 Making mistakes and learning from them, that’s what childhood is all about. Parents try different methods to correct the behaviour of their kid, such as discipline and punishment. Discipline has a very positive impact on the child which not just teaches, or encourages but also helps them know about the standard code of behaviour, which is expected from them.
Making mistakes and learning from them, that’s what childhood is all about. Parents try different methods to correct the behaviour of their kid, such as discipline and punishment. Discipline has a very positive impact on the child which not just teaches, or encourages but also helps them know about the standard code of behaviour, which is expected from them.
On the other hand, punishment is used to reduce the recurrence of the misbehaviour by penalizing the child for unwanted behaviour. Its aim is to stop the child from performing any act which he/she should not do and for this some hurtful or unpleasant technique is used to stop him/her.
In this post, you will find the differences between discipline and punishment.
Content: Discipline Vs Punishment
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Discipline | Punishment |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Discipline refers to a method of training a child to follow rules, so as to regulate his/her behavior towards the society or environment. | Punishment implies imposing penalty, as a payback for the wrongdoing in the past, in the hope that the child won't continue the same behavior in future. |
| What is does? | It presents a choice. | It demands compliance. |
| Involves | Making a child learn from his/her mistakes. | Making a child pay for his/her mistakes. |
| Use | To teach children to obey rules or polish their behavior. | To fix the behavior of the child. |
| Calls for | Learning acceptable behavior | Fearing a consequence |
| Teaching method | Positive | Negative |
| Concerned with | What does the child need to do? | What is wrong with the child? |
| Long term effect | It causes the child to incorporate rules and hold themselves responsible for their behavior. | It causes the child to call for external control, so as to behave in the right manner. |
| Self Esteem | Increased | Lowered |
| Parent-Child Relationship | Strengthened | Damaged |
Definition of Discipline
Discipline can be defined as that process, which helps the child or teen understand in what way he/she should act or behave in the world and learn self-control. When a person is disciplined, he/she follows the instructions and obeys the rules of society. It is all about making your child learn what’s called acceptable behaviour and what’s not.
It is understood as the state of systematic conduct of a person, acquired or learned by proper training in self-control and compliant to the norms and standards which the society approves.
- Discipline is a sort of training which corrects, shapes strengthen or refines the behaviour or attitude of the child.
Effective discipline involves guiding the child’s behaviour, setting boundaries, teaching principles, defining fair and reasonable rules and stating expectations so as to develop such habits, attitudes, code of conduct, etc. in them, which are widely accepted. For this purpose rewards and punishments are used to increase the occurrence of desirable behaviour and decrease the occurrence of undesirable behaviour.
Also Read: Difference Between Positive and Negative Reinforcement
Definition of Punishment
Punishment refers to the form of operant conditioning which involves the infliction of certain unpleasant consequence, upon an individual for the wrongdoing. It is basically retribution to an undesirable act or behaviour, which is not at all acceptable. It follows the operant response and seeks to decrease the possibility of its occurrence in future. It is based on fear and suffering, to make the child adhere to the rules and learn the lesson.
It comprises of penalties and restrictions, which makes a child fear from the consequences. The thought behind the infliction of punishment is that:
- Punishment to change the behaviour: If a child feels bad of his/her actions, then they will discontinue such activity in future or they will be triggered to reform their behaviour in future.
- Retributive punishment: A penalty or pain is inflicted upon by the authority, as a consequence.
- Restorative punishment: Changing the behaviour of the child while restoring the damages caused by the behaviour or act.
However, there are a number of researches which proved that punishment is not the right technique to encourage positive behaviour.
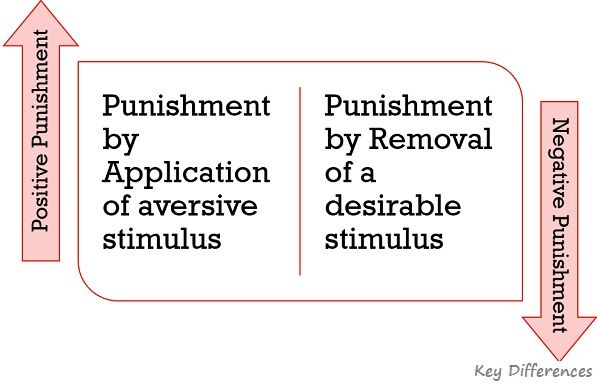
Types of Punishment
- Positive Punishment (Punishment by Application): It is the kind of punishment in which an aversive stimulus is given for the misdeed.
- Negative Punishment (Punishment by Removal): In this form of punishment, a desirable or pleasant stimulus is taken away, after the occurrence of the misdeed.
Also Read: Difference Between Reinforcement and Punishment
Key Differences Between Discipline and Punishment
Read out the points given below, to have a better understanding of the difference between discipline and punishment:
- Discipline implies to instruct or guide a disciple, to obey and pursue the particular code of conduct, in an attempt to prevent future behavioural problems. On the contrary, Punishment is the imposition of pain or hardship, as a deterrent, so as to make the teen feel ashamed of their behaviour or actions.
- While discipline presents a choice, punishment demands compliance of the rules on the part of the child.
- Discipline aims at making the child learn from his mistakes so that he/she can develop good behaviour in future. As against, in punishment, the basic objective is to make the child pay for the misdeed.
- Discipline is used to teach the child to obey rules or polish their behaviour. In contrast, punishment is meant to fix the behaviour of the child, to decrease the likelihood of the occurrence of the offence, either by adding an unpleasant stimulus or removing a pleasant one.
- Discipline is all about learning new behaviour which is widely accepted, whereas punishment is all about fearing a consequence of the wrongful act.
- Discipline is a positive method of teaching or correcting behaviour, but punishment is considered as a negative method.
- The discipline focuses on ‘What a child needs to do to correct the behaviour?’ In contrast, Punishment is concerned with ‘What is wrong with the child?’
- Over time discipline causes the child to integrate rules and hold themselves responsible for their behaviour. As opposed, punishment causes the child to call for external control, so as to behave in the right manner, in the long term.
- Discipline tends to increase the self-esteem of the child, whereas Punishment often lowers the self-esteem of the child.
- Discipline encourages good behaviour by way of open communication between the child and parent and develops a great bond between them. Conversely, Punishment develops a revengeful and rebellious behaviour in the child and also weakens their relationship.
Example
Steve (12 years old) saw a new laptop at his friend’s house. As he was amazed, he starts operating it without his friend’s permission and while carrying it to the bed, it fell on the floor mistakenly, due to which its screen gets damaged. So, he ran away while his friend was not around, but his friend’s mother saw him.
Now, in case of Discipline
- His friend’s parents can talk to Steve about the incident, in the presence of his parents and teach him that it is wrong to use another person’s belongings without their permission. And also guide him that he should take care of the personal stuff belonging to others if he has borrowed them for use.
- Also, his friend’s parents can ask Steve to pay for the damage caused to the laptop due to him, along with a written apology to his friend.
But in case of Punishment
- His friend’s parents can tell their child to bring Steve’s laptop or any other favourite stuff, and get it damaged so that he will understand how it feels.
- Also, after knowing about the incident, Steve’s parents can tell him, that they will not allow him to visit any of his friend’s house for the next one year so that he will learn not to repeat the same thing again.
Conclusion
Everyone wants their child to learn good and right behaviour, which helps them in becoming a successful and responsible citizen of the society. While discipline relies on behavioural codes which are accepted both socially and morally, but punishment relies on imposing retribution, either physical or mental.







John Brand Lauji says
I love this. So happy I read such information.