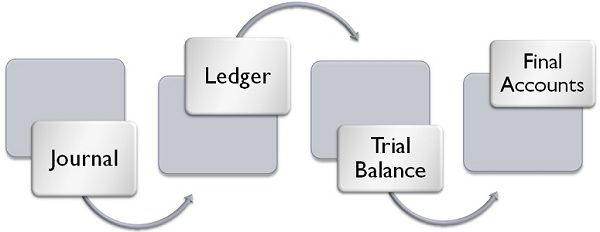
 Double entry system of bookkeeping says that every transaction affects two accounts. There is a proper procedure for recording each financial transaction in this system, called as accounting process.The process starts from journal followed by ledger, trial balance, and final accounts. Journal and Ledger are the two pillars which create the base for preparing final accounts. The Journal is a book where all the transactions are recorded immediately when they take place which is then classified and transferred into concerned account known as Ledger.
Double entry system of bookkeeping says that every transaction affects two accounts. There is a proper procedure for recording each financial transaction in this system, called as accounting process.The process starts from journal followed by ledger, trial balance, and final accounts. Journal and Ledger are the two pillars which create the base for preparing final accounts. The Journal is a book where all the transactions are recorded immediately when they take place which is then classified and transferred into concerned account known as Ledger.
Journal is also known as book of primary entry, which records transactions in chronological order. On the other hand, Legder, or otherwise known as principal book implies a set of accounts in which similar transactions, relating to person, asset, revenue, liability or expense are tracked. In this article, we have compiled all the important differences between Journal and Ledger in accounting, in tabular form.
Content: Journal Vs Ledger
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Journal | Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The book in which all the transactions are recorded, as and when they arise is known as Journal. | The book which enables to transfer all the transactions into separate accounts is known as Ledger. |
| What is it? | It is a subsidiary book. | It is a principal book. |
| Also known as | Book of original entry. | Book of second entry. |
| Record | Chronological record | Analytical record |
| Process | The process of recording transactions into Journal is known as Journalizing. | The process of transferring entries from the journal to ledger is known as Posting. |
| How transactions are recorded? | Sequentially | Account-wise |
| Debit and Credit | Columns | Sides |
| Narration | Must | Not necessary. |
| Balancing | Need not to be balanced. | Must be balanced. |
Definition of Journal
The Journal is a subsidiary day book, where monetary transactions are recorded for the first time, whenever they arise. In this, the transactions are regularly recorded in an orderly manner, so that they can be referred in future. It highlights the two accounts which are affected by the occurrence of the transaction, one of which is debited and the other is credited with an equal amount.
A short note is given in support of each entry, which gives a brief description of the transaction, known as Narration. The complete process of recording the entries in the journal is known as Journalizing. It has five columns which are Date, Particulars, Ledger Folio, Debit, and Credit. A journal can be:
- Single Entry: Entry having one debit and a corresponding credit.
- Compound Entry: Entry having one debit and more than one credit or entry having more than one debit for a single debit or two or more debit and two or more credits. In the case of compound entry, it should be kept in mind that the total of debit and credit will tally.
Definition of Ledger
Ledger is a principal book which comprises a set of accounts, where the transactions are transferred from the Journal. Once the transactions are entered in the journal, then they are classified and posted into separate accounts. The set of real, personal and nominal accounts where account wise description is recorded, it is known as Ledger.
While posting entries in the ledger, individual accounts should be opened for each account. The format of a ledger account is ‘T’ shaped having two sides debit and credit. When the transaction is recorded on the debit side the word ‘To’ is added, however, if the transaction is to be recorded on the credit side, then the word ‘By’ is used in the particular column along with the account name.
At the end of the financial year, the ledger account is balanced. For this purpose, first of all, the totals of the two sides is determined, after that, you need to calculate the difference between the two sides. If the amount on the debit side is more than the credit side, then there is a debit balance, but if the credit side is higher than the debit side, then there is a credit balance. Suppose if an account has a debit balance, then you have to write “By Balance c/d” on the credit side with the difference amount. In this way both the sides will tally.
Now, at the beginning of the new period, you have to transfer the opening balance to the opposite side (i.e. On the debit side as per our example) as “To Balance b/d”. Here c/d refers to carried down, and b/d means brought down.
Key Differences Between Journal and Ledger
The difference between journal and ledger can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- The Journal is a book where all the financial transactions are recorded for the first time. When the transactions are entered in the journal, then they are posted into individual accounts known as Ledger.
- The Journal is a subsidiary book, whereas Ledger is a principal book.
- The Journal is known as the book of original entry, but Ledger is a book of second entry.
- In journal, transactions are recorded in chronological order, whereas in ledger, transactions are recorded in analytical order.
- In the journal, the transactions are recorded sequentially. Conversely, in the ledger, the transactions are recorded on the basis of accounts.
- Debit and Credit are columns in the journal, but in the ledger, they are two opposite sides.
- In the journal, narration must be written to support the entry. On the other hand, in the ledger, there is no requirement of narration.
- Ledger accounts must be balanced, but journal need not be balanced.
Conclusion
In the beginning, we talked about the procedure of recording a transaction. It involves a series of actions like they are first recorded in the journal, from there they are classified and grouped into separate accounts and posted into the ledger, which is then transferred to trial balance and at the end the final accounts are prepared.These steps provide a base to prepare the financial accounts of a company. If any of the above steps is missing, then it would be hard to prepare the final accounts.





Riki Ahmed says
Thank you.
Akshaya Gopalan says
Very clear and understandable. Thank you
Jagdish Rajpurohit says
Very easy to understand. My sincere thanks to the team, thank you very much.
psingh says
great comparison chart you have written that describe the best way to learn difference between journal and ledger
Abhijith TJ says
Thank you………..very clear……..i am very happy…….
Duke says
Thank you so much
Steve says
How can I subscribe to these lessons ?
Surbhi S says
You can subscribe to our youtube channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCbr1DdpSQ2GBXByIVbP3KWA
Suhail Qaderi says
thanks alot it was very clear and thanks again : )
Femi says
Thanks
Saboor Hussain Awan says
Thank you.
Nav says
great simple explanation.
Tenkhosi says
Helpful, thank you
Accounts Definition says
Very well described article on differences between Journal and Ledger. The helpful article described in simple understandable words.
thomas says
Thanks for enlightenment.
very helpful and simple to understand..
Martha says
Very easy to understand
Nicholas O. Odwar says
Very clear and easy to understand, particularly for those of us with no finance background. Thank you very much.