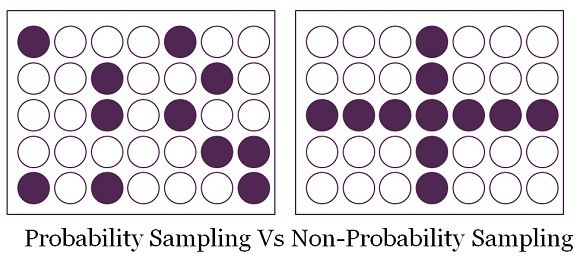
 Sampling means selecting a particular group or sample to represent the entire population. Sampling methods are majorly divided into two categories probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In the first case, each member has a fixed, known opportunity to belong to the sample, whereas in the second case, there is no specific probability of an individual to be a part of the sample.
Sampling means selecting a particular group or sample to represent the entire population. Sampling methods are majorly divided into two categories probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In the first case, each member has a fixed, known opportunity to belong to the sample, whereas in the second case, there is no specific probability of an individual to be a part of the sample.
For a layman, these two concepts are the same, but in reality, they are different in the sense that in probability sampling every member of the population gets a fair chance of selection which is not in the case with non-probability sampling. Other important differences between probability and non-probability sampling are compiled in the article below.
Content: Probability Vs Non-Probability
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Probability Sampling | Non-Probability Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Probability sampling is a sampling technique, in which the subjects of the population get an equal opportunity to be selected as a representative sample. | Nonprobability sampling is a method of sampling wherein, it is not known that which individual from the population will be selected as a sample. |
| Alternately known as | Random sampling | Non-random sampling |
| Basis of selection | Randomly | Arbitrarily |
| Opportunity of selection | Fixed and known | Not specified and unknown |
| Research | Conclusive | Exploratory |
| Result | Unbiased | Biased |
| Method | Objective | Subjective |
| Inferences | Statistical | Analytical |
| Hypothesis | Tested | Generated |
Definition of Probability Sampling
In statistics, probability sampling refers to the sampling method in which all the members of the population has a pre-specified and an equal chance to be a part of the sample. This technique is based on the randomization principle, wherein the procedure is so designed, which guarantees that each and every individual of the population has an equal selection opportunity. This helps to reduce the possibility of bias.
Statistical inferences can be made by the researchers using this technique, i.e. the result obtained can be generalised from the surveyed sample to the target population. The methods of probability sampling, are provided below:
- Simple Random Sampling
- Stratified Sampling
- Cluster Sampling
- Systematic Sampling
Definition of Non-Probability Sampling
When in a sampling method, all the individuals of the universe are not given an equal opportunity of becoming a part of the sample, the method is said to be Non-probability sampling. Under this technique as such, there is no probability attached to the unit of the population and the selection relies on the subjective judgment of the researcher. Therefore, the conclusions drawn by the sampler cannot be inferred from the sample to the whole population. The methods of non-probability sampling are listed below:
- Convenience Sampling
- Quota Sampling
- Judgment or Purposive Sampling
- Snowball Sampling
Key Differences Between Probability and Non-Probability Sampling
The significant differences between probability and non-probability sampling
- The sampling technique, in which the subjects of the population get an equal opportunity to be selected as a representative sample, is known as probability sampling. A sampling method in which it is not known which individual from the population will be chosen as a sample is called nonprobability sampling.
- The basis of probability sampling is randomization or chance, so it is also known as Random sampling. On the contrary, in non-probability sampling randomization technique is not applied for selecting a sample. Hence it is considered as Non-random sampling.
- In probability sampling, the sampler chooses the representative to be part of the sample randomly, whereas, in non-probability sampling, the subject is chosen arbitrarily, to belong to the sample by the researcher.
- The chances of selection in probability sampling, are fixed and known. As opposed to non-probability sampling, the selection probability is zero, i.e. it is neither specified not known.
- Probability sampling is used when the research is conclusive in nature. On the other hand, when the research is exploratory, nonprobability sampling should be used.
- The results generated by probability sampling, are free from bias while the results of non-probability sampling are more or less biased.
- As the subjects are selected randomly by the researcher in probability sampling, so the extent to which it represents the whole population is higher as compared to the nonprobability sampling. That is why extrapolation of results to the entire population is possible in probability sampling but not in non-probability sampling.
- Probability sampling test the hypothesis but nonprobability sampling generates it.
Video: Probability Vs Non-Probability Sampling
Conclusion
While probability sampling is based on the principle of randomization where every entity gets a fair chance to be a part of the sample, non-probability sampling relies on the assumption that the characteristics are evenly distributed within the population, which makes the sampler believe that any sample so selected would represent the whole population and the results drawn would be accurate.




mulie says
It very nice note.
Gigil Marme says
Very helpfull
Arundathi says
Very easy to understand..Good one
Brian Clinton says
very helpful i like it
Khomotso says
like it,easy to understand
Mary says
Very helpful and easy to understand. Who is the author of this piece? I want to acknowledge hi/her in my report.
Surbhi S says
Surbhi S.
Mussa Soposa says
i like it, its very helpful when we are discussing in our course of research and i felt to be a real researcher., real appreciated!!!!!!!
Simran Kapoor says
It was a lot helpful , thanks!
Surbhi S says
Thank you so much friends for constantly appreciating Key Differences for its work. It really means a lot to us. Keep reading 🙂
Menesia Panduleni says
who published your work Surbhi, I need to acknowledge your work and in which town
Alvaro says
Thanks
Dhruba Timalsina says
wow its nice presentation
Snenhlanhla says
It was easy to follow and understand. very helpful.
Julia says
Very helpful to me. Thank you.
Carol says
Thank you. Just what I needed
John Spitzberg says
Very well presented. I am a “dummy” and probably need a “dummified version, but still very well done. Thank you.
Isha Garg says
Very easy, clear and concise. You are doing a great job. Keep it up
Adeoye Caroline says
This is very clear enough. Thanks alot
EKTA JETLY says
EASY TO LEARN AND UNDERSTAND
LIKE IT.
THANKS.
M. E. Vidhate says
Nice notes
Like it.
Thanx.
Animashaun Oluremi says
very helpful
Mohamed Syed Fofanah says
Good work.
Salad says
I am greatly appreciating this classification thanks and long live
Rahul Das says
it is extremely helpful, highly appreciable and strongly recommendable.
Isaiah jacob says
Very very nice. And it is so helpful
angelina bazuka says
really it is helpful and make you understand well thanks
Shoaib says
Good job. Its very helpful.
Philipo ngilini says
Interested
sreelatha ganesh says
very well explained….
Rose says
I loved the notes. Quite precise. Thank you.
RJay says
Nice piece helped me out a lot
Edishegi says
Good job and more likely. Thank you
Sufia says
It was really easy to understand, the concept is very clear.
Thanks a ton!
Mohamud Haji Osman Mayow says
The session was grateful and easy to understand
thanks trillion
Mourice says
wonderful piece. really helpful and quite educative.
Ana Carol says
Great article, Surbhi S! Thank you for clarifying the distinction between probability and non-probability sampling.
manjale says
thank you teacher