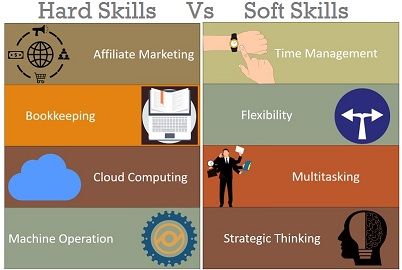
 Hard Skills refers to the skills which a person must possess to perform a specific kind of job. For example: To get the job of the programmer, a person needs to have coding skills. On the other hand, Soft Skills are not associated with a particular job, rather it includes the basic skills, i.e, communication skills, leadership skills, work ethics, professional skills, adaptive skills, etc. as it determines the ability of the candidate to gel up in the working environment.
Hard Skills refers to the skills which a person must possess to perform a specific kind of job. For example: To get the job of the programmer, a person needs to have coding skills. On the other hand, Soft Skills are not associated with a particular job, rather it includes the basic skills, i.e, communication skills, leadership skills, work ethics, professional skills, adaptive skills, etc. as it determines the ability of the candidate to gel up in the working environment.
To get a decent job, with a high package an individual must possess hard skills and soft skills because that’s the most important thing to crack the interview in the first attempt itself.
But do you guys know that as much as hard skills are important to increase the value of your resume, soft skills are important to make a difference between you and the rest of the candidates applying for the job? How an employee responds to various situations, mainly depends on these two skills.
So, here we are going to talk about the difference between hard skills and soft skills.
Content: Hard Skills Vs Soft Skills
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Hard Skills | Soft Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Hard skills imply the technical skills specific to the job, which a person has acquired through proper training and learning. | Soft skills refer to the set of personality traits, which defines an individual's relationships in a work environment, with others. |
| What is reflects? | How perfect a candidate is, for the job? | How perfectly a candidate adapt or fit into the work environment? |
| Constitutes | Key occupational requirements for the job. | Widely acceptable skills. |
| Acquired through | Formal Education and Training Programme. | Informal process, i.e. upbringing, and social surroundings. |
| About | Techniques, mechanism and professional competence. | Relationships and social competence. |
| Specific to | Job | People |
| Orientation | Aptitude oriented | Attitude oriented |
| Measurability | Measurable | Immeasurable |
| Provability | Easy to prove using evidence, such as certificate, degree, diploma, awards, etc. | Associated with personal attributes, and so these are difficult to prove because they are intangible. |
| Transferability | Possible | Depends on a person to person |
| Impact on personality | No | Yes |
Definition of Hard Skills
Hard Skills are purely job-specific, which are primarily related to the concrete knowledge, expertise and abilities of a person in performing a particular task. It is the set of technical skills and abilities required for carrying out the job satisfactorily and so it is often listed in the job descriptions. It determines an individual’s proficiency in performing the task.
Further, it can be gained and sharpened through formal education, training and practice, i.e. schooling, vocational training, internships, online courses, work experience etc. It can be easily measured, observed and learned.
It forms a basis for the designing of educational curriculum, job profiling and technical capabilities required by the industry. It is the pre-requisite to apply for any job or enter into any career. In simple words, technical knowledge of any specific discipline is a hard skill.
For example
| Field | Hard Skills |
|---|---|
| Production | Equipment Design |
| Order processing | |
| Quality Assurance | |
| Plant Design and Layout | |
| Safety Engineering | |
| Process Engineering | |
| Sales | Account management |
| Customer Service | |
| Sales Analysis | |
| Telemarketing | |
| Showroom Management | |
| Direct Sales | |
| Finance and Accounting | Auditing |
| Capital Budgeting | |
| Tax Management | |
| Risk Management | |
| Fund Management | |
| Financial Reporting | |
| Information Technology | CAD |
| Software Development | |
| UNIX | |
| Website Designing | |
| Algorithm Development | |
| Languages C++, JAVA, Python, etc. | |
| Software Testing | |
| Research & Development | Product Testing |
| Statistical Analysis | |
| Simulation Development | |
| Field Studies | |
| Prototype Development | |
| Diagnostics |
Definition of Soft Skills
Soft Skills are the interpersonal skills which indicate the way in which an individual connects and interacts with other people. These are non-job specific, as these skills are broadly applicable across various job titles and profiles. These are associated with intangible personal attributes, attitudes, social and management abilities of a person which facilitates a person to work and adapt easily into a workplace.
- Portrays a person’s ability to interact with others.
- Differs from one field to another.
- Improves individual’s communication skills. career prospects and job performance.
Soft Skills can be gained through the informal learning process, for example, one can learn etiquettes and table manners, by associating with people, attending social get together and parties.
These are acquired, but they cannot be measured. It shapes your relationship with other people or also regulates an individual’s approach towards work and life.
Importance of Soft Skills
- It helps in maintaining interpersonal relations.
- It plays a crucial role in effective decision making.
- It improves communication skills.
- It facilitates professional development and career growth.
Key Differences Between Hard Skills and Soft Skills
The difference between hard skills and soft skills are elaborated in the points below:
- Soft skills imply the interpersonal skills and personality traits, that determines an individual’s way of working on his own as well as with others. On the flip side, Hard skills can be understood as the technical skills specific to the job, which a person must possess to get the desired job.
- While hard skills tell you the fitness or suitability of the candidate, for the job, soft skills show how easily the candidate will adapt himself or herself into the work environment.
- Hard skills are the basic occupational requirement for the job. As against, soft skills are the universally acceptable skills in various job titles.
- Hard skills are acquired through formal education and training, practical learning and so on in different disciplines. Conversely, Soft skills are learned and acquired over a period of time, often influenced by the place of birth, parents, family, friends, environment and day to day life experiences.
- Hard Skills is all about techniques, mechanism and professional competence, whereas soft skills are about interpersonal relationships and social competence.
- While hard skills are specific to the job, i.e. it may vary from one person to another, soft skills are specific to people, i.e. these are innate qualities which a person may develop or learn over time.
- Hard Skills are teachable abilities, in the sense, it can be defined and measured. On the other hand, Soft skills are self-driven and subjective in nature, which cannot be measured.
- Hard Skills are easy to prove, with the help of evidence, such as certificate, graduate degree, diploma, awards, etc. On the contrary, soft skills are associated with personal attributes, and so these are difficult to prove, because of the absence of evidence, but they are reflected in a person’s behaviour.
- Hard Skills, can be transferred by way of teaching, as Chartered Accountants (CA), teach students and help them in becoming a CA. Similarly, lawyers, doctors, engineers, fashion designers, etc can also impart education to produce professionals. However, exact transfer of soft skills is not possible, i.e. even if a soft skills trainer, trains his/her students in an effective manner, but what a student is getting from different techniques used to teach soft skills like role play, case study, games, training supplement, live demonstrations, presentations etc. highly depends on the student himself.
- Hard skills do not have much impact on the personality of a person, for instance: Suppose a person takes admission in Engineering, then his knowledge base and technical skills would definitely increase, but there won’t be any change in personality attitude and behaviour. As against, soft skills have a very positive impact on the person, which can be reflected in his/her way of speaking, behaving, interacting, etc.
Example
Let’s talk about Management, the hard skills which a manager must possess are Budgeting, Employee Evaluation, Business Planning, Decision Making, Project Management, Policy Formulation, etc. On the other hand, their soft skills will include communication skills, leadership skills, team building, public speaking etc.
Conclusion
After discussing the two, it is clear that hard skills are important to get a particular position, but soft skills play a critical role in effective utilization of hard skills, so as to achieve the objectives of employment.
So, these two complement each other, in essence, hard skills will help you to apply for the interview, but you need soft skills to get the job and keep it.
Further, hard skills can be hired independently of the soft skills, i.e. even if the person is well versed in the specific subject, and has got the required education, he/she can be hired for the job, but soft skills cannot be sold independently, in the sense, one must have the minimum degree of hard skills, i.e. formal education and training to get hired.






Gassim Ahmed Ali says
very good articles and we hope be apple tp apply them in life reality, thanks very much