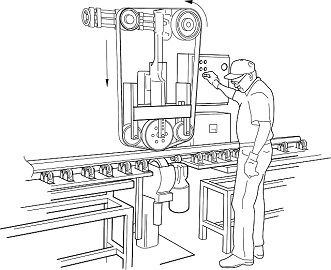
 Operations Management is that branch of management that deals with the government of that section of the organization which is concerned with the production of goods and services. However, operations management is primarily used with service operations, whereas manufacturing operations are mainly studied in production management, but for non-manufacturing facets operations management can be used.
Operations Management is that branch of management that deals with the government of that section of the organization which is concerned with the production of goods and services. However, operations management is primarily used with service operations, whereas manufacturing operations are mainly studied in production management, but for non-manufacturing facets operations management can be used.
One of the biggest difference between manufacturing and service operations is that in case of the latter, the service provider is unable to hold stock of the service for future, but with former, the stock to be manufactured can be made ready, in anticipation of future demand of production.
Content: Manufacturing Vs Service Operations
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Manufacturing Operations | Service Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Manufacturing operations refers to the specific processes, in which a firm engages itself, to add value to products, for selling it to the customers. | Service operations implies the processes that involve the provision of services to the clients and business users, as per their demand. |
| Measurement of Productivity | Easily measured | Cannot be measured |
| Form of output | Tangible and standardized, but can also be customized. | Intangible and customized |
| Input and Output | Always uniform | May or may not be uniform |
| Location | Close to the supply of input. | Close to the market, so that client's reach is easy. |
| Capital cost | Capital cost is high in operations but can achieve economies of scale. | Training cost is high, but can operate with low capital costs. |
| Labor cost | Unskilled or technically skilled manpower is employed, and so labor cost is low. | Skilled and experienced manpower is employed, so labor cost is comparatively high. |
| Lead time | Long | Comparatively shorter |
| Quality standards | Implemented easily | Difficult to implement |
Definition of Manufacturing Operations
Manufacturing operations refers to bringing together the people, processes, tools and equipment to convert the raw material into finished goods by adding value, to meet customer’s requirements and specifications and making it ready for sale. It implies a continuous process of observing and enhancing the production processes, with the aim of increasing efficiency and productivity.
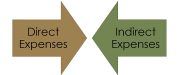
The three components of manufacturing operations are direct material, direct labour and direct expenses (also known as production overhead), that takes into account various costs incurred during the process and can be attributed outrightly to the production.
- Direct Material: Direct material implies all the raw material and supplies needed to produce a useful product. Direct material costs can be allocated to a particular product or cost centre.
- Direct Labor: Wages and salaries of the workers, foreman, supervisors, employees and production manager, who are directly engaged in the manufacturing process, constitute direct labour cost.
- Direct Expenses: Those expenses which are incurred during the process of production but are not covered under direct material cost and direct labour cost are considered as direct expenses. It includes rent for hiring specific equipment, royalty for production, the cost for product specific design, etc.
Definition of Service Operations
Service operations refer to the process of providing services to the clients and business users, on demand and as per their specifications, for a fee. Here the word ‘services’ connotes economic activities in which the service provider supply or fulfil the need of another person or organization for adequate consideration and creates time, place or psychological utility.
In other words, service operations imply a process of transforming consumers into satisfied consumers. It aims at coordinating and undertaking those activities, processes and technology needed to render desired and acceptable services to the consumers.
The functions performed by service operations are service desk, technical support, third-line support, application management, customer service and information technology operations management. Further, the processes covered are event management, request fulfilment, problem management, access management, storage management, and incident management.
Key Differences Between Manufacturing and Service Operations
The most important differences between manufacturing and service operations are discussed in the points given below:
- Manufacturing operations can be understood as those processes wherein the organization engages in the manufacture of goods, so as to sell the same to the final customer. On the other hand, service operations point out those process which involves the provision of services to the clients and satisfying their needs.
- One of the greatest disadvantages with service operations is that its productivity cannot be measured, as we can measure the productivity of manufacturing operations.
- In the case of manufacturing operations, the output produced is in a tangible form, which may be standardized as per the market demand, or customized, as per the demand of a consumer. As against, in service operations, the form of output is intangible, i.e. saving of time, resources, efforts, advice, or psychological utility, which is always customized as per the needs of the client or user.
- When it comes to uniformity of input and output, these are always uniform in case of manufacturing operations. On the contrary, it may or may not be same in case of service operations, as it changes as per customer’s specifications.
- Manufacturing operations are performed by manufacturing concerns which are located near to the supply of raw material and other inputs so as to save time and cost of transportation. In contrast, service providers engaged in service operations are usually located at the market, so that the customers can easily reach the service centre.
- If we talk about capital cost, as big machines and equipment are installed in the manufacturing concerns for manufacturing operations, the cost is comparatively high, but the concern can achieve economies of scale, by producing in bulk quantities. As opposed to service operations, the cost of training to the staff is usually high, but it can operate with a low capital cost.
- In manufacturing operations, usually unskilled or technically skilled workforce is hired, and so the labour cost is low. On the flip side, in service operations, skilled and professionally trained personnel is hired, which makes the labour cost high.
- The lead time in case of manufacturing operations is high, as compared to service operations.
- In the case of manufacturing operations, as the products are standardized, the quality standards can be easily implemented and checked, as to whether the products possess the specific quality or not. Conversely, in case of service operation, due to the customization of input and output, the implementation of quality standards is quite hard.
Conclusion
By and large, manufacturing operations the manufacturer produces the product and then wait for its sale. Hence, there is always a risk, whether the stock will be purchased by the customers or it will remain unsold. On the other hand, in service operations, the service provider provides services only when there is a demand for services.




Leave a Reply