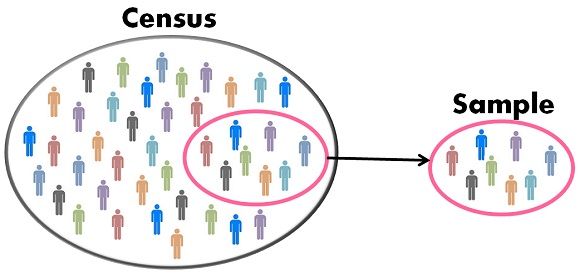
 Census and sampling are two methods of collecting survey data about the population that are used by many countries. Census refers to the quantitative research method, in which all the members of the population are enumerated. On the other hand, the sampling is the widely used method, in statistical testing, wherein a data set is selected from the large population, which represents the entire group.
Census and sampling are two methods of collecting survey data about the population that are used by many countries. Census refers to the quantitative research method, in which all the members of the population are enumerated. On the other hand, the sampling is the widely used method, in statistical testing, wherein a data set is selected from the large population, which represents the entire group.
Census implies complete enumeration of the study objects, whereas Sampling connotes enumeration of the subgroup of elements chosen for participation. These two survey methods are often contrasted with each other, and so this article makes an attempt to clear the differences between census and sampling, in detail; Have a look.
Content: Census Vs Sampling
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Census | Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A systematic method that collects and records the data about the members of the population is called Census. | Sampling refers to a portion of the population selected to represent the entire group, in all its characteristics. |
| Enumeration | Complete | Partial |
| Study of | Each and every unit of the population. | Only a handful of units of the population. |
| Time required | It is a time consuming process. | It is a fast process. |
| Cost | Expensive method | Economical method |
| Results | Reliable and accurate | Less reliable and accurate, due to the margin of error in the data collected. |
| Error | Not present. | Depends on the size of the population |
| Appropriate for | Population of heterogeneous nature. | Population of homogeneous nature. |
Definition of Census
A well-organised procedure of gathering, recording and analysing information regarding the members of the population is called a census. It is an official and complete count of the universe, wherein each and every unit of the universe is included in the collection of data. Here universe implies any region (city or country), a group of people, through which the data can be acquired.
Under this technique, the enumeration is conducted about the population by considering the entire population. Hence this method requires huge finance, time and labour for gathering information. This method is useful, to find out the ratio of male to female, the ratio of literate to illiterate people, the ratio of people living in urban areas to the people in rural areas.
Definition of Sampling
We define sampling as the process in which the fraction of the population, so selected to represent the characteristics of the larger group. This method is used for statistical testing, where it is not possible to consider all members or observations, as the population size is very large.
As statistical inferences are based on the sampling observations, the selection of the appropriate representative sample is of utmost importance. So, the sample selected should indicate the entire universe and not exhibit a particular section. On the basis of the data collected from the representative samples, the conclusion is drawn from the whole population. For instance: A company places an order for raw material by simply checking out the sample.
The units which constitute sample is considered as ‘Sampling Units’. The full-fledged list containing all sampling units is called ‘Sampling Frame’.
Key Differences Between Census and Sampling
The paramount differences between census and sampling are discussed in detail in the given below points:
- The census is a systematic method that collects and records the data about the members of the population. The sampling is defined as the subset of the population selected to represent the entire group, in all its characteristics.
- The census is alternately known as a complete enumeration survey method. In contrast, sampling is also known as a partial enumeration survey method.
- In the census, each and every unit of population is researched. On the contrary, only a handful of items is selected from the population for research.
- Census, is a very time-consuming method of survey, whereas, in the case of sampling, the survey does not take much time.
- The census method requires high capital investment as it involves the research and collection of all the values of the population. Unlike sampling which is a comparatively economical method.
- The results drawn by conducting a census is accurate and reliable while there are chances of errors in the results drawn from the sample.
- The size of the sample determines the probability of errors in the outcome, i.e. the larger the size of population the less are the chances of errors and the smaller the size; the higher are the chances of errors. This is not possible with census as all the items are taken into consideration.
- Census is best suited for the population of heterogeneous nature. As opposed to sampling which is appropriate for homogeneous nature.
Conclusion
Many people interpret census as the opposite of sampling, in which all the members of the population are taken into account instead of only a fraction. But the census is based on the sampling frame to enumerate population. Therefore, it is quite clear that these two quantitative research methodologies are different, but it can’t be said that one is above the other.



sam k says
its clearly understood
Tiana says
Can you compare census-based results and sample-based results? i.e. baseline study included all the subjects in the sample, but due to cost restrictions the follow-up study can only be done in a sample?
Ashmit Gupta says
Nice
BILAL AHMAD says
Absolutely simple but diligent work
Tatijana Taonga Mapara says
Clearly understood.
Thanks
mohit says
thanks a lot