 Strategic Control is all about following the trail or movements of the strategy as it is implemented in order to identify the areas of issue or potential areas of the issue so that necessary adjustments can be made. On the other hand, operational control is a subset of management control whose aim is to regularly monitor and check the routine business operations so as to confirm the consistency and quality in business activities.
Strategic Control is all about following the trail or movements of the strategy as it is implemented in order to identify the areas of issue or potential areas of the issue so that necessary adjustments can be made. On the other hand, operational control is a subset of management control whose aim is to regularly monitor and check the routine business operations so as to confirm the consistency and quality in business activities.
Strategic Control focuses on attaining future goals and not past performance. The main idea behind that is to look for room for improvements and corrections so as to lead the organization in the desired direction, rather than pointing out mistakes or errors that took place in the past.
In contrast, an operational control system is designed in a manner that confirms – the day-to-day activities of the business are directed towards the achievement of predetermined goals and objectives.
Concept of Control
In an organization, there are three stages of action in which control is being exercised:
- Feedforward Control: In feedforward control, inputs are evaluated and necessary corrective steps are taken prior to the completion of a particular sequence of operation.
- Steering Control: In steering control, action is evaluated and corrective actions are put in force, while the operation is undertaken. This is also called concurrent, or real-time control.
- Feedback control: In feedback control, the results of the action as assessed and corrective steps are taken after the operation is complete so that desired results are produced in the future.
In this post, we have covered all the points that will clear your doubts regarding the difference between strategic control and operational control.
Content: Strategic Control Vs Operational Control
- Comparison Chart
- Definition
- Key Differences
- Relevant Questions
- Types of Strategic Control
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Strategic Control | Operational Control |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Strategic Control implies a process of controlling the formulation and implementation of an organization's plan and strategy. | Operational Control systems are framed to make certain that the routine operations are in line with the company's plans and objectives. |
| Based on | Feedforward and Steering Control | Feedback Control |
| Exercised by | Top-level executives | Functional level executives |
| Primary concern | Guiding the future direction of the company | Action control |
| Determines | Is the company moving in the right direction? | How efficiently the company is performing? |
| Factors Affecting | External environment | Internal Environment |
| Strives for | Effectiveness | Efficiency |
| Time Horizon | Long Term | Short Term |
| Focuses on | Monitoring and evaluation of the strategic management process. | Individual tasks and operations |
Definition of Strategic Control
Strategic Control is a type of organizational control, which ensures that the organization is functioning in the right direction. It is better known as steering control. Its objective is to attain the results which are established at the time of formulation of the strategy. Thus, it helps the top management to analyze whether the strategic management process is appropriate, compatible, and performing as desired.
It ascertains whether the opted strategy is proceeding in the intended direction and bringing out the desired results and taking necessary steps to avoid deviations whenever required. It evaluates the extent to which the firm concentrates on the need to implement strategies.
At the time of formulation of strategy, assumptions are made by the strategists about the company’s internal and external environment. So, the lag in time exists between strategy formulation and its implementation and due to this time lag, the assumptions made by the strategists would come out as invalid or no longer relevant.
In addition, the process of strategy implementation is a time-consuming one. Hence, it is pertinent to assess the validity of the strategy on a continuous basis and alter it as per requirements and conditions prevalent.
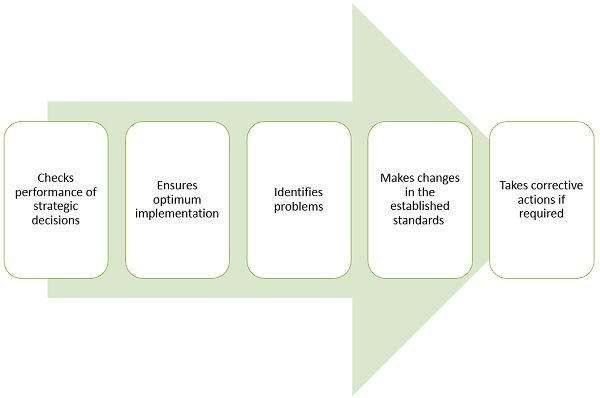
What Strategic Control does?
- Checks performance of strategic decisions
- Ensures optimum implementation of plans and policies
- Identifies problems
- Makes changes in the established standards (if possible and required)
- Takes corrective actions if required for the desired objective
Also Read: Difference Between Strategy Formulation and Strategy Implementation
Definition of Operational Control
The process of ensuring that there is an effective and efficient performance of the task is called operational control. It imposes post-action evaluation and control, for a short period, which encompasses evaluation of performance against the objectives set by the firm.
Its aim is to ensure optimum allocation and utilization of the organization’s resources by way of performance evaluation of the organizational units like divisions, departments, or SBUs in order to ascertain their contribution to the achievement of organizational objectives. That is why the evaluation techniques depend on internal analysis and not on environmental monitoring.
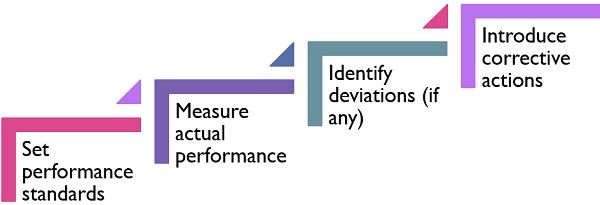
Steps for Operational Control
- Set performance standards
- Measure actual performance
- Identify deviations (if any)
- Introduce corrective actions
The focus of operational control is on the result of the strategic action, that assesses the overall organization’s performance, different SBU’s and other divisions and units.
Techniques used for Operational Control
- Financial Techniques
- Network Techniques
- Management by Objectives
- Memorandum of Understanding
Also Read: Difference Between Strategic Planning and Operational Planning
Key Differences Between Strategic Control and Operational Control
As we have discussed the basic concept of the two forms of organizational control, we will talk about the difference between strategic control and operational control, in points:
- Strategic Control is a tool to keep a check on the execution of the strategic plan just like an early warning system, which ensures that the necessary steps for the achievement of the organizational goals are performed effectively. On the contrary, Operational Control keeps a check on the allocation and utilization of resources, which is a post-action control, which determines the contribution of various units in the attainment of the organization’s objectives.
- Strategic Control is based on feedforward and steering control, whereas Operational Control relies on feedback control.
- The power of exercising strategic control is in the hands of top-level executives. As against, operational control is exercised by functional-level executives as directed by top-level management.
- The primary concern of strategic control is to guide the future direction of the company. In contrast, the primary concern of operational control is to control the activities,
- Strategic Control ascertains whether the company is progressing in the right direction. On the contrary, operational control ascertains how efficiently the company is performing?
- Strategic Control takes into account external factors, as the relevancy of the strategy is primarily dependent on the external business environment. Conversely, operational control takes into account internal factors.
- Strategic Control strives for effectiveness, whereas Operational Control strives for efficiency.
- Strategic Control is a long-term process as it attempts to steer the company over a long period of time typically five years or more. In contrast, operational control is a short-term process that attempts to take necessary steps to correct the deviations from the set standards and so it ranges from one month to one year.
- Strategic Control stresses the changing assumptions which determine a strategy, evaluate it on a continuous basis, as it is executed, and take those steps which are essential so as to adjust the strategy to prevalent needs and conditions. Oppositely, operational control focuses on the events that occurred recently for the uninterrupted functioning of business operations.
Relevant Questions for Strategic Control
- Is the premises created at the time of formulation of strategy proving to be correct?
- Is the implementation of strategy is done properly?
- Is there any requirement for change in the strategy? If the answer is yes, what sort of change is needed which guarantees strategic effectiveness?
Relevant Questions for Operational Control
- How is the performance of the organization?
- Are the resources of the organizations being utilized in an optimum manner?
- What actions are required to be taken which confirm appropriate utilization of the resources so as to meet the objectives of the organization?
Types of Strategic Control
There are four main types of strategic control: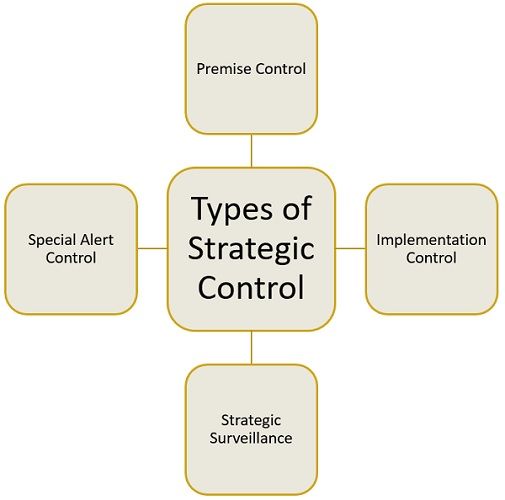
- Premise Control: A strategy relies on a premise or assumption about the internal and external factors of the business. Its aim is to identify the primary assumptions, monitor changes, and determine the effect of these changes on the company’s strategy and implementation.
- Implementation Control: It ascertains whether the plans and programs framed for the implementation of the strategy are leading the organization towards the accomplishment of predetermined objectives or not. In addition, if it is found that the resources allocated are not reaping the benefits which are expected of them, then the resources allocated are withheld. In conclusion, it causes strategic rethinking.
- Strategic Surveillance: Strategic Surveillance is about generalized and comprehensive control that tends to observe an array of activities and events, inside and outside the firm, which is expected to intimidate the progress of the firm’s strategy.
- Special Alert Control: Special alert control is based on a trigger mechanism to facilitate instant response and reassessment of the strategy while considering abrupt events. To exercise such control, contingency strategies can be formulated and responsibility can be assigned to the crisis management department to handle unanticipated events.
Also Read: Difference Between Strategic Planning and Strategic Management
Conclusion
Strategic Control allows the top management to look at the big picture and ensuring that all the pieces of the picture are aligned in the manner, it should have been aligned. On the other hand, operational control ensures that specific tasks and actions are performed in a proper manner.







Leave a Reply