 Based on variability, the costs has been classified into three categories; they are fixed, variable and semi-variable. Fixed costs, as its name suggests, are fixed in total i.e. irrespective of the number of output produced. Variable costs vary with the number of output produced. Semi-variable is the type of costs with the characteristics of both fixed and variable costs.
Based on variability, the costs has been classified into three categories; they are fixed, variable and semi-variable. Fixed costs, as its name suggests, are fixed in total i.e. irrespective of the number of output produced. Variable costs vary with the number of output produced. Semi-variable is the type of costs with the characteristics of both fixed and variable costs.
Many cost accounting students are not able to bifurcate fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs are one that does not change with the change in activity level in the short run. Conversely, Variable cost refers to the cost of elements, which tends to change with the change in the level of activity. While working on production costs, one should know the difference between fixed and variable costs.
So, read the given article in which we have compiled all the important points of distinction in tabular form and examples.
Content: Fixed Cost Vs Variable Cost
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The cost which remains same, regardless of the volume produced, is known as fixed cost. | The cost which changes with the change in output is considered as a variable cost. |
| Nature | Time Related | Volume Related |
| Incurred when | Fixed costs are definite, they are incurred whether the units are produced or not. | Variable costs are incurred only when the units are produced. |
| Unit Cost | Fixed cost changes in unit, i.e. as the units produced increases, fixed cost per unit decreases and vice versa, so the fixed cost per unit is inversely proportional to the number of output produced. | Variable cost remains same, per unit. |
| Behavior | It remains constant for a given period of time. | It changes with the change in the output level. |
| Combination of | Fixed Production Overhead, Fixed Administration Overhead and Fixed Selling and Distribution Overhead. | Direct Material, Direct Labor, Direct Expenses, Variable Production Overhead, Variable Selling and Distribution Overhead. |
| Examples | Depreciation, Rent, Salary, Insurance, Tax etc. | Material Consumed, Wages, Commission on Sales, Packing Expenses, etc. |
Definition of Fixed Cost
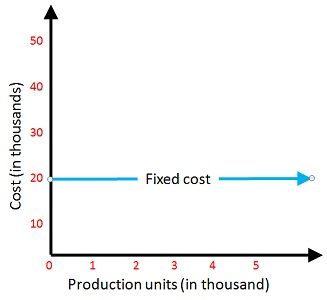
The cost which remains constant at different levels of output produced by an enterprise is known as Fixed Cost. They are not affected by the momentary fluctuations in the activity levels of the organization.
Fixed Costs remaining constant does not mean that they will not change in the future, but they tend to be fixed in the short run. This can be explained with an example, If your company is operating the business in a rented building, so whether you produce tons of output or you produce nothing, you have to pay the rent of the building, so this is a fixed expense which is constant over a period until the rent of the building increases or decreases.
Fixed cost will be the same in total but changes in per unit. To explain this, we have an example If the fixed cost is Rs. 10000 and the output produced in the first, second and third quarters are 4000, 5000 and 3000 units. Now, in this situation, what you can see is, the total fixed cost is unchanged in all the three-quarters, but the unit fixed cost in the first quarter is Rs. 10000/4000 units, i.e. Rs. 2.5, in the second quarter, it is Rs. 10000/5000 units, i.e. Rs. 2 and in the third quarter it is Rs. 10000/3000 units, i.e. Rs. 3.33.
There are two types of Fixed Costs:
- Committed Fixed Cost
- Discretionary Fixed Cost
Definition of Variable Cost
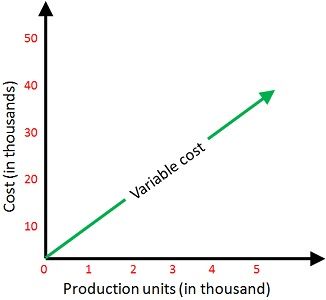
The cost which changes with the changes in the quantity of output produced is known as Variable Cost. They are directly affected by the fluctuations in the activity levels of the enterprise.
Variable cost varies with the variations in the volume, i.e. when there is an increase in production, the variable cost will also increase proportionately with the same percentage, and when there is no production, there will be no variable cost. The Variable cost is directly proportional to the units produced by the enterprise.
Now, variable cost remains the same in per unit but changes in total. You can understand this with an example, i.e. if the variable cost is Rs. 6 per unit and output produced in the first, second and third quarters is 5000, 6000 and 4000 units. You might wonder that the output level is changed in all three-quarters, so the variable cost will also change, but only in the total amount but not in the unit price. So the variable cost in the first quarter is 5000*6 = Rs. 30000, in the second quarter it will be 6000*6 = Rs. 36000 while in the third quarter, it is 4000*6 = Rs. 24000.
The Variable cost is divided into two categories, they are:
- Direct Variable Cost
- Indirect Variable Cost
Key Differences Between Fixed Cost and Variable Cost
The following point are substantial, so far as the difference between fixed cost and variable cost in economics is concerned:
- Fixed Cost is the cost which does not vary with the changes in the quantity of production units. Variable Cost is the cost which varies with the changes in the number of production units.
- The Fixed cost is time-related, i.e. it remains constant over a period. Unlike Variable Cost which is volume related, i.e. it changes with the change in volume.
- Fixed Cost is definite; it will incur even when there is no units are produced. Conversely, Variable Cost is not definite; it will incur only when the enterprise does some production.
- Fixed cost changes in per unit. On the other hand, variable cost remains constant in per unit.
- Examples of fixed costs are rent, tax, salary, depreciation, fees, duties, insurance, etc. Examples of variable costs are packing expenses, freight, material consumed, wages, etc.
- Fixed Cost was not included at the time of inventory valuation, but Variable Cost is included.
Video: Fixed Vs Variable Cost
Conclusion
Now, from the discussion mentioned above, it might be clear that the two costs are perfectly opposite to each other, and they are not the same in any respect. There are many doubts while we talk about these two, but with this article, you will surely be satisfied. So, this is all for the difference between Fixed Cost and Variable Cost.





Doubt chiile says
This is awesome, thanks for the simple terms you used for everyone to understand it, I liked it
Doubt chiile says
Thanks for the simple terms you used for everyone to understand it, I have liked it.
Ganga newar says
Nice 👍
Minhal says
This is awesome sauce 👌
I love it 😍