 The basic difference between internal check and internal audit is that internal check is a routine checking procedure, which involves cross-checking of every aspect of the work performed, at the time when it is performed, and recording the same. On the contrary, in internal audit, each and every component of the work is examined, by an independent staff, specially recruited for the purpose.
The basic difference between internal check and internal audit is that internal check is a routine checking procedure, which involves cross-checking of every aspect of the work performed, at the time when it is performed, and recording the same. On the contrary, in internal audit, each and every component of the work is examined, by an independent staff, specially recruited for the purpose.
The aim of internal audit is to provide an independent and objective assurance that the company’s risk management, governance, internal check and internal control systems are functioning in a satisfactory manner. Further, it is important to note that the effectiveness of any system implemented in the organization greatly depends on the staff employed to undertake the same.
This written account will help you clear all the doubts regarding the differences between internal check and internal audit.
Content: Internal Check Vs Internal Audit
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Internal Check | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Internal Check is a system, wherein division of work and allocation of responsibilities are organized in such a manner that the work of one employee is spontaneously looked over by another. | Internal Audit is the ongoing critical examination of the financial and operational activities of the concern, by an internal auditor. |
| Method | Work of one person is automatically checked by another person. | Work performed by the employees is examined by a separate group. |
| Commencement of Work | Commences from the moment a transaction is entered. | Once the transaction has been recorded in the books. |
| Involved evaluation of | Accounting and clerical accuracy | Effectiveness of management control |
| Performed by | Existing staff | A specially dedicated team of auditors |
| Cost Involvement | Economical | Comparatively Expensive |
| Thrust of System | Prevention of errors and frauds | Detection of errors and frauds |
| Tool for | Arrangement of the work | Examination of the work |
| Time of Checking | Checking is performed simultaneously when the work is performed. | Examination of the work takes place after the work is completed. |
| Report | Summary of day to day transactions acts as a report to the supervisor. | Submits his/her report to the management. |
Definition of Internal Check
Internal Check can be defined as a method of arrangement of the operations of factory, office, warehouse, store, etc, wherein the work of one employee automatically comes under the scrutiny of another employee, so as to minimize the risk of errors and frauds. So, for the commitment of fraud one employee has to collude with another.
It is one of the major segment of the internal control system, enforced in the firm whereby no one person is authorized to undertake and enter every facet of the financial transaction. Therefore, the work is divided into different parts and each part is assigned to a different employee and in this way, the work of one employee is subject to the perusal of another employee.
Features of Internal Check
The salient features of Internal Check are illustrated below: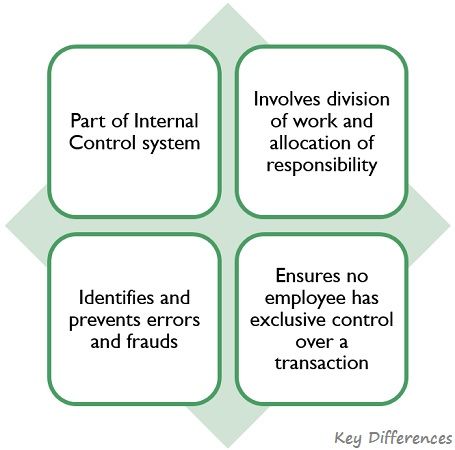
Elements of Internal Check
- Introducing checks on everyday transactions.
- Continuous operation of checks as a part of the routine system.
- Work of one person complements the work of another.
Also Read: Difference Between Internal Control and Internal Audit
Definition of Internal Audit
Internal Audit refers to the systematic and continuous assessment activity which takes place within an organization, wherein operations relating to accounting and finance are reviewed by the team of auditors, so as to provide protective and constructive service to the company’s management. It ensures that:
- Business transactions are accurately and appropriately recorded.
- Books of accounts are systematically maintained as per the relevant provisions.
- No possibility of manipulation of accounts and misappropriation of business property.
An Internal Audit is a form of control, whose aim is to measure and appraise the effectiveness of other types of control. It involves the verification of business operations by the staff specially appointed for the purpose.
Features of Internal Audit
The salient features of internal audit are depicted in the figure below: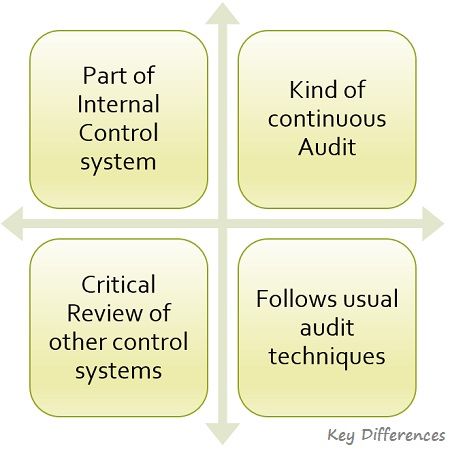
Scope of Internal Audit
The scope of internal audit is represented below: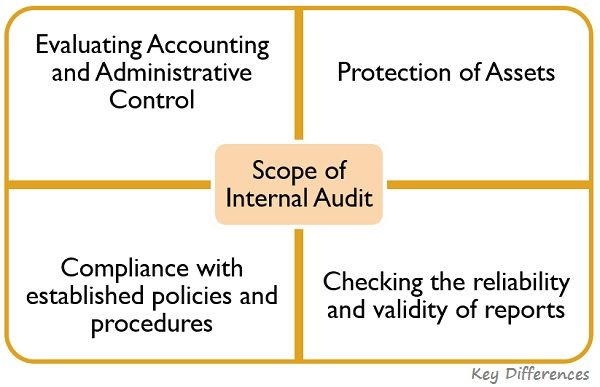
The primary objective of the internal audit is to support the management in effectively discharging the responsibilities by providing them with logical analysis, recommendations and suggestions with respect to the reviewed operations.
Also Read: Difference Between Internal Audit and External Audit
Key Differences Between Internal Check and Internal Audit
The points stated hereunder will explain to you the differences between internal check and internal audit:
- Internal Check is a system implemented in the firm, in which the work performed by one staff member is by itself checked up by the other staff member so that the chances of error or fraud is least. On the other hand, internal audit, as the name suggests, is the audit conducted internally in the organization. It implies the systematic critical examination of the books of accounts by the staff of the concern.
- In an internal check, the entire process is designed in a logical manner by dividing the work so that no person has absolute control on each and every aspect of the transaction. Conversely, in internal audit, the work performed by the employees, are examined and cross-verified by a separate group, specifically appointed for the purpose.
- The internal check begins from the moment a transaction is entered. As against, internal audit starts from the point, when the transaction has been recorded in the books.
- The internal check involves checking of accounting and clerical accuracy, whereas internal audit is all about checking the effectiveness and scope of management control.
- The internal check is performed by the existing employees. In contrast, for the purpose of internal audit, the company appoints a special team of auditors.
- As an internal check is carried out by the existing workers, no extra cost is involved in it. On the contrary, in internal audit, as the work is performed by a specially dedicated team recruited for the purpose of conducting an audit, it is a bit expensive.
- While internal check prevents the occurrence of errors and frauds, internal audit detects errors and frauds.
- The internal check is well known for arrangement (designing) of work, by the allocation of responsibilities and tasks. As opposed, an internal audit involves an examination of work.
- The internal check is performed simultaneously, i.e. the checking is done, at the same time when the work is performed, so mistakes are checked at an early stage. On the other hand, an internal audit takes place, after the recording of the transactions.
- In an internal check, the summary of the day to day transactions acts as a report to the supervisor. Conversely, in an internal audit, the audit report is submitted by the auditor to the management.
Objectives of Internal Check
- To prevent the occurrence of error or fraud.
- To minimize the misappropriation of cash or goods by any staff member.
- To ensure that the firm accounting system provides reliable, complete, up-to-date and accurate information of each and every business transaction.
- To identify error or fraud at an early stage and correct them promptly.
- To enable protection to the firm’s resources against theft, carelessness, and inefficiency.
- To delegate work in a way that no segment of the business remains unchecked or unrecorded.
- To locate errors and frauds as and when they are committed, through independent checking.
Objectives of Internal Audit
- To substantiate the accuracy and authenticity of the accounting records, supplied to the management.
- To ensure the compliance of standard accounting policies and practices.
- To enable detection of error and frauds at an early stage.
- To analyse the internal check system at periodic intervals, so as to recommend improvements, along with carrying out special investigation for the management.
- To verify that the liabilities have been sustained for valid and legitimate activities.
- To make certain that the transactions are carried out by an authorized person and under the relevant authority.
Advantages of Internal Check
The figure given hereunder explains the advantages of internal check: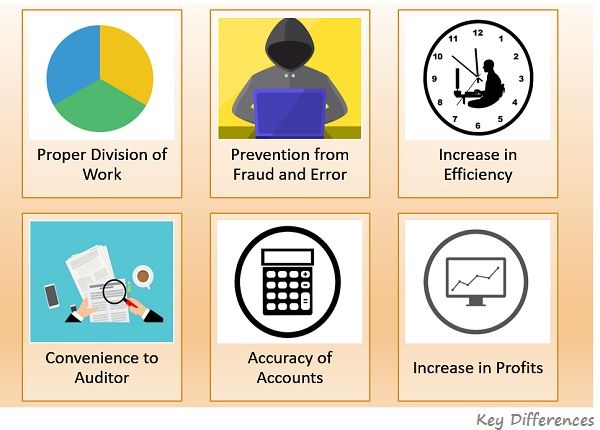
Advantages of Internal Audit
Have a look at the figure to understand the advantages of internal audit:
Conclusion
So, Internal Audit is a significant tool of management, which authenticates the accuracy of the accounting records on a regular basis. It reports to the management about the effectiveness of the internal check system as well as other kinds of control, implemented in the concern.






sushmita says
thank you so much
Yuvi says
Ok it’s awesome