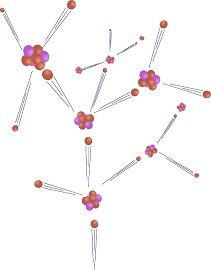
 The process in which heavy nucleus is broken into tiny nuclei, is called as nuclear fission. On the other extreme, nuclear fusion is defined as the reaction wherein lighter atoms come together and form a heavy nucleus.
The process in which heavy nucleus is broken into tiny nuclei, is called as nuclear fission. On the other extreme, nuclear fusion is defined as the reaction wherein lighter atoms come together and form a heavy nucleus.
With the rapid industrialisation, our demand for energy is increasing in the same ratio, because of the change in the way we live and do our work, as we are greatly dependent on machines to do our work, which consumes energy. It implies the strength and power that we require to perform the physical or mental activity. It comes in various forms and is capable of being converted from one form to another.
We get energy from various conventional and non-conventional sources, which include solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, geothermal energy and nuclear energy. Out of these energy sources, nuclear energy gives million times larger energy than the other sources. It liberates energy during nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions. These two reactions are often understood together, which most people juxtapose, but the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion lies in their occurrence, temperature, the energy required or produced.
Content: Nuclear Fission Vs Nuclear Fusion
Comparison Chart
Definition of Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is a process, wherein the nucleus of the large atoms like uranium or plutonium, is bombarded with the neutron of low-energy, breaks into small and lighter nuclei. In this process an enormous amount of energy is generated, as the mass of the nucleus (original), is slightly higher than the aggregate of the mass of its individual nuclei.
The energy liberated during the nuclear fission can be utilised in the production of steam, which in turn can be used to generate electricity. The nuclei formed during the reaction, are highly neutron-rich and unstable. These nuclei are radioactive, which continuously releases beta particles until each of them arrives at a stable end product.
Definition of Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion implies a nuclear reaction, wherein two or more lighter nuclei fuse to create one heavy nucleus, which produces a tremendous amount of energy, such as hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium. In nuclear fusion, two positively charged nuclei integrates to form a larger nucleus. The mass of the nucleus formed is a bit lower than the aggregate of the masses of the individual nuclei.
In this process, a substantial amount of energy is required to force low energy atoms to fuse. Moreover, extreme conditions are required for this process to take place, i.e. higher degrees of temperature and high pascals of pressure. The source of energy to all stars including Sun is the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium.
Key Differences Between Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Fusion
The differences between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- The nuclear reaction in which a heavy nucleus is broken into smaller nuclei, by releasing neutrons and energy, is called nuclear fission. A process in which two or more lighter atoms combine to create a heavy nucleus is called nuclear fusion.
- Nuclear fusion takes place naturally, such as in stars like the sun. On the other hand, nuclear fission reaction does not happen naturally.
- Conditions supporting nuclear fission includes the critical mass of the substance and neutrons. Conversely, nuclear fusion is possible only in extreme conditions, i.e. high temperature, pressure and density.
- In the nuclear fission reaction, the amount of energy required is less than the energy needed in a fusion reaction.
- Nuclear fission liberates an enormous amount of energy during the reaction. However, this is 3-4 times less than the energy released during nuclear fusion.
- Nuclear fission can be controlled through various scientific processes. As against this, nuclear fusion is impossible to control.
Similarities
- Both the two processes are a chain reaction, in the sense that one bombardment results in at least one other reaction.
- Both the processes result in comparatively less mass than the mass of the original atom.
Conclusion
Before the construction of nuclear power stations, nuclear energy was mainly used for destructive purposes only. Nuclear fission is the source of energy in a nuclear reactor, that helps in generation of electricity. At present, all the nuclear reactors, are used for commercial purposes are based on nuclear fission. However, nuclear fusion is also a safer method to produce energy. Further, the creation of high temperature for nuclear fusion is possible by exploding fission bomb.





Leave a Reply