 In general, leverage means affect of one variable over another. In financial management, leverage is not much different, it means change in one element, results in change in profit. It implies, making use of such asset or source of funds like debentures for which the company has to pay fixed cost or financial charges, to get more return. There are three measures of Leverage i.e. operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage. The operating leverage measures the effect of fixed cost whereas the financial leverage evaluates the effect of interest expenses.
In general, leverage means affect of one variable over another. In financial management, leverage is not much different, it means change in one element, results in change in profit. It implies, making use of such asset or source of funds like debentures for which the company has to pay fixed cost or financial charges, to get more return. There are three measures of Leverage i.e. operating leverage, financial leverage, and combined leverage. The operating leverage measures the effect of fixed cost whereas the financial leverage evaluates the effect of interest expenses.
Combined Leverage is the combination of the two leverages. While operating leverage delineates the effect of change in sales on the company’s operating earning, financial leverage reflects the change in EBIT on EPS level. Check out the article given below to understand the difference between operating leverage and financial leverage.
Content: Operating Leverage Vs Financial Leverage
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Operating Leverage | Financial Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Use of such assets in the company's operations for which it has to pay fixed costs is known as Operating Leverage. | Use of debt in a company's capital structure for which it has to pay interest expenses is known as Financial Leverage. |
| Measures | Effect of Fixed operating costs. | Effect of Interest expenses |
| Relates | Sales and EBIT | EBIT and EPS |
| Ascertained by | Company's Cost Structure | Company's Capital Structure |
| Preferable | Low | High, only when ROCE is higher |
| Formula | DOL = Contribution / EBIT | DFL = EBIT / EBT |
| Risk | It give rise to business risk. | It give rise to financial risk. |
Definition of Operating Leverage
When a firm utilizes fixed cost bearing assets, in its operational activities in order to earn more revenue to cover its total costs is known as Operating Leverage. The Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL) is used to measure the effect on Earning before interest and tax (EBIT) due to the change in Sales.
The firm, which employs high fixed cost and the low variable cost is regarded as high operating leverage whereas the company which has low fixed cost, and the high variable cost is said to have less operating leverage. It is fully based on fixed cost. So, the higher the fixed cost of the company the higher will be the Break Even Point (BEP). In this way, the Margin of Safety and Profits of the company will be low which reflects that the business risk is higher. Therefore, low DOL is preferred because it leads to low business risk.
The following formula is used to calculate Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL):
Definition of Financial Leverage
The utilization of such sources of funds which carry fixed financial charges in company’s financial structure, to earn more return on investment is known as Financial Leverage. The Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) is used to measure the effect on Earning Per Share (EPS) due to the change in firms operating profit i.e. EBIT.
When a company uses debt funds in its capital structure having fixed financial charges in the form of interest, it is said that the firm employed financial leverage.
The DFL is based on interest and financial charges, if these costs are higher DFL will also be higher which will ultimately give rise to the financial risk of the company. If Return on Capital Employed > Return on debt, then the use of debt financing will be justified because, in this case, the DFL will be considered favorable for the company. As the interest remains constant, a little increase in the EBIT of the company will lead to a higher increase in the earnings of the shareholders which is determined by the financial leverage. Hence, high DFL is suitable.
The following formula is used to calculate Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL):
Key Differences Between Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage
The following are the major differences between operating leverage and financial leverage:
- Employment of fixed cost bearing assets in the company’s operations is known as Operating Leverage. Employment of fixed financial charges bearing funds in a company’s capital structure is known as Financial Leverage.
- The Operating Leverage measures the effect of fixed operating costs, whereas Financial Leverage measures the effect of interest expenses.
- Operating Leverage influences Sales and EBIT but Financial Leverage affects EBIT and EPS.
- Operating Leverage arises due to the company’s cost structure. Conversely, the capital structure of the company is responsible for Financial Leverage.
- Low operating leverage is preferred because higher DOL will cause high BEP and low profits. On the other hand, High DFL is best because a slight rise in EBIT will cause a greater rise in shareholder earnings, only when the ROCE is greater than the after-tax cost of debt.
- Operating Leverage creates business risk while Financial Leverage is the reason for financial risk.
Conclusion
While the performance of financial analysis, Leverage, is used to measure the risk-return relation for alternative capital structure plans. It magnifies the changes in financial variables like sales, costs, EBIT, EBT, EPS, etc. The firms which use debt content in its capital structure are regarded as Levered Firms, but the company with no debt content in its capital structure is known as Unlevered firms. The multiplication of DOL and DFL will make DCL i.e. Degree of Combined Leverage.
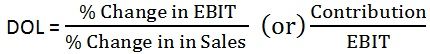
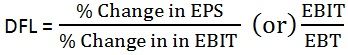





golam rabbani rahman says
Thanks, Ma’am. you’re doing a great job, I am enjoying to read your articles, it’s very simple and suitable to understanding.
Adinew Tsige Abebaw says
Thank you for the wonderful explanation and examples.
Maria says
Dear
Nice post! This is a very nice blog.