General Reserves comprise the share premium which the company receives from the shareholders.
However, the total stockholder’s equity remains unchanged. There is no effect on the par value per share, but with the issue of additional shares, the total number of outstanding shares increases.
Example of Stock Dividend
Suppose Videside Corporation has 1000 shares outstanding. The profit after tax is Rs. 50000. So, the earnings per share is Rs. 50 per share. The company’s management plans to issue a 20% stock dividend. Therefore, a shareholder holding 100 shares will receive 20 additional shares.
Objectives of Distributing Stock Dividends
- Bring market price per share within a popular trading range.
- Promoting more active trading, as the issue results in an increase in the number of outstanding shares.
- Reducing the rate of dividends may give the impression of profiteering.
- Improving prospects of raising additional funds.
Also Read: Difference Between Interim Dividend and Final Dividend
What is Stock Split?
A stock split is the process of subdivision of the outstanding stock units, with no change in the paid-up share capital. It results in a decrease in par value and the outstanding number of shares automatically gets multiplied. It is a non-event, i.e. it does not have any impact on the company’s equity or market capitalization. Hence, it does not change the net assets of the enterprise.
Stock Split is a corporate move, in which the face value of the company’s existing shares is split or divided into a certain ratio. This implies that, on the announcement of the stock split, the number of shares of the firm tends to increase. However, there is no change in market capitalization.
Reasons for Stock Split
- The company decides to take this action when the company prices are going very high, due to which the retail investors find it difficult to invest in them. So, a stock split results in a substantial decline in the market price per share, as the shares are split. This happens due to the increase in the number of shares. In this way, the company places its shares in a popular trading range which attracts more buyers. But, here it should not place the shares in the cats and dogs class.
- However, a stock split does not result in any change in market capitalization. Also, there will be no change in the value of the shareholder’s investment. Nevertheless, the value of each share decreases, due to the increase in their number.
- To make shares affordable for investors.
- Companies also go for the stock split to:
- Conceal the distribution of large profits as with the stock split the earnings per share reduces.
- Facilitate the future sale of new shares
- Provide a basis for exchange in case of a merger
- Please shareholders who expect this kind of action as an indicator of financial success
- Allow the listing of shares.
Effect of Stock Split
The effect of a stock split on the market value of shares is inversely proportional to the size of the split. It will have no effect on the paid-in capital, retained earnings and stockholders’ equity. Further, it also increases liquidity and demand.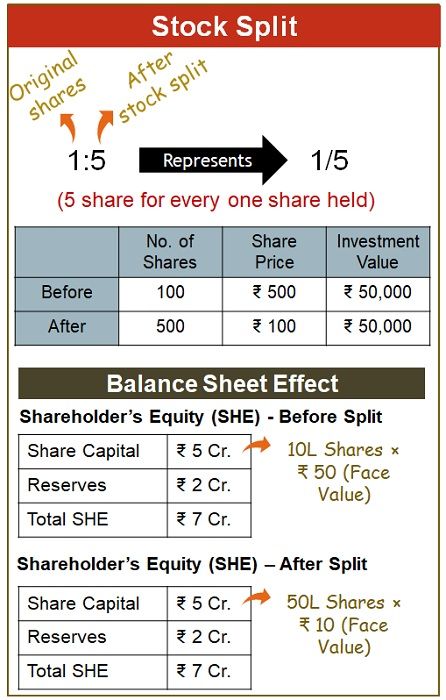
Example
Suppose you own 10 shares of Sinephi Ltd, which declares a stock split of 1:10. The current share price is ₹ 500 per share and each share has a face value of ₹ 100.
Hence, if you hold 10 shares of the company having a face value of ₹ 100 prior to the stock split, you would hold 100 shares with a face value of ₹ 10 after the stock split.
But the stock that was traded at ₹ 500 prior to the stock split will be traded at ₹ 50 in the market.
Also Read: Difference Between Share and Stock
Key Differences Between Stock Dividend and Stock Split
- Under stock dividends, the company issues additional shares to the shareholders in a certain proportion for free. Stock Splitting is nothing but division or splitting of the face value of a company’s shares. In this, the company divides its share into multiple shares.
- On declaring stock dividends, there is no change in the face value of shares. In contrast, in a stock split, the face value of the share decreases.
- Companies declare stock dividends on the event when they lack sufficient cash to distribute as dividends. On the other hand, a stock split aims at increasing the liquidity of the shares of the company.
- Stock Dividend increases the share capital of the company on one hand and on the other hand, decreases reserves. Conversely, in the case of a stock split, you will not find any change in the company’s share capital and reserves.
- The company announces stock dividends when it lacks cash liquidity. But a stock split is announced when the market price of a company’s shares is overvalued, and the company wants to make it tradable.
- A Stock Dividend of 10% implies that for every 10 shares held by the shareholder, he is going to get one additional share. Therefore, if the company has 10,000 outstanding equity shares, then the distribution of stock dividends would increase the outstanding shares to a total of 11,000 shares. A Stock Split of 1:2 means, the shareholder will have 2 shares for every 1 share held. Here, 1 represents the original number of shares and 2 implies the division.
-
What happens to the share price?
In a stock dividend, the stock price is adjusted as per the additional number of shares that the company issues. As against, in the case of the stock split, the share price gets halved in the ratio.
Similarities
- Here one should note that there is no change in the shareholder’s proportion in both cases.
- Both stock dividends and stock splits are an important part of dividend policy, involving the issue of new shares to the shareholders on a pro-rata basis.
- In both cases, the firm’s net assets, risk assumed, and firm’s earnings and the investor’s ownership percentage remain the same.
- Under these two schemes, the ultimate outcome would be an increase in the number of shares outstanding.
Conclusion
In the case of a stock dividend, regardless of the percentage of distribution, the distribution of the dividend takes place through the transfer of such amount from free reserves to paid-up share capital. While no such transfer takes place in case of a stock split.






Ravi Thakur says
very well explained. Ma’am, your content is very helpful.