 A society is composed of different types of groups which vary in terms of – social interaction, degree of intimacy of contact, degree of organization, range of group interest, size, etc. Primary Groups as the name suggests are the groups which are the main source of an individual’s relationships and socialization. Its main characteristic is that it has an intimate face-to-face association and cooperation.
A society is composed of different types of groups which vary in terms of – social interaction, degree of intimacy of contact, degree of organization, range of group interest, size, etc. Primary Groups as the name suggests are the groups which are the main source of an individual’s relationships and socialization. Its main characteristic is that it has an intimate face-to-face association and cooperation.
Secondary Group are the groups which are formal, impersonal, contractual and specialized in nature. When we are in a secondary group, the interaction is generally on a less personal level, as compared to the primary group.
Who coined the term ‘Primary Group’ and ‘Secondary Group’?
Charles Horton Cooley – an American Sociologist propounded the theory of Primary Group and Secondary Group, in the book ‘Social Organization‘ in the year 1909. His classification of the group into primary, secondary and tertiary was based on the degree of intimacy of contact, which came out as the broadly used concept relating to sociological groups.
Content: Primary Groups Vs Secondary Groups
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Primary Group | Secondary Group |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Primary Groups are those that are bound together by strong emotional bond and common interests. It provides the typical experience of social unity and harmony, to its members. | Secondary Groups are the groups which are formal, segmental and utilitarian. The relationship between members exists due to contractual obligation or interest. |
| Size | Small both in size and area. | Relatively larger and widespread. |
| Durability | Long-lasting and permanent. | Short term or long term, depending on the condition. |
| Interest of Members | Diffused | Specific |
| Found in | Family Setting | Educational and Employment Setting |
| Significance in the life of people | Greater significance | Little significance |
| Group focus | Relationship | Task |
| Relationship | Personal, Direct and Intimate | Impersonal and goal-oriented |
| Principle | Particularism | Universalism |
| Structure | Informal | Formal |
| Communication | Direct, quick and effective | Indirect |
| Member's Role | Stable | Interchangeable |
| Cooperation | Direct | Indirect |
Definition of Primary Groups
A primary group is a social group which is comparatively smaller in size. Further, it is characterized by close, personal, direct and long-lasting relationships. The group members care for each other, as well as they share a strong emotional bond. As they follow a similar culture and indulge in similar activities and that for a very long time, they know each other quite well.
These groups provide support, love, security, assurance and companionship, to the group members.
In a nutshell,
- Primary Group is the basis of all the social systems.
- It implies a small arrangement in which a handful of people come in personal contact with each other.
- Members of such groups often meet in-person for mutual help, accompaniment and interaction with each other.
Primary Groups are named so, because people come across these groups at an early stage of their life, as well as these groups play a significant role, in developing a person’s identity.
Also Read: Difference Between Formal Group and Informal Group
Definition of Secondary Groups
Secondary groups are the groups which a person becomes part of, in his/her later life. Moreover, these groups have less influence on personal identity. People choose such groups, according to their interests and preferences. It may include friends, colleagues, team, acquaintances, neighbours, and relatives.
Hence, one can find such groups at the office, dance class, cricket association, clubs, school, university, so on and so forth.
So in a secondary group,
- Human contact is casual and non-specific.
- Relationship between members are limited in scope and it is developed by experimentation and self-interest calculation.
- One member has an indirect influence over the other members.
These groups are characterised by the weak emotional bond. Further, the group members have very less personal knowledge of each other.
For example: Sports team, Society, Project Group, College Group, etc.
Also Read: Difference Between Group and Team
Key Differences Between Primary Group and Secondary Groups
The difference between primary and secondary groups has been boiled down in the points given below:
- Primary Groups are the groups which people experience or become part of, in their early stage of life. In this group, there is a sense of mutual cooperation, support, companionship and sharing of feelings. On the contrary, secondary groups are experienced by people in the later stages of their life. In such groups, the relations rely on reciprocal needs.
- When it comes to the size of the two groups, the secondary group is larger in size both in terms of the number of members and geographical area, as compared to the primary group, which has a limited number of members. Also, the members may belong to a particular region.
- Talking about the duration of the group, primary groups are long-lasting, as they persist over time. On the other hand, secondary groups are short-lived, because they are formed with a specific purpose, i.e. to carry out a certain task, and once the purpose is accomplished, these groups cease to exist.
- The interest of members in case of a primary group is diffused, as each member may have different interest, however, the central interest dominates the self-interest. Conversely, in case of a secondary group, the interest of the members are common for which they join the group. For instance: People who join a gym, have one common interest, i.e. to reduce weight and keep themselves healthy and fit.
- Primary Groups are commonly found in family settings, i.e. the members of the household often share a common background, and they know each other quite well. Also, they have a face to face contact with each other. As against, the secondary group is usually found in an educational and employment setting, like a class, batch, work team, etc.
- Primary Group plays a very important role in the lives of people as they tend to shape the personality, behaviour and character of people. As against, the secondary group has a little significance on the life of people.
- In the case of the primary group, the focus is on the relationship, but in the secondary group, the main focus is on the task or goal for which the group is joined.
- The relationship between group members is direct, intimate and personal, in the primary group. Unlike, the relationship between group members is impersonal and goal-oriented.
- In general, people experience or become part of the primary group in their early stage of life. But in their later stages of life, they become part of various secondary groups.
- Primary Group works on the principle of particularism i.e. each individual is important. As against, the secondary group works on the principle of universalism, which means that the group is open to all and anyone can join it.
- The structure of a primary group is informal, whereas secondary group has a formal structure.
- In the primary group, the members know each other and they have strong bonding, so they have direct, quick and effective communication. In contrast, communication is indirect in case of a secondary group.
- The best thing about the primary group is that the members have a stable role. However, in a secondary group, the role of people is interchangeable in nature.
- There is direct cooperation between members of a primary group, but indirect cooperation is present in case of a secondary group.
Characteristics of Primary Group
The salient characteristics of a primary group are stated in the points given below:
- Physical Proximity: People belonging to a particular primary group, share a close and intimate relationship with one another. and that is why physical nearness, of the group members, makes communication easy and quick.
- Small Size: Such groups are usually small in size. For example, in a Nuclear family, the mother, father and children are called a primary group. Further, when the group is small in size, the members have strong emotional ties with one another and know each other quite well. They also develop a group character.
- Stability: Relationship between the group members can only be strong when there is some degree of stability in the group. If the members enter and exit the group frequently, intimacy may not be developed between them.
- Similarity of Background: This means that the group members share a common experience, environment, history or circumstances.
- Limited Self Interest: People belonging to this group subordinate their self-interest to the common interest of the group. They join the group and take part in it cooperatively.
- Intensity of Shared Interest: Each member of the primary group share a common interest, which is relevant for all as well as valued by all.
Characteristics of Secondary Group
A Secondary Group is characterized by: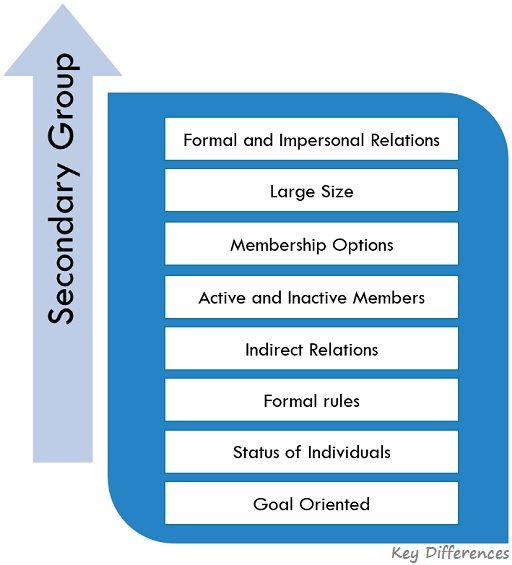
- Formal and Impersonal Relations: As there is little to no face to face interaction between the members, the members have a very small degree of influence over one another. Also, a member does not know the other person very well. Hence, the relation is formal and impersonal as well.
- Large Size: By large in size, we mean that the group may be spread in a large geographical area, or it may have numerous members.
- Membership option: Becoming a member of a particular group, depends on the choice of the person, i.e., Unlike the primary group, one can simply avoid being a part of a particular secondary group. For instance: If you don’t want to be a part of a particular batch of a dance class, you can simply change the batch and become part of another group.
- Indirect Relations: As the members are spread all over the world, so the communication between them takes place by indirect means, i.e. via mobile, video conferencing, email, and so forth.
- Active and Inactive Members: In a secondary group, there is very little personal contact between the members. Hence, there is a lack of intimacy and so some members are active, while others are inactive.
- Formal Rules: There is a well-established set of formal rules and regulations, which the members are expected to follow.
- Status of Individuals: The status of the members keeps changing with time and circumstances. Moreover, the status is based on the role played by the members.
- Goal-Oriented: Secondary Group is formed with a specific purpose or goal, and every member strives to achieve that goal.
Examples
| Primary Group | Secondary Group |
|---|---|
| Nuclear Family | Workgroup |
| Roommates of Hostel | Sports Team |
| Friend Circle | Club |
| Group of Cousins | Neighbors |
What are Tertiary Groups?
A tertiary group or otherwise called a reference group can be the one which is recognized as a model or ideal for defining an individual’s attitude, behaviour and evaluations. For instance: If the members of a particular group strive to become a member of another group, the latter becomes a tertiary group.
Conclusion
Groups are a part of the society and every individual is a member of one or more groups. To get a better understanding of the society, one needs to learn the behaviour of the groups, as it reflects the structure of the society, they are a part of.






JS says
thank you