 It is quite impossible for a person to perform all the business transactions, on his own. He/She needs someone for help, because of lack of time and business complexity. In such cases, people hire another person to perform work for them on their behalf. Such persons are Agents. The contractual agreement between principal and agent is the contract of the agency.
It is quite impossible for a person to perform all the business transactions, on his own. He/She needs someone for help, because of lack of time and business complexity. In such cases, people hire another person to perform work for them on their behalf. Such persons are Agents. The contractual agreement between principal and agent is the contract of the agency.
The word ‘agent’ is often confused with ‘servant’. A servant is one who serves others. The tasks performed by servants include – house cleaning, laundry, washing dishes, setting the table etc.
In this post, we have discussed the differences between agent and servant.
Content: Agent Vs Servant
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Agent | Servant |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | An agent is a person appointed by the Principal to act on his behalf. | A servant is the one employed to do work at that person's home as a gardener or cleaner, etc. |
| Works for | Principal | Master |
| Compensation | Commission | Salary or Wages |
| Legal Relationship | An agent can enter into contracts on behalf of his/her principal. Thus. he/she can bring the principal into a legal relationship with a third party. | A servant cannot bring the master and the third party into a legal relationship. |
| Direct Control and Supervision | An agent comes under direct supervision and control of the Principal. | A servant comes under direct supervision and control of the Master. |
| Work | An agent can work for many principals at the same time. | Servants can work for only one master at a time. |
| Acts | A principal is liable for all the acts of the agent performed within the scope of his authority. | A master is liable for all the acts of the servant performed in the course of his employment. |
| Duty Assignment | An agent can never act as a servant. | A servant can be assigned the duties of the agent and act like one in certain cases. |
Definition of Agent
An agent is a person who works for another or works on behalf of another. This means that a principal hires an agent to represent him/her in dealings or trade with a third party. So, we could say that agent is the binding thread between the principal and third parties.
With respect to the contract of the agency, there are two important points that act as its base. These are:
- All the acts which someone can do in person, he can do through an agent.
- The person, who performs an act through another, is equivalent to the performance of the act by him only, i.e. by the Principal himself. In this way, all the acts of the agent are considered as those performed by the Principal.
Who is eligible to appoint?
Well, any person who has attained the age of 18 years. Also, he/she should be of sound mind to appoint an agent.
Who is a Principal?
Any person for whom an agent performs the acts and is represented by the agent in dealings is the Principal.
Also Read: Difference Between Principle and Principal
Example
Jayesh appoints Vineet to buy cloth material on his behalf for his cloth business. In this case, Jayesh is the Principal, and Vineet is Agent.
Definition of Servant
A servant is a person who performs domestic duties for another person who hires him. The master employs a servant in a house to perform household chores or as a personal attendant to the master. In other words, any person who works in the service of someone else particular in the household is a servant. The master employs servants to extend help to the former and work on his command.
In this way, there is a special relationship between servant and master. Moreover, there are instances when a servant does some work for the master and as per law, the court assumes that the act is committed by the master himself. Therefore, if a servant performs any unlawful act, then the master will also be responsible if it is done in the course of his services.
The liability of a master depends on two main principles:
- Qui facit per alium facit per se: It implies that if someone gets something performed by another person then the former is deemed to be performing the act by himself.
- Respondant Superior: It implies that the master will be responsible for the acts performed by the servant.
Also Read: Difference Between Employee and Independent Contractor
Key Differences Between Agent and Servant
The points given below will explain the difference between agent and servant:
- An agent is a person whom the principal employs and is authorized to act on his behalf. Also, he/she has the power to create contractual relations between the principal and third party. As against, a servant is not representative in character. This is because a servant is not authorized to enter into contracts on behalf of his master.
- An agent does not work under the direct control and supervision of the principal. But, a servant has to work under the direct control and supervision of the master.
- An agent can work for many principals at a time. Whereas, a servant can work for only one master at a time.
- The principal has to give instructions to the agent about what is to be done. As against, the master has to instruct the servant about how the work is to be done along with what is to be done.
- The principal pays a commission to the agent. Conversely, the master pays salary/wages to the servant as compensation.
- The Principal is liable for all such acts which an agent commits that are within the scope of his authority. That is to say, the acts for which the agent has the authorization to perform. In short, the Principal will not be liable for any act committed which is outside the scope of authority. In contrast, a master will be liable for all the wrongful acts of the servant, when the acts are committed during the course of employment.
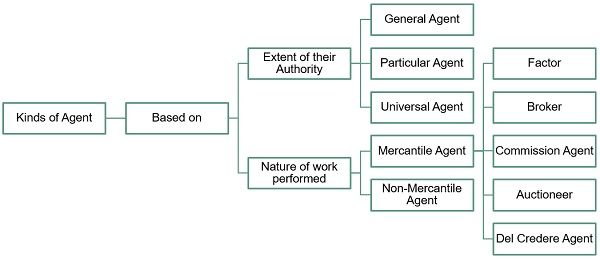
Kinds of Agent
Based on the extent of their authority there are three types of Agents:
General Agent
A person authorized to perform all the acts related to a particular trade, business or employment. His authority is continuous except otherwise terminated. His appointment takes place by way of a general power of attorney.
Particular Agent
A particular agent is someone who is allowed to perform specific transactions only. Therefore, he has limited authority and it ends as soon as the act is performed.
Universal Agent
Universal Agent is the one who has the permission to perform all the acts that his Principal can lawfully perform and the delegate.
Based on the nature of work performed, Agents are classified into:
Mercantile Agent
A Mercantile agent is the one appointed to sell or buy goods of business in the regular course of business. He can also send or take delivery of a consignment of goods or raise money using goods as collateral. These are commercial agents.
-
Factor
He is someone charged with the possession of goods. He/She has the power to buy or sell the goods or raise the money by using goods as collateral. He has permission to sell goods in his own name. Thus, he can enter into contracts of sale with outside parties.
-
Broker
A principal appoints a broker to negotiate and build contracts to deal in goods in the name of the Principal. His work is to negotiate between parties and make the sale of goods. Further, possession of goods is not given to a broker.
-
Commission Agent
The one who secures buyer for seller and seller for buyer and gets compensation in return for the efforts made by him is a commission agent. He is the one who purchases and sells goods in the market on the principal’s behalf, in his own name. Further, he does so on the best available terms or say favourable terms.
-
Auctioneer
An auctioneer is someone, whom the principal appoints to sell the goods at a public auction. Further, the auction price of the goods is received by an auctioneer.
-
Del Credere Agent
An agent who in consideration of extra payment, guarantees the solvency of the third party with whom he enters into the contract on behalf of the Principal. In other words, he is not just an agent but a guarantor too. Also, he commits to indemnify the principal if any damage is caused to him, due to the default in the performance of the contract by the party concerned.
Non-Mercantile Agents
These are non-commercial agents. It covers – advocate, insurance agent, wife, guardian, solicitor and so forth.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, a servant can be an agent too, but vice versa is not possible. Further, the rights and duties of an agent and principal will rest upon the contractual terms. However, there may or may not be any express contract between a master and servant.







Leave a Reply