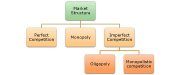
 Based on competition, the market structure has been classified into two broad categories like Perfectly competitive and Imperfectly competitive. Perfect Competition is not found in the real world market because it is based on many assumptions. But an Imperfect Competition is associated with a practical approach.
Based on competition, the market structure has been classified into two broad categories like Perfectly competitive and Imperfectly competitive. Perfect Competition is not found in the real world market because it is based on many assumptions. But an Imperfect Competition is associated with a practical approach.
The type of market structure decides the market share of a firm in the market. If there exists a single firm, it will serve the entire market, and the demand of the customers are satisfied with that firm only. But if we increase the number of firms to two, the market will also be shared by the two. Similarly, if there are about 100 small firms in the market, the market is shared by all of them in proportion.
Therefore, it is the market structure, which affects the market. So here we are going to describe the differences between perfect competition and imperfect competition, in economics.
Content: Perfect Competition Vs Imperfect Competition
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Perfect Competition | Imperfect Competition |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Perfect Competition is a type of competitive market where there are numerous sellers selling homogeneous products or services to numerous buyers. | Imperfect Competition is an economic structure, which does not fulfill the conditions of the perfect competition. |
| Nature of concept | Theoretical | Practical |
| Product Differentiation | None | Slight to Substantial |
| Players | Many | Few to many |
| Restricted entry | No | Yes |
| Firms are | Price Takers | Price Makers |
Definition of Perfect Competition
Perfect Competition is an economic structure where the degree of competition between the firm is at its peak. Given are the salient features of the perfect competition:
- Many buyers and sellers.
- Product offered is identical in all respects.
- Any firm can come and go, as per its own discretion.
- Both the parties to the transaction are having complete knowledge about the product, quantity, price, market and market conditions as well.
- Transportation and Advertising cost is nil.
- Free from government interference.
- The price for a product is uniform across the market. It decided by the demand and supply forces; no firm can affect the prices, that’s why the firms are price takers.
- Each firm earns a normal profit.
Example: Suppose you go to a vegetable market to buy tomatoes. There are many tomato vendors and buyers. You go to a vendor and inquire about the cost of 1 kg tomatoes, the vendor replies, it will cost Rs. 10. Then you go ahead and inquire some more vendors. The prices of all the vendors are same for the demanded quantity. This is an example of perfect competition.
Definition of Imperfect Competition
The competition, which does not satisfy one or the other condition, attached to the perfect competition is imperfect competition. Under this type of competition, the firms can easily influence the price of a product in the market and reap surplus profits.
In the real world, it is hard to find perfect competition in any industry, but there are so many industries like telecommunications, automobiles, soaps, cosmetics, detergents, cold drinks and technology, where you can find imperfect competition. By the virtue of this, imperfect competition is also considered as real world competition.
There are various forms of imperfect competition, described below:
- Monopoly: Single seller dominates the entire market.
- Duopoly: Two sellers share the whole market.
- Oligopoly: Few sellers are there who either act in collusion or competition.
- Monopsony: Many sellers and a single buyer.
- Oligopsony: Many sellers and few buyers.
- Monopolistic Competition: Numerous sellers offering unique products.
Key Differences Between Perfect Competition and Imperfect Competition
The main points of difference between perfect competition and imperfect competition in economics are depicted below:
- The competitive market, in which there are a large number of buyers and sellers, and the sellers supply identical products to the buyers; it is known as perfect competition. Imperfect competition occurs when one or more conditions of the perfect competition are not met.
- Perfect competition is a hypothetical situation, which does not apply in the real world. Conversely, Imperfect Competition is a situation that is found in the present day world.
- When it comes to perfect competition, there are many players in the market, but in imperfect competition, there can be few to many players, depending upon the type of market structure.
- In perfect competition, the sellers produce or supply identical products. As against, in imperfect competition the products offered by the sellers can either be homogeneous or differentiated.
- If we talk about perfect competition, there are no barriers to the entry and exit of the firms which is just opposite in the case of imperfect competition.
- In perfect competition, it is assumed that the firms do not influence the price of a product. Hence they are price takers but in imperfect competition, the firms are price makers.
Conclusion
Perfect competition is an imaginary situation which does not exist in reality, but imperfect competition is factual i.e. which genuinely exist.
Whichever market, you consider for this like for example if you consider the detergent market. There are many players like Tide, Rin, Surf Excel, Ariel, Ghadi, etc. producing similar product i.e. detergent.
At first instance, you may think that this is an example of perfect competition, but this is not so. If you dig a little deeper, you may find that all the products are different as well as they vary in their prices. Some are low budget detergents for capturing the market of price sensitive people while others are high budget detergents for quality sensitive people.




Junior Johnson says
Thanks much, am appreciating your lecture, very impressive God bless You 🙏🙏
Archana kumai says
Thank you so much 🤗
for your helpful notes ☺️
maria says
that was quiet amazing to explain my learners
khalphina says
it is simple and good explanation