 An elastic demand is one in which a slight change in the price will lead to drastic change in the demand for the product. It differs from an inelastic demand in the sense that a change in price may have no or little effect on the demand of consumers.
An elastic demand is one in which a slight change in the price will lead to drastic change in the demand for the product. It differs from an inelastic demand in the sense that a change in price may have no or little effect on the demand of consumers.
The elasticity of demand refers to the change in the quantity demanded of a product, due to the change in factors on which demand depends. Such variables are price, the price of related goods, income and so on. Unless and otherwise specified, price elasticity is termed as the elasticity of demand, which is the degree of responsiveness of a product with respect to the change in price. It can be elastic or inelastic for a particular commodity.
To understand the difference between elastic and inelastic demand, see the article presented hereunder.
Content: Elastic Demand Vs Inelastic Demand
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Elastic Demand | Inelastic Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | When a little change in the price of a product results in a substantial change in the quantity demanded, it is known as elastic demand. | Inelastic demand refers to a change in the price of a good result in no or slight change in the quantity demanded. |
| Elasticity Quotient | More than equal to 1 | Less than 1 |
| Curve | Shallow | Steep |
| Price and Total revenue | Move in the opposite direction | Move in the same direction |
| Goods | Comfort and luxury | Necessity |
Definition of Elastic Demand
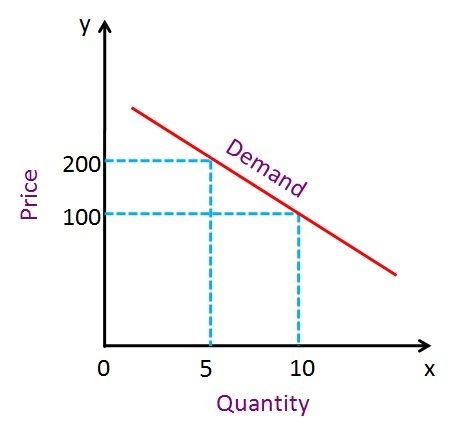
The demand that changes, as the price for product increases or decreases, it is known as elastic demand or price elasticity of demand. Such a demand is termed as price-sensitive demand.
It means a small change in the price of the product may lead to a greater change in the quantity demanded by the consumers, i.e. if the price of a product is increased then the consumers will stop purchasing the commodity or switch to the substitutes or buy less quantity of the product, or they will wait for the prices to become normal. On the other hand, if the price drops then the consumers will start buying some more quantity of the product, or it will attract some more customers.
Definition of Inelastic Demand
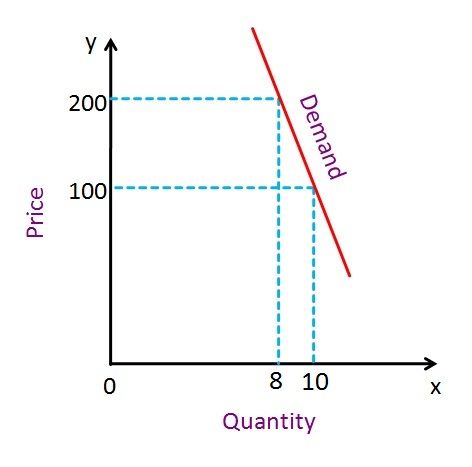
The demand is said to be inelastic when the demand for the given product or service does not change in response to the fluctuations in price. Such a demand is not much sensitive to price.
Items for need or necessities are the goods that have inelastic demand, i.e. water, salt, soap, petrol, etc. or the items to which people are addicted, like liquor, cigarettes, etc. or the items that have no close substitutes like medicines. When the demand for the given product is inelastic then no matter what the price is, people will not stop buying it. In the same way, if the price falls, there will not be much change in the quantity demanded by consumers.
Key Differences Between Elastic and Inelastic Demand
The differences between elastic and inelastic demand can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- Elastic Demand is when a small change in the price of a good, cause a greater change in the quantity demanded. Inelastic demand means a change in the price of a good, will not have a significant effect on the quantity demanded.
- The elasticity of demand can be calculated as a ratio of percent change in the demand of the commodity to the percent change in price, if the coefficient of elasticity of demand is greater than, equal to 1, then the demand is elastic, but if it’s less than one the demand is said to be inelastic.
- When the demand is elastic, the curve is shallow. Conversely, if the demand is inelastic, the slope will be steep.
- In the case of elastic demand, the price and total revenue move in opposite direction, however, with inelastic demand, the price and total revenue moves in the same direction.
- Items of comforts and luxuries have elastic demand whereas items of necessity have an inelastic demand.
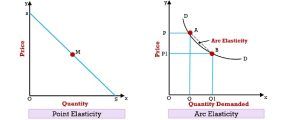
Price Elasticity of Demand
| ed > 1 | Relatively elastic demand. |
| ed = 1 | Unitary elastic demand |
| ed < 1 | Relatively inelastic demand |
| ed = ∞ | Perfectly elastic demand |
| ed = 0 | Perfectly inelastic demand |
Conclusion
The elasticity of demand represents the extent to which the variation in the price of a good will affect the quantity demanded by consumers. Products with no or less close substitutes have an inelastic demand. As compared to the products with a large number of substitutes, have an elastic demand because of the consumers switch to different substitute, if there is a small change in their prices. Therefore, it is true to say that the less the substitutes, the more the inelastic demand. In addition to this, if a huge part of the income is spent on purchasing the product, then also the demand for it is elastic, for the consumers who are highly price sensitive.




Tony says
I love this site.
Yogvendra says
Lovely!!!!
ola says
great website,,,,,,,thanking you
kwao felix says
thanks to you for the knowledge.
Himanshu says
Nyccc Article To Understand ..Easily..
Malikebu BT says
Well explained, greatly appreciate
Omojevwe Emmanuel says
Thank you very much for your time
Gasuk says
very interesting. this website helps in economic’s study. thanks a lot
aakar Singh says
Great
lawal khadijat says
This Website is useful, thank you so much.