 Trade implies the process of buying and selling goods and services to earn profit. It covers all the activities resulting from which goods produced are distributed for consumption. This trade can take place either at the national or international level. While trade occurring within the boundaries of the nation is internal trade.
Trade implies the process of buying and selling goods and services to earn profit. It covers all the activities resulting from which goods produced are distributed for consumption. This trade can take place either at the national or international level. While trade occurring within the boundaries of the nation is internal trade.
Conversely, International Trade refers to the exchange of capital, goods and services across international boundaries or territories between the residents. When there is trade between two or more countries, factors such as government policies, currency, judicial system, laws, economy, markets, etc, have a significant impact on trade.
In this post, we will talk about the differences between internal and international trade.
Content: Internal Vs International Trade
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Internal Trade | International Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Trade carried out within the geographical limits of the country is called internal trade. | Trade carried out beyond the geographical limits of the country is international trade. |
| Payment | Payment is made in the country's local currency. | Payment is made in foreign currency. |
| Transportation of Goods | Roadways and Railways | Airways and Waterways |
| Nature of Consumers | Homogeneous in terms of culture, tastes and preferences. | Heterogeneous in terms of culture, tastes and preferences. |
| Movement of good | Goods and services can move freely within the country. | Because of the imposition of tariffs and quotas on goods and services, there is a restriction on the movement of goods. |
| Countries Involved | Only one country is involved | A minimum of two countries are involved |
| Language Barrier | No | Yes |
| Cultural Differences | No | Yes |
What is Internal Trade?
When the trade is carried out within the geographical borders of the country, then this is called internal trade. It takes place between the individuals residing in the same country.
The trade takes place between buyers and sellers in the same locality, village, town or city. Also, it may occur between different states, but certainly within the same country. The alternative term for internal trade is domestic, home, intranational, or interregional trade.
No customs duty or import duty is applicable on such trade. This is because they are a part of domestic production and are meant for domestic consumption.
Example
- A trade between Ahmedabad and Raipur is an internal trade.
- Buying a product from a local shop or mall comes under internal trade.
Characteristics of Internal Trade
- Purchasing and selling goods and services are carried out within the country’s political boundaries.
- Payment for transactions is made in the domestic currency of the country.
- It involves transactions between the producers, consumers and the intermediaries.
- It comprises a supply chain network of middlemen, distributors and agencies involved in exchanging goods and services.
Types of Internal Trade
Internal Trade can be divided into two types:
- Wholesale Trade: Buying and selling goods in large quantities for reselling or intermediate use is wholesale trade. The traders who trade in wholesale goods are wholesalers.
- Retail Trade: Buying and selling goods in small quantities to the ultimate consumers is retail trade. The traders who deal in retail trade are retailers.
Also Read: Difference Between Domestic and International Business
What is International Trade?
International Trade refers to trade between two or more nations. It is governed by the laws, rules and regulations of the countries where trade is executed. Further, it is a branch of economics that deals with exchanging goods and services between people of different nations. Also, it not just involves the movement of goods and services. Instead, it also involves the movement of human resources, technology, capital and IP, i.e. Intellectual Property.
Every country aims at exporting manufactured goods and importing raw materials whenever necessary. While the countries sell manufactured goods at higher prices, they buy raw materials at a cheaper rate. The company that exports manufactured goods can use the surplus for developmental purposes.
It allows every country to enjoy such goods which it cannot produce even when it puts all the effort and money into it. However, one demerit of international trade is that it leads to across-the-border dependence.
Example
Trade Between Australia and America is an international trade.
Basis of International Trade
- International Specialization: Different countries of the world specialize in the production of such goods whose production requires special resources.
- Unavailability of a particular factor: Not all the resources are present in all the countries of the world. Meaning that some factors are available in specific countries only, so the countries need to import those resources.
- Cost differences: The cost of goods is different in different countries.
- Product Differentiation: There are instances when a country imports goods which it can produce well. It does so to consume large varieties of goods.
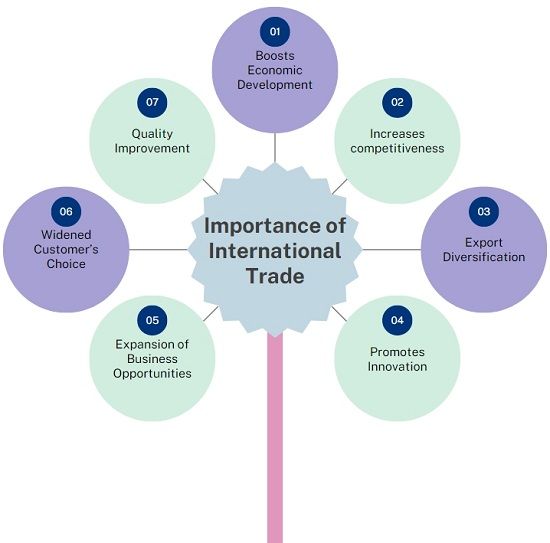
Importance of International Trade
- Boost Economic Development: It boosts economic development and decreases poverty, as it accelerates growth through the rise in business opportunities and investment.
- Increases competitiveness: There will be an increase in competitiveness by facilitating the countries to reduce the cost of factors, raise finance through investments, and move up the global value chain.
- Export Diversification: Trade assist in the diversification of exports by enabling countries to tap new markets and materials, which paves the way for new production possibilities.
- Promotes Innovation: International Trade leads to innovation because it facilitates the exchange of technology, know-how, as well as investment in R & D.
- Expansion of Business Opportunities: With the introduction of international trade, the world has become a small village, which has unlocked many opportunities for companies to open up new markets, lifting barriers and bans and easing exports.
- Widened Customer’s Choice: Trade widens the choice of the customers as it lowers the price by increasing the supply sources and competition as well.
- Quality Improvement: With the emergence of foreign companies in the domestic markets, there will be an enhancement in the quality, labour and environmental standards. This happens due to the rise in competition and exchange of trade practices amidst trade partners.
Also Read: Difference Between Foreign Trade and Foreign Investment
Key Differences Between Internal and International Trade
- Internal trade is an exchange between two businesses or parties belonging to the same country. In contrast, International trade is trade between two sovereign nations which are politically independent.
- In internal trade, stakeholders such as suppliers, producers, employees, distributors, etc., are of the same nation. In contrast, in international trade, stakeholders are of different nations.
- In international trade, different countries use different currencies to participate in the exchange. For example, Indian Rupee, American US Dollar, Japanese Yen, etc. In contrast, internal trade takes place through a single currency, which is the local currency of the country in which trade is executed.
- Policy Differences: In international trade, different countries participate. These countries have independent economic and other policies. Hence, these policies greatly impact the pattern of international trade like composition, volume and direction. Conversely, trade policies are the same throughout the nation, so there is an uninterrupted exchange of goods and services in internal trade.
- Endowment Differences: In International Trade, endowment differences are always there. Factor endowments of different countries are different. Some countries have a huge treasury of natural resources, while other countries have a pool of human resources. However, endowment differences do not exist in the case of domestic trade.
- Trade Restrictions: Countries follow certain rules and policies which often restrict or broaden international transactions. This may include heavy import duties, tariffs, quotas, customs, etc. They restrict imports and exports. On the other hand, bilateral agreements, subsidies, tax concessions, etc., boost imports and exports. However, these rules and policies do not exist in the case of internal trade.
- International Trade also encounters a number of specific issues like international liquidity, cooperation and understanding. Such issues have no concern with internal trade.
- Language: Not all countries have the same language, which is a barrier to international trade. That is why companies that are engaged in international trade often employ translators for this purpose. This problem does not arise in the case of domestic trade.
Conclusion
Above all, International Trade is of great importance for each country. No country is self-sufficient, and every country looks to maximize the advantages of large-scale production.






Leave a Reply