 Allowance refers to the financial benefit which an employer provides to employees in addition to the basic salary they draw, so as to meet the expenses that employees may incur to perform the job or because of it. Conversely, perquisites refer to a financial benefit which an employer provides to an employee because of their job or the designation they hold.
Allowance refers to the financial benefit which an employer provides to employees in addition to the basic salary they draw, so as to meet the expenses that employees may incur to perform the job or because of it. Conversely, perquisites refer to a financial benefit which an employer provides to an employee because of their job or the designation they hold.
These are like add ons to an employee’s compensation. It facilitates the management of a number of expenses for which the employee does not need to spend money from his own pocket.
In this post, we are going to discuss the difference between allowance and perquisite.
Content: Allowance Vs Perquisites
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Allowances | Perquisites |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Allowance implies the amount paid by an employer to the employees for meeting certain special expenses, i.e. discharging official duties or to meet personal expenses. | Perquisite refers to a facility, provided to the employee apart from their salary or allowance, owing to his/her designation or length of service. |
| Paid in | Cash | Cash or Kind |
| Purpose | Official or Personal Purpose | Personal Purposes |
| Impact on take home salary | It increases take home salary. | It does not effect take home salary. |
| Tax Liability | Increases tax liability | Reduces tax liability |
Definition of Allowance
Allowance is a fixed amount given to the employee at periodic intervals to cover special expenses incurred while discharging job-related duties. To put it simply, an allowance is a compensation for the incurrence of specific expenses.
Amount paid by the company in the form of allowance also constitutes a part of the salary. Also, the amount of allowance is considered to determine the total salary for the purpose of taxation.
From a tax point of view, the expenses are divided into three main categories: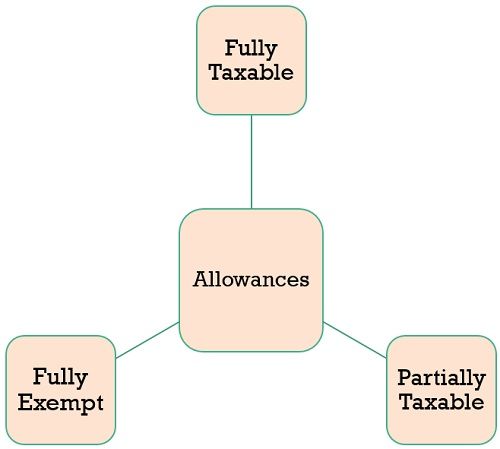
Fully Taxable Allowances
- Dearness Allowance: Dearness Allowance or DA is the allowance given to the salaried people as a cost of living adjustment allowance, so as to survive inflation.
- Entertainment Allowance: Entertainment allowance is given for reimbursing the expenses made on the customer’s hospitality. The lowest of the three amounts that follow is an allowable deduction for government employees – 1/5th of basic salary, the actual amount received, or ₹ 5000.
- Overtime Allowance: When employees work over and above their working hours, overtime allowance is provided to the employees.
- City Compensatory Allowance: In the urban cities where the cost of living is extremely high, city compensatory allowance is given to the employees to survive the inflated cost of living.
- Project Allowance: Allowance provided to employees for meeting project expenses, is called project allowance.
- Meal Allowance: Allowance provided for tiffin or meal is meal allowance.
- Cash Allowance: Cash Allowance is provided by the employer such as marriage allowance, bereavement allowance or holiday allowance, etc.
- Servant Allowance: Servant allowance is given by the employer to an employee to get the services of a servant.
- Medical Allowance: Allowance that an employer pays to an employee at a fixed rate, regardless of the treatment taken by the employee.
Partially Taxable Allowances
- House Rent Allowance: An allowance paid for the accommodation of the employees is called a house rent allowance.
- Children Education Allowance: It is exempt up to a certain amount per month per child, subject to a maximum of two children. Likewise, hostel subsidy up to a certain amount per month per child is also exempt, subject to a maximum of two children.
Fully Exempt Allowances
- Allowance paid to government servants in foreign countries: Government employees paid an allowance while serving in foreign countries.
- Sumptuary Allowance: This allowance is given to the judges of the Supreme Court and High Court.
Also Read: Difference Between Salary and Stipend
Definition of Perquisites
Perquisites or perks are casual emolument or the monetary value of personal benefit or amenity, connected to the office or position, over and above the salary. The employer provides perquisites to the employee, for free or at concessional rates. Further, no money is provided to the employee, if the employee does not use or avail of these amenities.
However, it does not indicate mere reimbursement of important expenditures, for discharging official duties.
Nowadays, an employee’s salary package covers the basic pay and perquisites such as company car, housing, servant, etc. It may arise while carrying out employment or profession.
- Prerequisite resulting from the employment relationship, then it is taxable as salary. But when it results from a profession, it is chargeable to tax as profits and gains of business and profession.
- Only those perquisites are taxable which has arisen legally. that is to say, if an employee has taken unauthorized advantage of the employer’s permission, it will not be regarded as a prerequisite.
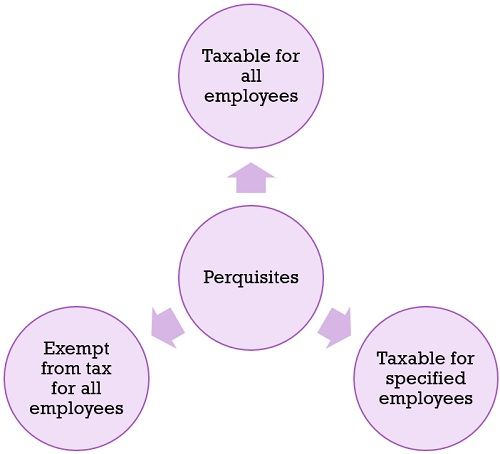
From the tax point of view there are three types of perquisites:
Perquisites Taxable for all Employees
- Rent-Free Accommodation: Rent-free accommodation provided to an employee by an employer. However, one should take note of the fact that Rent free official residence provided to the high court and supreme court judges is free from taxes. Also, Rent free furnished house given to officers of parliament is also free from tax.
- Concession in Rent: Concession in rent for accommodation which an employer provides to an employee.
- Payment by an employer concerning employee’s obligation: Any obligation which is to be payable by the employee, but paid by the employer, is regarded as a prerequisite.
- Payment of amount by the employer either directly or indirectly to affect the life assurance of the employee.
- Specified security or sweat equity shares allotted or transferred by the employer: Direct or indirect allotment or transfer of specified security or sweat equity shares by the employer or ex-employer either free of cost or at a concessional rate to the employer.
- Other fringe benefits: Value of any other fringe benefits prescribed by the Central Board of Direct Taxes such as credit card expense. club expenditure, use of movable assets, interest-free or concessional loan, etc.
Exempt perquisites
- Telephone: Telephone facility which an employer provides to an employee at the residence.
- Transport Facility: Provision of transport facility which an employer provides to the employee who is engaged in the business carrying of passengers or goods, to an employee which can be free of cost or at concessional rate.
- Privilege passes and privilege tickets: Indian railways offer privilege passes or ticket orders to their employees.
- Perquisites allowed outside India by the government: Perquisites allowed to a citizen for providing services in a foreign nation by the Indian government.
- Employer’s contribution to staff group insurance scheme.
- Payment of annual premium by the employer on personal accident policy: Annual premium payment made by the employer on personal accident policy initiated by an employee on employee’s life.
- Refreshment: Refreshments are provided to the employees in the office during working hours.
- Recreational Facilities: Recreational Facilities such as club facilities are provided to the employee’s personnel in general.
- Amount spent on training of employees: Amount spent on the training of the employees or on refresher management course plus boarding and lodging expenses incurred by the employer.
Perquisites taxable in the hands of specified employees
Here the term ‘specified employees‘ means – director employee or an employee who has considerable interest in the company, employees drawing more than ₹ 50k salary. The perquisites which are taxable in the hands of specified employees are:
- Provision of servants like sweeper, watchman, personal attendant, and gardener.
- Facility of use of gas, electricity, or water
- Free or concessional tickets
- Use of motor car
- Educational facilities to children, either free or at concessional rates
Valuation of Perquisites
As a rule of thumb, the amount of perquisites that are taxable in the hands of employees is the cost to the employer.
Also Read: Difference Between Gross Salary and CTC
Key Differences Between Allowance and Perquisites
The difference between allowance and perquisites are discussed in the points that follow:
- Allowance refers to the extra amount which an employer pays to the employee to cope with particular expenses for carrying out official duties. On the other hand, Perquisites refers to additional benefit, over and above the amount, which is legally due, because of employment agreement for the services rendered.
- Allowances are paid in cash whereas perquisites are usually given in consideration other than cash, however, if it is paid in cash, it is a reimbursement of the bill which is already paid by the employee when it is incurred.
- In case the allowances are provided for official purpose, it is exempted from tax, however, when the allowances are provided for personal purposes, it is taxable. Conversely, perquisites are provided in consideration other than cash, then it is valued according to the cost to the employer and so it is taxable.
- While allowances increase take-home salary, perquisites do not affect take-home salary.
- Allowance increases tax liability, whereas perquisites reduce tax liability.
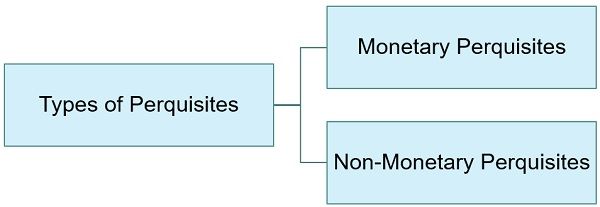
Types of Perquisites
- Non-Monetary Perquisites: Non-monetary perquisites are in the form of free facilities that the employees have access to either free of cost or at concessional rates. It must be noted that these prerequisites are taxable in the hands of specified employees. These are:
- Free domestic servant at employees home-like gardener, sweeper, watchman, etc.
- Free water, gas, and electricity at the home of the employee
- Free educational facility for the children of the employee
- Use of company’s motor car for free.
- The private journey is offered for the free or concessional rate to the employee or family of the employee.
- Monetary Perquisites: Monetary perquisites are the perquisites that can be claimed as reimbursement. These are taxable for all employees. It includes
- Reimbursement of certain bills like gas, water, and electricity.
- Reimbursement of school fees of the children.
- Reimbursement of motor car expenses like petrol or diesel expenses etc.
Conclusion
Allowances are like benefits provided to an employee in addition to their regular salary. Conversely, the prerequisite is a benefit be it financial or non-financial, offered to an employee owing to the job or designation.





Deepika says
Thank you for uploading easy questions
Priya says
Such a clear explanation are given which is easily understood by everyone.. Thank You