 Hypothesis testing starts with setting up the premises, which is followed by selecting a significance level. Next, we have to choose the test statistic, i.e. t-test or f-test. While t-test is used to compare two related samples, f-test is used to test the equality of two populations.
Hypothesis testing starts with setting up the premises, which is followed by selecting a significance level. Next, we have to choose the test statistic, i.e. t-test or f-test. While t-test is used to compare two related samples, f-test is used to test the equality of two populations.
The hypothesis is a simple proposition that can be proved or disproved through various scientific techniques and establishes the relationship between independent and some dependent variable. It is capable of being tested and verified to ascertain its validity, by an unbiased examination. Testing of a hypothesis attempts to make clear, whether or not the supposition is valid.
For a researcher, it is imperative to choose the right test for his/her hypothesis as the entire decision of validating or refusing the null hypothesis is based on it. Take a read of the given article to understand the difference between t-test and f-test.
Content: T-test Vs F-test
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | T-test | F-test |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | T-test is a univariate hypothesis test, that is applied when standard deviation is not known and the sample size is small. | F-test is statistical test, that determines the equality of the variances of the two normal populations. |
| Test statistic | T-statistic follows Student t-distribution, under null hypothesis. | F-statistic follows Snedecor f-distribution, under null hypothesis. |
| Application | Comparing the means of two populations. | Comparing two population variances. |
Definition of T-test
A t-test is a form of the statistical hypothesis test, based on Student’s t-statistic and t-distribution to find out the p-value (probability) which can be used to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
T-test analyses if the means of two data sets are greatly different from each other, i.e. whether the population mean is equal to or different from the standard mean. It can also be used to ascertain whether the regression line has a slope different from zero. The test relies on a number of assumptions, which are:
- The population is infinite and normal.
- Population variance is unknown and estimated from the sample.
- The mean is known.
- Sample observations are random and independent.
- The sample size is small.
- H0 may be one sided or two sided.
Mean and standard deviation of the two sample are used to make comparison between them, such that:
x̄1 = Mean of the first dataset
x̄2 = Mean of the second dataset
S1 = Standard deviation of the first dataset
S2 = Standard deviation of the second dataset
n1 = Size of first dataset
n2 = Size of second dataset
Definition of F-test
F-test is described as a type of hypothesis test, that is based on Snedecor f-distribution, under the null hypothesis. The test is performed when it is not known whether the two populations have the same variance.
F-test can also be used to check if the data conforms to a regression model, which is acquired through least square analysis. When there is multiple linear regression analysis, it examines the overall validity of the model or determines whether any of the independent variables is having a linear relationship with the dependent variable. A number of predictions can be made through, the comparison of the two datasets. The expression of the f-test value is in the ratio of variances of the two observations, which is shown as under:
The assumptions on which f-test relies are:
- The population is normally distributed.
- Samples have been drawn randomly.
- Observations are independent.
- H0 may be one sided or two sided.
Key Differences Between T-test and F-test
The difference between t-test and f-test can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- A univariate hypothesis test that is applied when the standard deviation is not known and the sample size is small is t-test. On the other hand, a statistical test, which determines the equality of the variances of the two normal datasets, is known as f-test.
- The t-test is based on T-statistic follows Student t-distribution, under the null hypothesis. Conversely, the basis of the f-test is F-statistic follows Snedecor f-distribution, under the null hypothesis.
- The t-test is used to compare the means of two populations. In contrast, f-test is used to compare two population variances.
Conclusion
T-test and f-test are the two, of the number of different types of statistical test used for hypothesis testing and decides whether we are going to accept the null hypothesis or reject it. The hypothesis test does not take decisions itself, rather it assists the researcher in decision making.
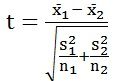
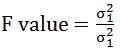





RV says
Very Nice!
Anand says
Thanks, very good information
Karin says
Excellent Information!!! Thank you!
Mahwish says
Excellent
Al-Assaf Nahla says
Thanks, very useful informations
Salim says
Excelent, very easy to understand, Thanks
Dibisa Gemechu says
I like it very much. Continue giving us such a wonderful explanation!
Aasma Ahmad says
Very informative and Excellent
Quinn says
Very helpful and clearly explained!
addi kal says
it is as clear as blue sky thanks alot
Ana Carol says
Hi Surbhi S,
I want to extend my appreciation for your article on the difference between T-test and F-test. The unique aspect that stood out to me was your clear explanation of the applications of both tests. The distinction between T-test, used for comparing means of two populations, and F-test, used for comparing population variances, was well articulated. Thank you for providing such a informative resource!