 In a product layout, the machines, material and other facilities are placed as per the order of processing. It is often used when the production is to be performed on a large scale. Process layout is a type of plant layout wherein like machines are grouped in a single department. It is primarily used when the production process is non-repetitive in nature.
In a product layout, the machines, material and other facilities are placed as per the order of processing. It is often used when the production is to be performed on a large scale. Process layout is a type of plant layout wherein like machines are grouped in a single department. It is primarily used when the production process is non-repetitive in nature.
The layout is an important concept of operations management, which implies the systematic organization and grouping of facilities and services of the plant that are used to manufacture the goods, within the factory. Machines are grouped, on different lines, wherein the selection is based on a number of factors.
So, there are various methods of grouping, which are commonly called as the types of layout, these are product layout, process layout, fixed position layout, cellular manufacturing layout, and hybrid layout. In this article, we will be discussing the difference between product layout
Content: Product Vs Process Layout
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Product Layout | Process Layout |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Product Layout is a type of layout design in which the resources needed to produce the product are arranged in one line, as per the sequence of operations. | Process Layout refers to the type of layout design wherein the resources having homogeneous processes or functions are combined together. |
| Product | Standardized | Customized |
| Workflow | Identical flow and sequence of operations for each unit. | Variable flow, relying on the nature of the job. |
| Inspection | Minimum inspection is there, during the sequence of operations. | Inspection is conducted multiple times during the sequence of operations. |
| Results in | Transfer lines | Group Technology |
| Production Time | Less | Comparatively high |
| Production Cost | High fixed cost and low variable cost. | Comparatively low fixed cost and high variable cost. |
| Effect of breakdown | Due to the interrelated system, machinery breakdown can seriously affect production. | Machinery breaks down does not have a significant affect on the final output. |
| Suitable for | Mass production with less job variety. | Moderate production with more job variety. |
Definition of Product Layout
Product layout, otherwise called as straight line layout or flow shop layout, is a layout design in which the resources, i.e. workstations, tools and equipment, which are to be used in the process of production are organized sequentially in a straight line of production, on the basis of the sequence of operations.
In this type of layout, the raw material is supplied to the very first machine, which passes through one machine to another in the line, automatically. And in this way, the output of the previous machinery becomes the input to the next and at the end of the final output is delivered by the last machine.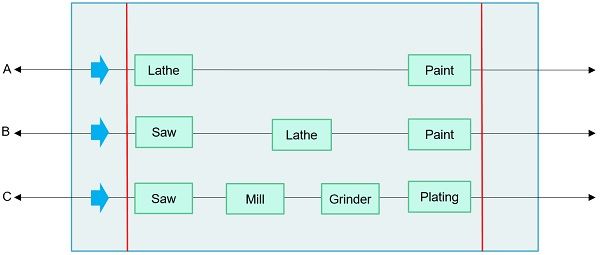
As it is a product-oriented layout, and so the primary importance is given to the product. Hence, the production lines will be specific to the particular type of product only. Further, all the resources needed to fabricate the product are to be located at the point demanded by the sequence of operations.
Definition of Process Layout
Process Layout also called a job shop layout or functional layout that kind of layout wherein identical processes or functions are categorized together. Process Layout is mainly used when products and services to be delivered, are diversified in nature and it is not feasible to allot specific resources to the particular product or service.
In process layout, the quantity of raw material is supplied to a machine, located anywhere in the factory, that conducts the first operation. For the next operation, the half-processed goods are taken to another machine for further processing, which is located in another part of the factory. In this way, the goods travel long distances, in a twisted path. And so the distance between the department should be less, to save time and efforts.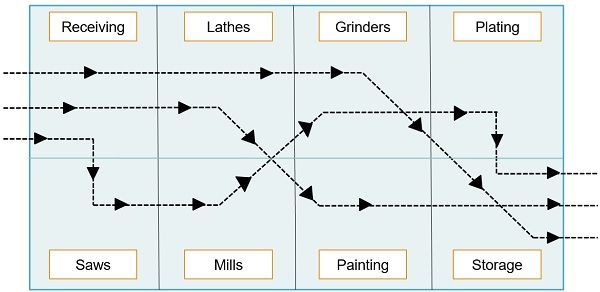
So, machines in each department process the products which are supplied to them and due to this very reason, these machines are called general purpose machines. Further, work is assigned to each department according to loading schedule, so as to make sure that machines are completely loaded.
Key Differences Between Product and Process Layout
The difference between product and process layout can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- Product layout is one such layout design wherein the resources i.e. machine and equipment used to fabricate the product is sequenced, on the basis of their appearance. On the flip side, process layout refers to the layout design in which those resources are grouped together which have similar processes or functions.
- Product layout is used when the product is standardized and are to be produced in large quantities. As against, process layout is used when diversified products are to be produced and that too in small batches of various products.
- In a product layout, there is a homogeneous workflow and sequence, of operations for each unit. Conversely, in a process layout, the workflow is variable, which depends on the nature of the job.
- In a product layout, products are inspected at a minimum level, during the production. In contrast, in a process layout, products are inspected a number of times, during the production process.
- While product layout results in transfer lines, process layout leads to group technology.
- As there is a sequence of facilities and resources in a product layout, the production time is comparatively less as compared to process layout, because a lot of time consumed in the transportation of material.
- Coming to the production cost, in a product layout, the fixed cost is high whereas variable cost is low. On the contrary, in a process layout, the fixed cost is low, and the variable cost is high.
- As the production process is interconnected in a product layout, and so machinery breakdown may severely affect the process. Conversely, in process layout, machinery breakdown, may not affect the output.
- Product layout is best suited for mass production with less job variety. As against, process layout is appropriate for moderate production with high job variety.
- The objective of product layout is to achieve a smooth and quick flow of bulk quantities of products, through a system. On the other end, the objective of the process layout is to facilitate the processing of material or supply of services that have varied processing needs.
Conclusion
When it comes to suitability, product layout is appropriate for the industries that manufacture standardised products on a high scale like paper, rubber, oil refineries, cement, chemical, soap, etc. On the contrary, process layout is best for light and heavy engineering industries and customised furniture industries.





Kenneth says
Excellent resources