 Bill Discounting and Factoring are two types of short-term finance through which the financial requirements of a company can be fulfilled quickly. The former is related to the borrowing from the commercial bank while the latter is associated with the management of book debts.
Bill Discounting and Factoring are two types of short-term finance through which the financial requirements of a company can be fulfilled quickly. The former is related to the borrowing from the commercial bank while the latter is associated with the management of book debts.
The term factoring includes entire trade debts of a client. On the other hand, bill discounting includes only those trade debts which are supported by account receivables. In short, bill discounting, implies the advance against the bill, whereas factoring can be understood as the outright purchase of trade debt.
So, there exist a fine line of differences between bill discounting and factoring, which are explained in the article provided below.
Content: Bill Discounting Vs Factoring
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Bill Discounting | Factoring |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Trading the bill before it becomes due for payment at a price less than its face value is known as Bill Discounting. | A financial transaction in which the business organization sells its book debts to the financial institution at a discount is known as Factoring. |
| Arrangement | The entire bill is discounted and paid, when the transaction takes place. | The factor gives maximum part of the amount as advance when the transaction takes place and the remaining amount at the time of settlement. |
| Parties | Drawer, Drawee and Payee | Factor, Debtor and Client |
| Type | Recourse only | Recourse and Non Recourse |
| Governing statute | The Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881 | No such specific act. |
| Financier's Income | Discounting Charges or interest | Financier gets interest for financial services and commission for other allied services. |
| Assignment of Debts | No | Yes |
Definition of Bill Discounting
Bill Discounting is a process of trading or selling the bill of exchange to the bank or financial institution before it gets matured, at a price which is less than its par value. The discount on the bill of exchange will be based on the remaining time for its maturity and the risk involved in it.
First of all the bank satisfies himself regarding the credibility of the drawer, before advancing money. Having satisfied with the creditworthiness of the drawer, the bank will grant money after deducting the discounting charges or interest. When the bank purchases the bill for the customer, it becomes the owner of the respective bills. If the customer delays the payment, then he has to pay interest as per prescribed rates.
Further, if the customer defaults payment of the bills, then the borrower shall be liable for the same as well as the bank can exercise pawnee’s rights over the goods supplied to the customer by the borrower.
Definition of Factoring
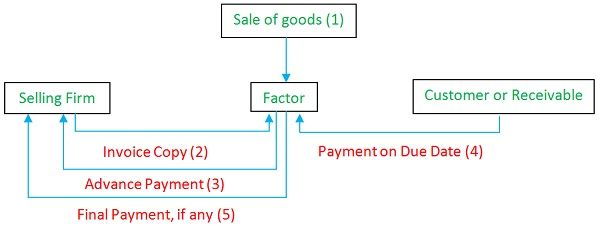
Factoring is a transaction in which the client or borrower sells its book debts to the factor (financial institution) at a discount. Having purchased the receivables the factor finances, money to them after deducting the following:
- An appropriate margin (reserve)
- Interest charges for the financial services
- Commission charges for the supplementary services.
Now, the client forwards the collection from the customer to the financial institution or he gives the instruction to forward the payment directly to the factor and settles the balance dues. The bank provides the following services to the client: Credit Investigation, Debtors Ledger Maintenance, Collection of Debts, Credit Reports on Debtors and so on.
The types of factoring are as under:
- Disclosed Factoring: All the parties know about the factoring arrangement.
- Undisclosed Factoring: The parties do not know about the factoring arrangement.
- Recourse Factoring: In the case of default in payment by the customer the borrower pays the amount of bad debts.
- Non-recourse Factoring: The factors himself bears the amount of bad debt, and that is why the commission rate is higher.
Key Differences Between Bill Discounting and Factoring
The following are the major differences between bill discounting and factoring:
- Selling of bills at a discount to the bank, before its maturity is known as Bill Discounting. Selling of the debtors to a financial institution at a discount is Factoring.
- The bill is discounted, and the whole amount is paid to the borrower at the time of the transaction. Conversely, the maximum part of the amount is provided as an advance, and the rest of the amount is given as balance when the dues are realized.
- The parties to bill discounting are a drawer, drawee, and payee whereas the parties to factoring are the factor, debtor, and borrower.
- The bill discounting is always recourse, i.e. if the customer defaults in payment of debt, then the payment is made by the borrower. On the other hand, the factoring can be recourse and nonrecourse.
- The Negotiable Instrument Act, 1881 contains the rules relating to bills discounting. In contrast to factoring which is not covered under any act.
- In bill discounting the financier gets the discounting charges for financial services, but in the case of factoring the factor gets interest and commission.
- In factoring, the debts are assigned which is not done in bill discounting.
Conclusion
In bill discounting, bills are traded while in the case of factoring accounts receivable are sold. There is a big difference between these two topics. In bill discounting the bank provides a particular service of financing, but if we talk about factoring additional services are also provided by the financier.



SUSHIL GAUR says
It is a nice way of presentation and making subject matter easy to understand and writing in examinations.
Prasad says
Nicely explained.
Teddy says
You made it so easy to understand, even better than my Textbook! No other site had as good material or presentation as yours. Bravo!
Pratik Madrecha says
Awesome! Please keep going
premal kacharia says
Very good information for exporters who require short-term finance.
Saswat Das says
Well explained.