 TPM is a subset of TQM. TPM is a method that deals with the maintenance of equipment. It helps in reaching perfect production with no breakdowns, no defects, no small stops and no mishaps. It focuses on proactive and preventive maintenance. This will magnify the operational efficiency of the equipment.
TPM is a subset of TQM. TPM is a method that deals with the maintenance of equipment. It helps in reaching perfect production with no breakdowns, no defects, no small stops and no mishaps. It focuses on proactive and preventive maintenance. This will magnify the operational efficiency of the equipment.
But, TQM is a proven approach that assures the survival of the organization even in cut-throat competition. It is a philosophy derived from ideas introduced by quality Gurus, over the years. It calls for everyone in the organization in a constant attempt to enhance the quality and increase customer satisfaction.
Content: TQM Vs TPM
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | TQM | TPM |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | TQM is a system of management that stands on the principle that all the employees should wholeheartedly work to maintain high standards, in all the aspects of the company's operations. | TPM is a maintenance initiative involving novel ideas for maintaining plant and equipment to remarkably increase production levels and simultaneously boosting employee morale and job satisfaction. |
| Focuses on | Quality (Output and Effect) | Equipment (Input and cause) |
| Objective | Reach incredible quality levels, defects can arise parts per million | Complete elimination of wastes and losses (Zero Defect Approach) |
| Participation | It is voluntary and at the discretion of the management. | It demands effective participation from all employees. |
| Training | Classroom oriented | Workplace oriented |
| Emphasizes on | Customer Satisfaction, employee involvement and continuous improvement | Machine and equipment downtime, and its efficiency. |
| Ways to achieve the goal | Systematize the management. | Employee Participation |
| Orientation | Software Oriented | Hardware Oriented |
What is TQM?
Total Quality Management (TQM) is an integrative management system that focuses on quality while providing value to customers. It implies the quest for quality in the organization. It concentrates on ongoing and accruing gains in quality, productivity and cost reduction. Achievement of these gains is possible by way of continuous improvement in product design. It looks for participation from every department, section and activity to promote constant improvement efforts.
It is a Japanese approach to quality that relies on three main philosophies:
- Never-ending push to improve i.e. continuous improvement
- Involvement of every employee in the organization
- The goal for customer satisfaction, i.e. meeting or exceeding customer expectations.
In this process, the organization aims for continuous improvement at each level. Customer Satisfaction is the core of the entire process.
Q: Quality – Level of excellence a product or service provides.
M: Management – Process involving planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling.
Basic Concepts
- Committed and participative management to supply long term thorough organizational support.
- Consistent focus on customers. It covers both internal and external customers.
- Effective participation and commitment of the whole workforce.
- Ongoing improvement of business and production processes.
- Treatment of suppliers as partners
- Setting performance standards for the processes.
Principles of TQM
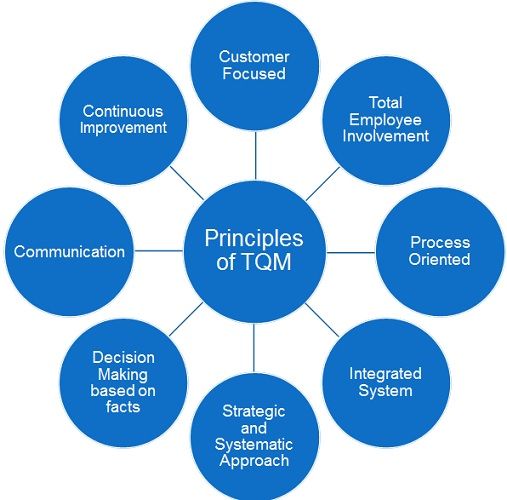
Total Quality Management is a management concept that centres around quality. It depends on the participation and commitment of all members that aim to achieve long term success by way of customer satisfaction. Also, it is an indispensable part of the strategic decision making of the company’s upper-level management. It deals with continuous improvement in all the work.
Elements of TQM
- Design Standardization
- Taguchi Methods (Control of Variability)
- Quality Function Deployment
- Performance Measurement and Statistical Quality Control
- Employee Involvement
- Small-Group Activities
Video: Total Quality Management
Also Read: Difference Between Quality Assurance and Quality Control
What is TPM?
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) implies a maintenance procedure related to a defined concept for upkeeping plants and equipment. It aims to noticeably increase production while at the same time increasing the morale of the employees and job satisfaction. Achievement of these goals is possible only through continuous improvement in the design of the product.
It is a strategy based on the philosophy that everyone should take part in the maintenance and not just the maintenance team.
P: Productive – Production of goods and services that fulfil or exceed customers’ expectations.
M: Maintenance – Keeping the equipment and plant of the organization in good condition every time.
TPM is a different way of looking at maintenance. In TPM, machines, equipment, workers and processes are used to keep up and enhance the integrity of production and the quality of the system.
The main objective of TPM is to increase overall effectiveness which is the basic metric to measure TPM performance.
The aim of TPM is to improve productivity. And for this, an analysis of equipment availability takes place first. The goal of TPM is to reach perfect production and put an end to abrupt breakdowns.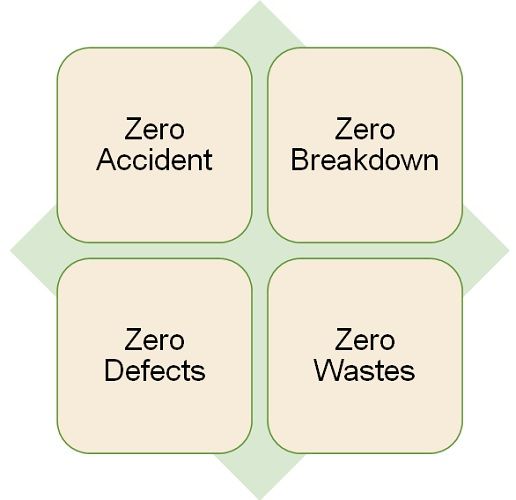
Objectives of TPM
- Avoid wastage in a dynamically changing economic environment.
- Pricing goods without compromising their quality.
- Cost reduction.
- Produce a low batch quantity at the least possible time.
- Goods supplied to the customers have to be non-defective.
History of TPM
TPM is an innovative concept of Japan, which came into being in the year 1951 when preventive maintenance was coined. The concept of preventive maintenance was derived from the USA. Seiichi Nakajima from Japan was the one behind the development of traditional TPM.
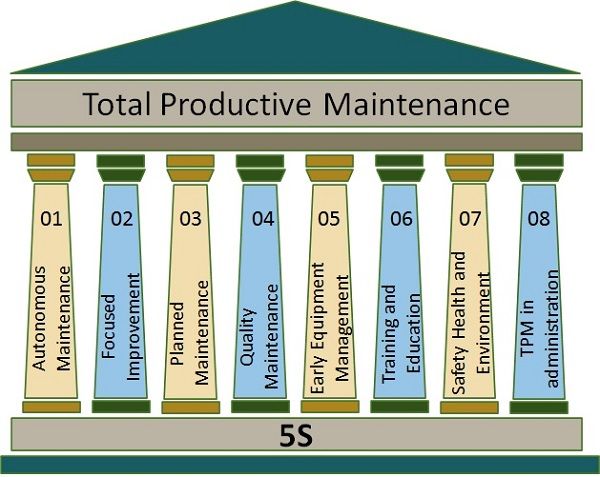
The first company to introduce plant wide preventive maintenance is Nippon Denso in the year 1960. This company is in the business of creating parts for Toyota. Further, there are 8 pillars on which TPM is built. These are based on the 5-S system.
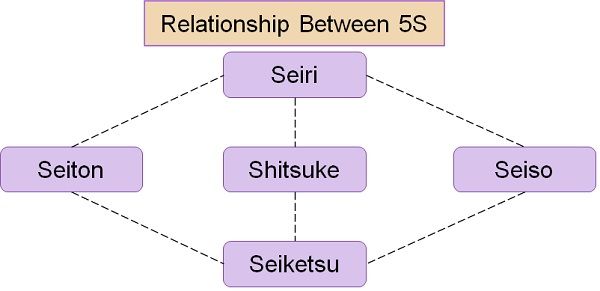
What is the 5-S system?
- Seiri: Organize – Throwing away all the unnecessary and unrelated material from the workspace.
- Seiton: Orderliness – Arrange everything in a neat and tidy manner in sequential order in its proper place. There has to be a place for everything and everything should be there in its place.
- Seiso: Cleanliness – Clean the place of work and maintain that.
- Seiketsu: Standardize – Standardization of all work processes and make them consistent.
- Shitsuke: Sustain – Reinforcement of the first four steps in a constant manner.
Pillars of TPM
Autonomous Maintenance
Make certain that operators are highly trained on day to day maintenance, i.e. cleaning, lubricating and inspecting along with delegating the responsibility only to their hands. By doing so, the machine operators get an ownership feeling of their equipment. Also, their knowledge of that equipment increases by constantly working on it.
Focused Improvement
It relies upon the Japanese approach ‘Kaizen’ which implies improvement. In production, kaizen needs continual improvement in the functions and processes. It looks at the big picture, i.e. the whole process is considered at once and various ideas are found to make improvements in that.
Planned Maintenance
It is related to the study of metrics such as rate of failure and historical downtime. After that scheduling of maintenance tasks takes place. This scheduling is on the basis of the calculated failure rates or downtime periods. In short, we could say that, because there is a certain time to undertake maintenance on the equipment, the firm can schedule maintenance at the time when the equipment is not in operation or operating at low capacity.
Quality Maintenance
It lays emphasis on working design error detection and prevention, in the process of production. In doing so, we use root cause analysis mainly 5 why’s. This will help in identifying and putting an end to the recurring sources of errors or defects.
Early Equipment Management
In this hands-on knowledge and understanding of equipment is obtained by way of TPM and using the same to make improvements in new equipment.
Training and Education
It is quite obvious that there is a lack of knowledge regarding the equipment that can deflect the TPM program. Training and Education apply to all, including operators, management staff and maintenance personnel. It aims to make certain that everyone is in agreement when it comes to the TPM process.
Safety, Health and Environment
Maintaining safety at the workplace means employees can carry out their tasks in a safe place and there is no risk of life or health. It is important to create an environment that makes efficient production, but this should not be at the cost of the health and safety of the worker.
TPM in administration
TPM must look farther the plant floor by concentrating on and removing areas of waste in administrative functions. In short, it involves improvement in order processing, procurement and scheduling.
Also Read: Difference Between Lean and Six Sigma
Key Differences Between TQM and TPM
- TPM is the process of making the best possible use of equipment, through the active involvement of various departments. On the other hand, TQM is a method of management which aims at improving quality and productivity in a business organization.
- While Total Quality Management is all about improvement in the quality of the offerings. Total Productive Maintenance focuses on maintaining the equipment in good condition all the time.
- TPM strives for the full-fledged elimination of losses and wastes. It follows a zero-defect approach. In contrast, TQM works for reaching incredible quality levels.
- In TQM the participation of employees is voluntary and is at the decision of the management. As against, TPM requires effective participation from every member of the organization.
- In TQM, training is classroom-oriented. Whereas in TPM, training is workplace oriented.
- The primary emphasis of TQM is on customer satisfaction, employee involvement and continuous improvement. As against, TPM lays emphasis on machine and equipment downtime, and its efficiency.
- To achieve the TQM goal, it is necessary to systematize the management. Conversely, to meet the TPM goal, employee participation is a must.
- While TQM is software-oriented, TPM is hardware-oriented.
Similarities
- There is a need for full-fledged commitment toward the program by the top-level management.
- Empowerment of employees for initiating corrective action and
- A long-range outlook has to be accepted because TPM may take a long time for implementation usually a year. Also, it is a continuous process.
Conclusion
Above all, TQM is a comprehensive concept which is nothing but an uninterrupted quest for excellence. This is possible by developing the right skills and attitudes in the employees to prevent defects and satisfy customers completely.
Conversely, TPM is a system of productive manufacturing that calls for complete participation from managers, supervisors, engineers, operators and technicians. This will improve the overall effectiveness of the equipment.







Etoro Utin says
Wow
Rashmita says
Too nice
Vinay says
Nicely explained.