 Monopoly refers to a market structure where there is a single seller dominates the whole market by selling his unique product. On the other hand, Monopolistic competition refers to the competitive market, wherein few sellers in the market offer near substitutes to the customers.
Monopoly refers to a market structure where there is a single seller dominates the whole market by selling his unique product. On the other hand, Monopolistic competition refers to the competitive market, wherein few sellers in the market offer near substitutes to the customers.
In economics, the market is not just a place whereby parties engage in an exchange of goods or services for money but it refers to a system wherein there are many buyers and sellers for a product or service having complete knowledge about market conditions, who bargain and settle the price of the product to make the deal. The market is classified into various categories like area, time, regulation, competition and so on.
Based on competition, the market is divided as perfect competition and imperfect competition. Further, there are three types of imperfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly and monopolistic competition. Many people have trouble in understanding the difference between monopoly and monopolistic competition, so here we’ve simplified it for you.
Content: Monopoly Vs Monopolistic Competition
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Monopoly | Monopolistic Competition |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Monopoly refers to a market structure where a single seller produces/sells product to large number of buyers. | Monopolistic competition is a competitive market setting wherein there are many sellers who offer differentiated products to a large number of buyers. |
| Number of players | One | Two to Ten or even more. |
| Product differentiation | Extreme | Slight |
| Degree of control over price | Considerable but very regulated. | Some |
| Competition | Does not exist. | Stiff competition exist between firms. |
| Demand curve | Steep | Flat |
| Barriers to entry and exit | Many | No |
| Difference between firm and industry | No | Yes |
Definition of Monopoly
A type of market structure, where the firm has absolute power to produce and sell a product or service having no close substitutes. In simple terms, monopolised market is one where there is a single seller, selling a product with no near substitutes to a large number of buyers. As the firm and industry are one and the same thing in the monopoly market, so it is a single-firm industry. There is zero or negative cross elasticity of demand for a monopoly product. Monopoly can be found in public utility services such as telephone, electricity and so on.
Under this marketing setting, a firm is the price setter; however, the pricing of the product is done taking into account the elasticity of demand for the product, so that the demand for the product and profit will be maximum. Look at the diagram given below:
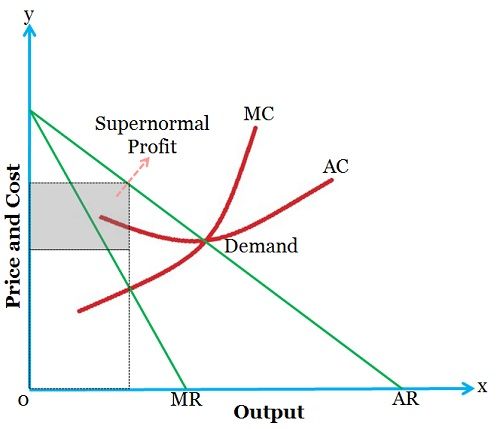 where MR = Marginal Revenue
where MR = Marginal Revenue
AR = Average Revenue
MC = Marginal Cost
AC = Average Cost
Definition of Monopolistic Competition
A market setting wherein scores of sellers sell a differentiated product is called monopolistic competition. Products are differentiated, by their brand name, packaging, shape, size, design, trademark, etc. Although the product sold by different firms in the industry remain close substitutes for the rivals, as the products are not identical but similar. Monopolistic competition is prevalent in the manufacturing industry, such as tea, shoes, refrigerators, toothpaste, TV sets, etc. The salient features of monopolistic competition are given below:
- A large number of sellers.
- Differentiated products, yet close substitutes.
- Free entry into and exit from the industry.
- Perfect factor mobility
- Full knowledge of market conditions.
Under this setting, the consumers buy more when the prices of the product are lower than at higher prices. By equating marginal revenue with marginal cost, the firm’s profit can be maximised, which can be seen in the given below diagram:
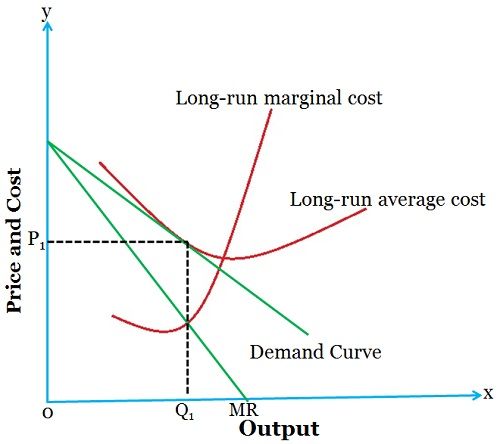 As you can see in the diagram, the point at which MR (Marginal Revenue) and MC (Marginal Cost) meet, is the price level, where P1 is the price and Q1 is the output to be produced.
As you can see in the diagram, the point at which MR (Marginal Revenue) and MC (Marginal Cost) meet, is the price level, where P1 is the price and Q1 is the output to be produced.
Key Differences Between Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition
The following points are noteworthy so far as the difference between monopoly and monopolistic competition is concerned:
- A market structure where a single seller produces/sells the product to a large number of buyers is called a monopoly. A competitive market setting wherein many sellers offer differentiated products to a large number of buyers, is called monopolistic competition.
- There is a single sellers/producers in a monopoly market whereas there can be two to ten or more players in the monopolistic competition.
- In a monopoly market structure, a single product is offered by the seller and there is extreme product differentiation. On the contrary, in a monopolistic competition, as the product offered by different sellers are close substitutes, and so, there is slight product differentiation.
- In a monopoly market, the degree of control over price is considerable but regulated. As against this, in a monopolistic competition, there is some control over price.
- No competition exist in a monopoly market while stiff competition due to non-price competition exists between firms the monopolistically competitive market.
- As there are no close substitutes of the product, demand for the product in monopoly is inelastic. As opposed to monopolistic competition, as the products offered by the different sellers are not identical but similar, hence its demand is highly elastic.
- Under monopoly, there are high entry and exit barriers, due to the economic, legal and institutional causes. On the other hand, in monopolistic competition, there is an unrestricted entry into and exit from the industry.
- As a single firm regulates the whole market, there is no difference between firm and industry in the monopoly. So, it is a single-firm industry. Unlike, monopolistic competition, the difference between firm and industry exists, i.e. a firm is a single entity, and a group of firms is called industry.
Conclusion
In a monopoly market, it is possible for a firm to charge distinct prices from various customers, for the same product. So, the firm can adopt price discrimination policy. On the other hand, as non-price competition is prevalent in the market, therefore, price discrimination is not possible, so, no firm can charge different prices from different customers.




Yousaf Khan says
Such differences has written in very easy words which I support by heart. But things which I want didn’t find. As differences between monopsony and monopolistic competition.
Giririj says
Where One buyer and few/many seller.
Philisiwe says
I’m very interested about this
it is useful thanks