 Revaluation Account is prepared only when there is any change in the value of asset and liabilities of the partnership firm, at the time of admission, retirement, and death of a partner. On the other hand, Realisation Account is opened when the firm goes into liquidation, so as to close the books of accounts and also to compute the net effect (profit or loss) arising due to the realisation of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Revaluation Account is prepared only when there is any change in the value of asset and liabilities of the partnership firm, at the time of admission, retirement, and death of a partner. On the other hand, Realisation Account is opened when the firm goes into liquidation, so as to close the books of accounts and also to compute the net effect (profit or loss) arising due to the realisation of assets and settlement of liabilities.
Revaluation account and Realisation Account are two types of nominal account, which are concerned with the partnership. The primary difference between these two accounts lies in a number of factors like the time of preparation, contents, objective and so forth. In the given article, we’ve compiled all the difference between revaluation and realisation account.
Content: Revaluation Account Vs Realisation Account
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Revaluation Account | Realisation Account |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Revaluation account is an account prepared to ascertain the variation in the values of the assets and liabilities of the firm. | Realisation account is an account prepared to ascertain the net profit or loss on the sale of assets or discharge of liabilities. |
| Comprise of | Only those assets and liabilities which are revalued. | All the assets and liabilities. |
| Preparation | At the time of reconstitution. | At the time of dissolution. |
| How many times it can be prepared? | It can be prepared at various events during the life of the firm. | It can be prepared only once, i.e. when the firm is dissolved. |
| Accounting entries | Based on the difference in the book value and the revalued amount of assets and liabilities. | Based on the book value of assets and liabilities. |
| Remaining balance | Transferred to the capital account of old partners. | Transferred to the capital account of all partners. |
Definition of Revaluation Account
In accounting, revaluation account implies an account opened by the firm to keep a record of gains or losses, when assets are revalued, and liabilities are reassessed, on reconstitution of the firm. Reconstitution of the firm occurs in the following forms:
- Admission of a new partner
- Change in profit and loss sharing ratio
- Retirement of existing partner
- Death of a partner
Whenever the firm is reconstituted, it is generally preferred to check whether the assets appear at their current market price in the books of the firm. If it is discovered that the assets are undervalued or overvalued, then these are subject to revaluation. Likewise, liabilities are reassessed, if found overstated or understated, so as to ensure that these are presented at their correct values in the firm’s books. Many times, unrecorded assets or liabilities are discovered, which is also entered in the books.
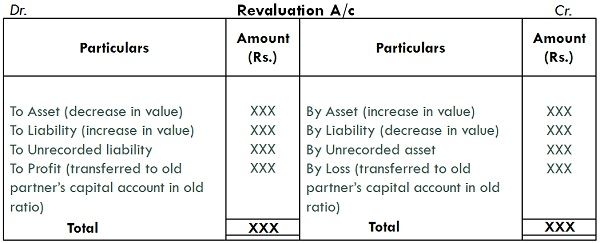
Therefore, revaluation account is prepared by the firm, to capture all gains or losses on the assets and liabilities. Any balance of the account is taken to the old partners capital account in the ratio in which they share profits and losses. The account is credited when:
- Increase in assets
- Decrease in liabilities
And debited when:
- Decrease in assets
- Increase in liabilities
Definition of Realisation Account
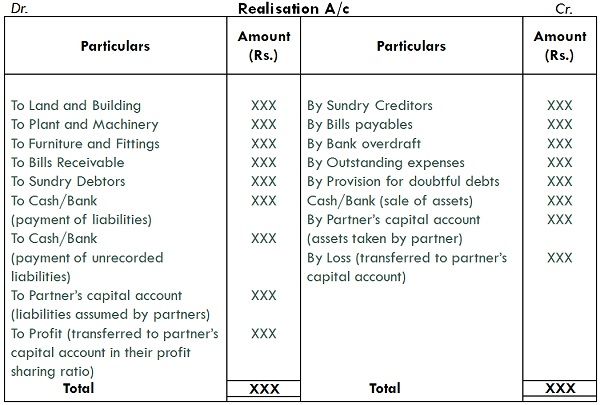
Realisation account refers to an account opened by the firm when it goes to dissolution to record the profit made from the sale of assets and loss suffered on the settlement of liabilities.
When the partnership firm is subject to dissolution, its account books are closed and profit earned, or loss incurred on the realisation of assets and payment of liabilities is reckoned. And to do so, realisation account is prepared, to identify the net profit or loss, which is transferred to all partner’s capital account in the ratio in which profit and loss are shared by them.
All the assets and external liabilities are transferred to this account except:
- Cash in hand
- Bank balance
- Fictitious Assets
Key Differences Between Revaluation and Realisation Account
The points given below are noteworthy so far as the difference between revaluation and realisation account is concerned:
- An account opened by the firm to know whether there is any change in the value of assets and liabilities of the firm, during reconstitution, is Revaluation account. On the other hand, realisation account is an account prepared to ascertain the net profit or loss on the sale of assets or discharge of liabilities, during dissolution.
- Revaluation account comprises of only those assets and liabilities, whose values are revised. Conversely, realisation account contains all the assets and liabilities.
- These two accounts mainly differ in relation to the time of preparation of the two, i.e. revaluation account is prepared when the firm is reconstituted, whereas realisation account is prepared when the firm is dissolved.
- Revaluation account is prepared at various events like admission, retirement or death of partners. Unlike realisation account is prepared only once, and that is when the firm discontinues its operations.
- In the case of revaluation account, accounting entries are made on the basis of the difference in the book value and the revalued amount of assets and liabilities. As against this, accounting entries are made at the book value of the assets and liabilities.
- The balance of revaluation account is transferred to the old partners capital account. In contrast, the remaining amount of the realisation account is taken to all partners capital account.
Specimen
Revaluation Account
Realisation Account
Conclusion
Revaluation account and realisation account is prepared by the firm at different events and also for different purposes. The main purpose of the preparation of revaluation account is that whatever the profit earned or loss suffered belongs to the partners who existed in the firm. On the contrary, realisation account is prepared, simply to know what profit/loss the firm earns or suffers, by selling off the assets and disbursing liabilities, at the time of closure of the firm.





sachin says
nice