 While in “Trial Balance“, the use of the terms ‘Debit’ and ‘Credit’ is to represent the nature of accounts. In “Balance Sheet“, use of the terms like Assets and Liabilities indicate what the business owns and what it owes, respectively.
While in “Trial Balance“, the use of the terms ‘Debit’ and ‘Credit’ is to represent the nature of accounts. In “Balance Sheet“, use of the terms like Assets and Liabilities indicate what the business owns and what it owes, respectively.
Trial Balance is a part of the accounting process, which is a summary of debit and credit balances taken from all the ledger accounts. Every transaction affects two sides, i.e. every debit has a corresponding credit and the reverse is also true. The total debit and credit balances are equal in the trial balance.
In contrast, the Balance Sheet is the statement that exhibits the company’s financial position, by presenting the assets, liabilities, and capital on a particular date.
In this post, we are going to talk about the differences between Trial Balance and Balance Sheet.
Content: Trial Balance Vs Balance Sheet
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Trial Balance | Balance Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A Trial Balance is a statement that depicts the balances of all ledger accounts. | Balance Sheet is a statement expressing the position of assets and liabilities of the firm, as on a particular date. |
| Part of the Financial Statement | No | Yes |
| Purpose | To check the arithmetical accuracy of the accounting entries passed. | To ascertain the financial position of the enterprise. |
| Necessity | Optional | Compulsory |
| Information | It contains information related to general ledger accounts. | It shows information about the assets and liabilities of the company. |
| Stock | Includes information about the opening stock | Includes information about the closing stock |
| Auditing | The trial balance need not be audited. | Balance Sheet need to be audited. |
| Accurate | When the total of debits equals the total of credits. | When the asset side equals the liabilities side. |
| Accounts include | All the personal, real and nominal accounts are included. | Includes only personal and real accounts. |
| Use | Created for internal use only | Both internal as well as external use |
| Frequency of Preparation | It is prepared monthly, quarterly, half-yearly or annually. | It is prepared for every financial year |
| Source of information | Ledger Accounts | Trial Balance |
What is Trial Balance?
A trial balance is a statement which lists all the balances of the Real, Personal and Nominal Accounts irrespective of the Capital or Revenue nature of the accounts. It contains two columns debit and credit. If the recording and posting of the transactions take place properly and systematically, then the total of both columns would be identical.
But, if the total of both columns differs then there are chances of errors in the recording and posting.. However, some errors are not revealed through trial balance which includes:
- Compensating errors
- Errors of omission
- Errors of commission
- Errors of principle
Trial Balance is the third step in the accounting process. This means, at the stage summarization of all accounts takes place at this stage. A trial balance is a statement prepared at a specific date with debit and credit balances of various ledger accounts, for testing the arithmetical accuracy of the company’s books of accounts. It helps in the preparation of the final accounts of the company.
One can prepare a trial balance by arranging all ledger account balances, by categorizing them into debits and credits to test the correctness of the accounts.
Also Read: Difference Between Error of Omission and Error of Commission
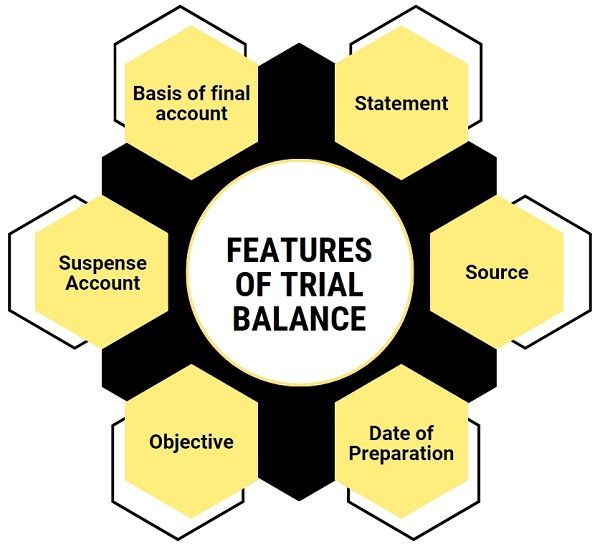
Features of Trial Balance
- Statement: It is a list or statement and not an account.
- Source: Trial Balance is prepared using a ledger account and cashbook.
- Date of Preparation: As the trial balance is for the internal use of the company, it can be prepared on any date. Generally, it is prepared at a fixed interval of time.
- Objective: It checks the arithmetic accuracy of the accounts. If both sides of the trial balance are equal, it is regarded as correct. However, there are certain exceptions.
- Suspense Account: If both sides of the trial balance are showing different totals, then it is an indicator of errors in the account. Hence, the difference is taken into the suspense account.
- Basis of final accounts: It serves as the basis for preparing the final accounts of the company.
Objectives
- Trial Balance is such a tool of accounting that tests the arithmetical accuracy of the accounts. If the recording is done correctly, then the trial balance will automatically tally.
- Checking whether the principles of the double entry system are properly applied.
- As you know preparation of the final account is compulsory for all companies. So, it facilitates in the preparation of the Income Statement and Balance Sheet to know the company’s financial position and performance.
- Helpful in making comparisons of the previous year’s balances to arrive at the right conclusion.
- Preparing a summary of various ledger accounts. We could say that all the information concerning the ledger accounts is available from the trial balance.
- While preparing the final accounts of a company, adjustments are to be made in closing stock, outstanding expenses, advance income, etc.
- Helps in locating or detecting errors at the time of casting, posting and balancing. Once the error is detected, it can be verified.
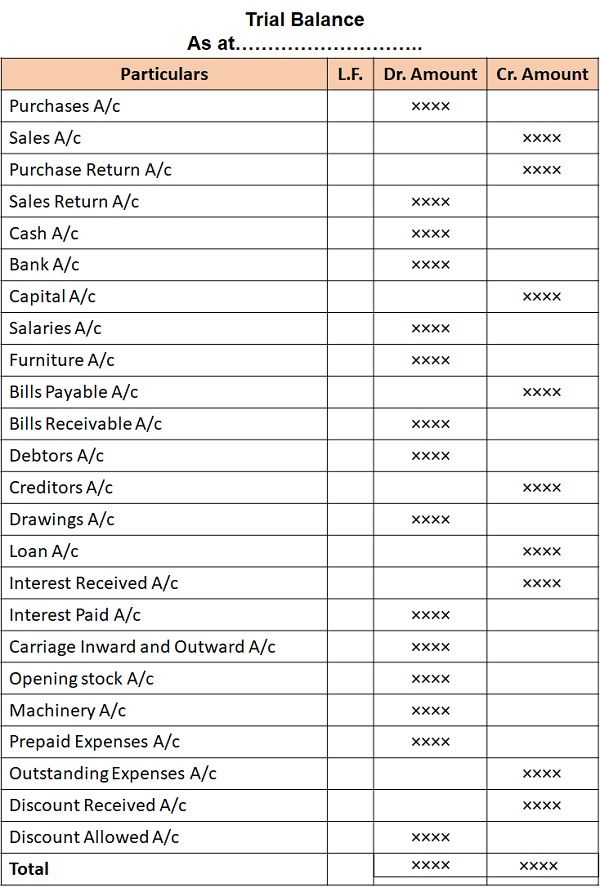
Format
Methods of Preparation of Trial Balance
- Totals Method
- Balances Method
- Total cum Balances Method
Also Read: Difference Between Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement
What is Balance Sheet?
Balance Sheet is like a mirror of the business as it shows the status of the company at a particular date, in just one glance. It reflects the assets – what the company owns, and liabilities – what the company does. There are two formats for presenting the Balance sheet. They are – horizontal or vertical.
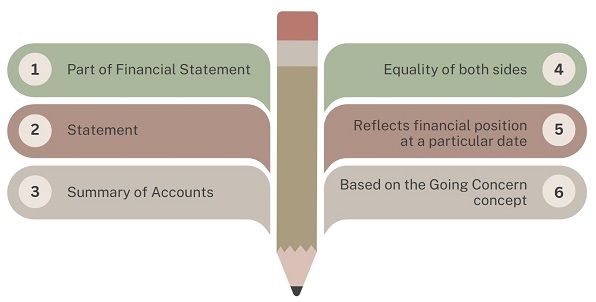
Features of Balance Sheet
- Part of Financial Statement: Balance Sheet is an important part of the financial statement or final account of a company.
- Statement: The Balance Sheet is a statement and not an account. Therefore, it does not use the prefix ‘To’ or ‘By’ at the beginning of any item.
- Summary of Accounts: It depicts the summary of personal and real accounts that are open. This means it consists of those accounts which are not yet closed by transferring the same to trading and profit and loss account.
- Equality of both sides: The totals of the assets and liabilities side of the balance sheet must be equal. If they are not equal then it means there is an error which needs rectification.
- Reflects financial position at a particular date: As discussed above, the balance sheet reflects the financial position of the company on a specific date.
- Based on the Going Concern concept: It is based on the going concern concept, which means that the company will continue its operations in the coming future.
Why a Balance Sheet is a statement and not an account?
There are several reasons why you cannot say that a balance sheet is not a ledger account. These are:
- While an account relies on journal entries, the balance sheet does not depend upon journal entries.
- A ledger account gives a small description of the entered transactions, concerning the account for the period. However, a balance sheet has no such description.
- We mark the top left and right corners of the ledger account as Dr. and Cr. But we do not mark Balance Sheet this way.
- As per the double entry system, the assets and liabilities sides of the balance sheet are equal. However, the two sides of an account rarely tally. And that’s why balancing is required.
Objectives of Balance Sheet
- Determination of the nature and value of business assets.
- Ascertainment of the nature and amount of external liabilities
- Identifying the financial solvency position of the enterprise. A company is said to be solvent when its assets are more than its liabilities.
- Determining the correct financial position of the company at a specific point in time.
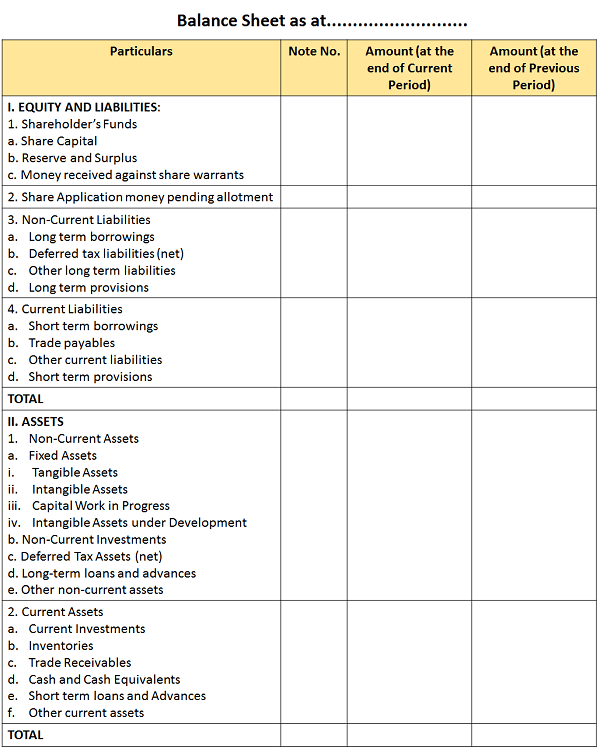
Format
Functions of Balance Sheet
- The balance sheet indicates the closing value of the resources and obligations of the company at the end of the financial year.
- It facilitates the calculation of working capital and capital employed by the company.
- With the help of the available data from the balance sheet, the company’s financial strength can be measured easily.
- Balance Sheet gives important information to the users, which assists in deciding about the future in advance.
Also Read: Difference Between Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Account
Key Differences Between Trial Balance and Balance Sheet
- Balance Sheet is a statement that a company prepares every year to present the assets, liabilities and equity on a particular date.
- Trial Balance presents the balances of all ledger accounts. As against, Balance Sheet presents the position of assets and liabilities of a company on a particular date.
- The purpose of the preparation of the trial balance is to verify the arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts. On the other hand, the company prepares a balance sheet to demonstrate the financial position of the company, at a given date.
- Trial Balance shows the opening stock for the period as a balance. Conversely, Balance Sheet shows the balance of Closing stock as an asset.
- The preparation of the Balance Sheet is compulsory. In contrast, the preparation of the Trial Balance is at the discretion of the company’s management. In fact, if there is no doubt regarding the correctness of the transactions posted in the books, then the company can skip the preparation of the trial balance.
- In general, the company prepares a trial balance at the end of the month or at the end of the accounting period, i.e. the company prepares it as per the requirement of the entity. On the other hand, the organization prepares a balance sheet only at the end of the accounting period.
- The Balance Sheet is an integral part of the Financial Statement while Trial Balance is not a part of the Financial Statement.
- The preparation of the Trial Balance takes place after posting the transactions into the ledger. Whereas, the preparation of the balance sheet takes place after the preparation of the Trading and Profit & Loss Account.
- The Balance Sheet of corporations is printed and published, whereas the trial balance is neither printed nor published.
Similarities
- First of all, they are statements and not accounts. So, we do not enter the items with the prefix ‘To’ or ‘By’
- The company prepares both statements as per the balances of ledger accounts.
- Further, they are prepared on a particular date.
- They keep a track of only those accounts which have a closing balance. Hence, all those accounts whose debit and credit sides are equal, are not taken to either of the two.
Conclusion
Above all, companies must prepare a balance sheet. Also, the auditors’ signature is essential on it in the case of companies. As against, the preparation of Trial Balance is not compulsory at all. Hence, companies can prepare trial balance as per their requirement. In contrast, the company prepares a balance sheet at a particular date which is usually at the end of the accounting year.






Sierra says
Nice
Pavan says
what is the difference between currency and money
Vaibhav Patil says
Thank you so much
JOHN ONESMO says
what if debt side is not equal to credit side in trial balance.
Surbhi S says
When there is a disagreement in the debit and credit side of the trial balance, then the trial balance is tallied by transferring the difference in the suspense account.
lyn says
Should trial balances for the same period but run from accounting software at different dates be identical?
Ashutosh says
A goood information
Accounts Definition says
A valuable post on differences between trial balance and balance sheet. Thanks for sharing.
DINESH says
Very helpful post. Thank you
Sandra says
Nice