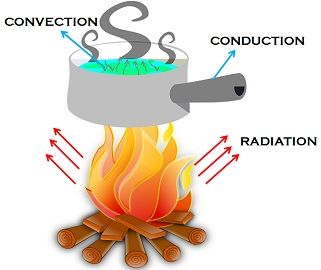
 While conduction is the transfer of heat energy by direct contact, convection is the movement of heat by actual motion of matter; radiation is the transfer of energy with the help of electromagnetic waves.
While conduction is the transfer of heat energy by direct contact, convection is the movement of heat by actual motion of matter; radiation is the transfer of energy with the help of electromagnetic waves.
The matter is present around us, in three states, solid, liquid and gas. The conversion of matter from one state to another is termed as a change in state, that takes place due to the exchange of heat between the matter and its surroundings. So, heat is the transition of energy from one system to another, due to the difference in temperature, which occurs in three different ways, that are conduction, convection and radiation.
People often misconstrue, these forms of heat transfer but, they are based on diverse physical interaction to transfer energy. To study the difference between conduction, convection and radiation, let’s take a look at the article provided below.
Content: Conduction Vs Convection Vs Radiation
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Conduction | Convection | Radiation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Conduction is a process in which transfer of heat takes place between objects by direct contact. | Convection refers to the form of heat transfer in which energy transition occurs within the fluid. | Radition alludes to the mechanism in which heat is transmitted without any physical contact between objects. |
| Represent | How heat travels between objects in direct contact. | How heat passes through fluids. | How heat flows through empty spaces. |
| Cause | Due to temperature difference. | Due to density difference. | Occurs from all objects, at temperature greater than 0 K. |
| Occurence | Occurs in solids, through molecular collisions. | Occurs in fluids, by actual flow of matter. | Occurs at a distance and does not heats the intervening substance. |
| Transfer of heat | Uses heated solid substance. | Uses intermediate substance. | Uses electromagnetic waves. |
| Speed | Slow | Slow | Fast |
| Law of reflection and refraction | Does not follow | Does not follow | Follow |
Definition of Conduction
Conduction can be understood as the process, which enables direct transfer of heat through the matter, due to the difference in temperature, between adjacent parts of the object. It happens when the temperature of the molecules present in a substance increase, resulting in vigorous vibration. The molecules collide with surrounding molecules, making them vibrate too, resulting in the transportation of thermal energy to neighbouring part of the object.
In simple terms, whenever two objects are in direct contact with one another, there will be a transfer of heat from the hotter object to the colder one, which is due to conduction. Further, the objects which permit heat to travel easily through them are called conductors.
Definition of Convection
In science, Convection implies the form of heat transfer, by real movement of matter, that occurs only in fluids. Fluid alludes to any substance, whose molecules move freely from one place to another, such as liquid and gases. It happens naturally or even forcefully.
Gravity has a great role to play in natural convection such that when the substance is heated from below, leads to the expansion of the hotter part. Due to buoyancy, the hotter substance rises as it is less dense and the colder substance replaces it by sinking at the bottom, due to high density, which when gets hot moves upward, and the process continues. In convection, on heating up the substance, it’s molecules disperse and moves apart.
When the convection is performed forcefully, the substance is compelled to move upwards by any physical means such as the pump. E.g. Air heating system.
Definition of Radiation
The heat transfer mechanism in which no medium is required is called radiation. It refers to the movement of heat in waves, as it does not need molecules to travel through. The object need not be in direct contact with one another to transmit heat. Whenever you feel heat without actually touching the object, it is because of radiation. Moreover, colour, surface orientation, etc. are some of the surface properties on which radiation depends greatly.
In this process, the energy is transmitted through electromagnetic waves called as radiant energy. Hot objects generally emit thermal energy to cooler surroundings. Radiant energy is capable of travelling in the vacuum from its source to the cooler surroundings. The best example of radiation is solar energy that we get from the sun, even though, it is miles aways from us.
Key Differences Between Conduction, Convection and Radiation
The substantial differences between conduction, convection and radiation are explained as under:
- Conduction is a process in which heat is transported between parts of a continuum, through direct physical contact. Convection is the principle, wherein heat is transmitted by currents in a fluid, i.e. liquid or gas. Radiation is the heat transfer mechanism, in which the transition takes place through electromagnetic waves.
- Conduction shows, how heat is transferred between objects in direct contact, but Convection reflects how heat travels through liquids and gases. As against this, radiation indicates how heat travels through places having no molecules.
- Conduction takes place as a result of the difference in temperature, i.e. heat streams from high-temperature area to low temperature area. Convection happens due to the variation in density, such that the heat moves from low-density region to high-density region. On the contrary, all object release heat, having a temperature more than 0 K.
- Conduction usually occurs in solids, through molecular collision. Convection occurs in fluids by mass motion of molecules in the same direction. In contrast, Radiation takes place through the vacuum of space and does not heat up the intervening medium.
- The transfer of heat is through heated solid substance, in conduction, whereas in convection the heat energy is transmitted by way of intermediate medium. Unlike, ration uses electromagnetic waves to transfer heat.
- The speed of conduction and convection is slower than radiation.
- Conduction and convection do not follow the law of reflection and refraction, whereas, radiation obeys the same.
Conclusion
Thermodynamics is the study of heat transfer and the changes related to it. Conduction is nothing but the heat transfer from the hotter part to the colder one. Convection is the heat transfer by up and down motion of the fluid. Radiation occurs when heat travels through empty space.






MIKEY MIKESTER says
I appreciate the website, the contents are worth reading.
Dawryn says
yes it is worth it
bugal says
thank you
chedda says
will the radiation be more powerful than the conduction?
Student at ees says
I really like this article it helped me a lot
Ajaysinh says
Very interesting and straight forward explanation is given . thank you
Me says
I agree and it gives a straight out explanation
Sam says
Very good article
Mohamadreza says
Thank you so much
This article is simple and easy to understand.
Not vince says
Nice article good job
Farshid says
I like the article. Simply describe the definition and understandable in a simple language.
A_boy says
I like it
A_boy says
I like this.
pewds says
yes its good
Taryn says
This was helpful for me!
robot says
statistically correct for a human
M says
Excellent summary on the matter
Surbhi S says
Thank you all for sharing your valuable views with us. It motivates us t do even better. Keep reading. 🙂
Kunjamani says
Really helpful to me as a student i get the needed knowledge from your source once again thank you very muchhhh…….
jeff says
it was really helpful
noah says
very helpful
person says
I love it, it helped me a lot.
Brady Taylor says
This article really did help me a lot, mostly because it is simple and gives a great definition
Marissa Latham says
Hello marissa here! I just want to say that this website helped me so much. Thank you for letting me borrow some of your time today…thank you and goodbye!!!
pranita lohar says
Thank you for the info.
Bob says
Helps me a lot thanks.
Sherif says
A comprehensive breakdown of conduction, convection and radiation.
It’s worth reading,thanks to the writer.
Soliyana says
This article has made it easier for me to understand the concept of conduction, convection and radiation.
Thank you.
Dr. N.S. Rajendran says
scientific points, highly informative
Ruvini says
This is highly informative. Thank you very much.
I have a small doubt to get cleared.
What happens when the heat transfer is between a liquid and a solid. For example in heat exchangers like automobile radiator, heat flows from the coolant (liquid) to the radiator material (solid) and then form the radiator material (solid) to the outside (air).
Can you explain the heat transfer principles in this case.
Thanking you in advance.
Isaac Onoja says
Great work. Thanks
Golden says
Your work here gave a clearer understanding. Thanks.
lucas says
It has made my work in 5th grade so much easy
unknown says
this helped me in my 6th grade science class
Mia says
thank you this helped me during my test
noah says
so cool