 A civil lawsuit begins when a person or an enterprise fails to perform any obligation owed to another person. The aggrieved party gets monetary compensation as damages for the loss suffered by him. The loss can be physical, mental or monetary. And the liability that arises in the case of a civil lawsuit is nothing but a civil liability.
A civil lawsuit begins when a person or an enterprise fails to perform any obligation owed to another person. The aggrieved party gets monetary compensation as damages for the loss suffered by him. The loss can be physical, mental or monetary. And the liability that arises in the case of a civil lawsuit is nothing but a civil liability.
But, in the case of a criminal lawsuit, it is not the victim who initiates the case rather the government prosecutes on behalf of the victim. And when the defendant is proven guilty in the court of law for the crime. The court will order a sentence which can be in the form of a fine or imprisonment or both. So, the liability arising in the case of a criminal lawsuit is criminal liability.
In this post, we will talk about the difference between civil and criminal liability.
Content: Civil Liability Vs Criminal Liability
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Civil Liability | Criminal Liability |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Civil Liability is a legal obligation in which the court orders a party to pay compensation or follow duty. | Criminal Liability is a liability that arises when a person performs any forbidden act. |
| Arises when | Civil Offence | Criminal Offence |
| Which law is followed? | Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 | Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 |
| Remedy | Compensation or Duty to perform something | Fine/Penalty |
| Fine or Imprisonment | ||
| Fine and Imprisonment | ||
| Prosecuted by | Aggrieved Party | Government |
| Burden of Proof | The balance of probability | Beyond reasonable doubt |
Definition of Civil Liability
A plaintiff imposes civil liability against the defendant. In the case of civil proceedings, the plaintiff has the right to demand compensation or damages from the defendant, for the loss suffered by him. It can be in the form of:
- Liability as duty
- Liability as cost
In civil liability, the aggrieved party is entitled to seek redressal from the defendant such as the right to sue for damages for personal injury. The loss must have to be sustained by the aggrieved party, to get the reward for damages. The loss can be a personal injury, damage to property, financial loss etc.
The plaintiff usually seeks financial compensation for the injury or loss of the non-criminal act performed by the defendant.
In finer terms, when a person is guilty of committing a non-criminal act that resulted in harm to the aggrieved party, then that person is legally required to pay monetary compensation to the aggrieved party, as awarded by the judge presiding over the case.
Types of Cases that attract Civil Liability
- Breach of Contract: When one party fails to perform the contract, the other party can claim damages for the loss suffered due to the non-performance of the contract.
- Torts: These cases are related to allegations of the unintentional or intentional wrongful act which resulted in emotional, physical or financial loss to the party concerned. It includes negligence and defamation. breach of statutory duty, fraud, and discrimination.
- Class Action Cases: In these cases, one of the parties is a group of people whose representation is done collectively by one or more members of that group. This group has suffered loss or harm due to the same cause.
Also Read: Difference Between Tort and Crime
Definition of Criminal Liability
A victim imposes criminal liability against the accused. In case of any criminal proceedings, victims look for punishment which can be in the form of imprisonment or penalty for the wrongdoer. For example Murder, theft, sedition, rape, assault, etc.
In criminal cases, generally, a state prosecutes the defendant in the court of law. Moreover, in such cases, it is assumed that both physical and mental element is present in any criminal offence.
Principles of Criminal Liability
It is the responsibility of the prosecution to establish two elements to create a criminal liability:
- Actus Reus (Prohibited Act)
- Mens Rea (Guilty Mind)
This implies that the prosecutor has to prove that the defendant has committed the guilty act while having a guilty state of mind. The prosecution must prove the same to the judge beyond a reasonable doubt. Because the absence of any of the two elements will result in the acquittal of the defendant.
- Actus Reus: The physical outcome of the conduct of a person which is substantially harmful and may attract punishment.
- Mens Rea: In general, if the mind of the person committing the act is innocent, then there is no criminal liability. So, mens rea is the essence to make a person criminally liable. That is to say, wrongful intention or blameworthy condition of mind must be present.
So, the first element is the performance of the prohibited act and the second element is the wrongful mental state. This means that simply having the intent to commit a criminal act is not punishable in the eyes of law. Also, making preparation for committing a criminal act is not punishable. However, criminal liability arises when a person goes a step further into the stage of preparation and makes attempt to commit an act which is forbidden by law.
Also Read: Difference Between Civil and Criminal Law
Key Differences Between Civil and Criminal Liability
The pointers stated here will explain the difference between civil and criminal liability:
- Civil liability is a liability arising due to the civil wrong committed by an individual. It is a legal obligation wherein the defendant must compensate the damages or follow the court’s order with regard to the civil lawsuit. Criminal Liability is a liability arising due to a criminal act committed. In this, the government prosecutes the individual for allegedly committing the crime.
- When someone has committed civil wrong, it attracts civil liability. Conversely, if someone has committed any crime, it may attract criminal liability.
- We follow the Code of Civil Procedure to determine civil liability. Whereas the Code of Criminal Procedure determines criminal liability.
- In the case of a civil lawsuit, civil liability arises when the aggrieved party prosecutes the case. On the other hand, in the case of a criminal lawsuit, criminal liability arises wherein the government prosecutes the case on behalf of the victim.
- Civil liability can take the form of damages or compensation. Also, it can take the form of duty to perform something which the court orders. In contrast, criminal liability can take the form of fine/penalty, fine or imprisonment, fine and imprisonment, fine or Imprisonment or both
- In the case of civil liability, the court’s decision is based on the standard of preponderance of probabilities. As against, in the case of criminal liability, the basis of decision of the court is the provability of the guilt of the accused beyond a reasonable doubt.
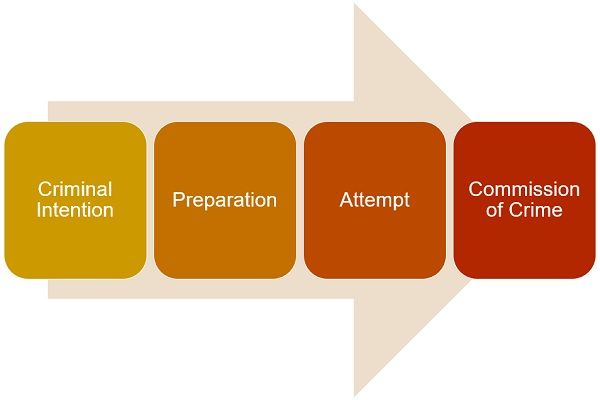
Stages of Crime
- Criminal Intention:
The first stage towards the commission of a criminal act is criminal intention. It is a conscious exercise of the mind. It forces a person to perform an act for the purpose of completing any purpose. Moreover, the law does not punish people for their wrong thoughts or criminal intent. Also, the court does not give punishment for mere guilty intention as it is a bit difficult for the prosecution to prove the criminal intent of a person. - Preparation:
It is a stage in which someone arranges all the stuff required for the commission of the intended criminal offence. Just like criminal intention, the preparation itself is not punishable by law. This is because it is not easy to prove that all the essential preparations were made for the commission of the offence. However, there are certain exceptions where preparation is also punishable. - Attempt:
The alternative term for the attempt is a preliminary crime. As per law any attempt to commit the offence is punishable by law. It is the action toward the commission of a crime when the accused has made necessary preparation for the crime. - Commission of Crime:
The final stage to commit the crime is an accomplishment. When the accused gets successful in the attempt, the outcome is the commission of a crime and the accused will be guilty of an offence. However, if the person remains unsuccessful then the accused will be guilty of the attempt.
Also Read: Difference Between Fine and Penalty
Conclusion
In a nutshell, as per law, depending on the severity of the offence, it is differentiated into two categories, i.e. civil offence and criminal offence. Civil offence can result in civil liability whereas criminal offence can lead to criminal liability.







hossein says
Very good
RUTAGANDA REBECCA says
It is very good, explains clearly
thank you so much the publisher
Nishanthi Ainkaran says
Such a clear and clever way of explanation. Thank you .