 The error of omission refers to the error in which a transaction is not at all recorded in the books, either completely or partially. As against, the error of commission implies the error in which the transaction is incorrectly recorded in the books.
The error of omission refers to the error in which a transaction is not at all recorded in the books, either completely or partially. As against, the error of commission implies the error in which the transaction is incorrectly recorded in the books.
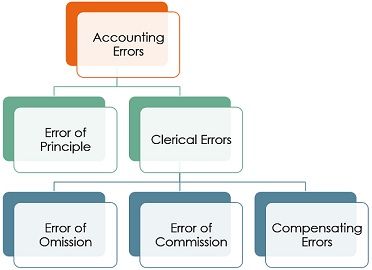
While recording and posting the entries, the occurrence of errors is quite common. Errors are the mistakes committed by the accounts staff while recording and maintaining the books, which cannot be corrected by overwriting.
Errors are divided into two types, i.e. an error of principle and clerical errors. Errors of principle indicate the error of recording a transaction against the basic convention or principle of accounting. On the other hand, Clerical Errors, as the name suggests, are the errors committed by the firm’s clerical staff, in the ordinary course of recording the transaction in a journal or posting it into the ledger.
Now clerical errors are subdivided into three types – Error of Omission, Error of Commission and Compensating Errors. In this article, we are going to talk about the differences between the error of omission and error of commission.
Content: Error of Ommission Vs Error of Commission
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Error of Omission | Error of Commission |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The error of omission is when a transaction is not recorded in the account books, in whole or in part. | The error of commission is when there is an incorrect recording of transactions in the account books. |
| Reason of occurrence | Mistake | Carelessness, negligence or lack of knowledge |
| Rectification | Simply correct the entry made. | Debit/Credit the wrong account and post it to the correct account. |
| Agreement of trial balance | Agrees in case of complete omission and Disagrees in case of partial omission. | May or may not agree |
Definition of Error of Omission
Omission means to leave, exclude, forget or skip something. So, the error of omission means an error in accounting in which the accountant forgets or miss an entry while recording the same in the subsidiary books or posting it into the ledger.
Therefore, a financial transaction does not appear in the books of accounts, as it is missed out unintentionally. Further, there is no debit or credit entry in the ledger for such omission, so the trial balance will tally.
Types of Error of Omission
- Complete Omission: As the name suggests, when a transaction is not recorded in the journal and so, it is not posted in the ledger as well. it is called a complete omission. Such errors do not affect the trial balance, because both debit and credit sides are affected by the same amount.
- Partial Omission: Partial omission of errors is when the transaction is recorded in the book of original entry, i.e. journal or subsidiary books, but are not taken to the ledger. This leads to the disagreement of trial balance because it affects only one account.
Definition of Error of Commission
An error is said to be an error of commission when it is incorrectly recorded in the books of accounts. It occurs when the accounts clerks or bookkeeper deliberately commit the error, due to ignorance, inexperience, carelessness, lack of complete knowledge. It encompasses:
- When the wrong amount is entered in the subsidiary books.
- When an entry is posted twice.
- When subsidiary books are wrongly cast, i.e. totalled.
- When the wrong amount is posted in the ledger.
- When an amount is posted on the wrong side.
- When the balancing of an account is incorrect.
- When the wrong total is carried forward from one page to another.
In the first two cases only, the trial balance will tally, while in rest of the cases the trial balance will not agree.
Key Differences Between Error of Omission and Error of Commission
The difference between error of omission and error of commission are discussed in the points given below:
- The error of omission refers to the error arising while recording the transaction in the subsidiary books or positing the entries to ledger, in which the entry is omitted or skipped from recording. On the other hand, Error of commission arises when the transaction is recorded, but an error takes place during the recording process, wherein the transaction is incorrectly recorded.
- The error of omission occurs by mistake, wherein an entry is missed from accounting records. As against, the error of commission occurs due to negligence, carelessness and lack of full knowledge of accountancy.
- When it comes to rectification of entry, the error of omission can be corrected by simply correcting the entry passed. Conversely, the error of commission can be corrected by passing a rectification entry, wherein you need to debit or credit the account which is wrongly debited or credited and post it into the correct one.
- In case of error of omission, the trial balance agrees in case of complete omission and Disagrees in case of partial omission. In contrast, when there is an error of commission, the trial balance may or may not agree.
Conclusion
While recording the entries, if it is identified that an error is committed one can correct the same by neatly striking out the previous (wrong) entry and passing the correct entry. However, if the error is detected after some time, then in such a case, one has to pass a rectification entry to correct the wrong entry.





danny ethan says
Thanks for the informational content, keep sharing.