 Assets refer to the economic resources of the business which the firm acquires either out of its own funds or borrowed funds which are expressed in terms of money. These are meant for use in the business and will increase the firm’s profit-earning capacity.
Assets refer to the economic resources of the business which the firm acquires either out of its own funds or borrowed funds which are expressed in terms of money. These are meant for use in the business and will increase the firm’s profit-earning capacity.
On the other hand, Liability refers to the amount payable by the firm to external parties. It is the claim of external parties like creditors, banks, debenture holders, etc. on the assets of the firm arising due to past transactions. In business, it is quite common to borrow money at any point in time, no matter what the size of the business is.
In common parlance, liabilities represent a legal obligation to pay a certain sum of money to a party. But in accounting, it means the amount owed by the firm and payable by the firm to others in money or goods.
What is Equity?
Equity refers to the residual interest in the company’s assets when all the liabilities and expenses are deducted. It is the excess of aggregate assets over aggregate liabilities. It shows the owner’s claim which comprises items such as capital and reserves. The value of equity increases when owners contribute towards equity and decreases when profit is distributed to owners.
Also Read: Difference Between Debt and Equity
In this post, we are presenting to you all the differences between assets and liabilities.
Content: Assets Vs Liabilities
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Assets | Liabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Asset implies resources that owned and controlled the enterprise, as a result of past events from which economic benefits are expected to derive in the future. | Liabilities refer to the economic obligations of the firm, resulting from past events which can be identified and measured accurately. |
| Represents | What business owns | What business owes |
| Meant to | Provide future-benefits | Settle in future |
| Depreciation | Fixed Assets are depreciable, while current assets are not. | Liabilities are non-depreciable |
| Nature of Balance | Every asset has a debit balance | Every liability has a credit balance |
| Accounting Treatment | An increase in assets is debited, decrease in assets is credited. | An increase in liability is credited, decrease in liability is debited. |
Definition of Asset
An asset can be defined as a resource that a firm owns, with an intent to use it for the purpose of generating revenues in the future. It can be a tangible object or an intangible right, possessed by the firm and the amount due to it from others. Assets add value to the business, as well as helps in meeting commitments and providing economic benefits in the coming time.
These are the items that hold a certain value and are used by the firm to carry out operations. Assets of the enterprise, be it tangible or intangible are covered under “real accounts”.
Example
Que Ltd. owns a number of outlets at different locations in the country. These outlets help in reaching the customers and selling them different products.
Points to Note
- The resource need not have physical existence to be called an asset. That is to say, a resource can be a right that is capable of generating revenue for the business. An asset without any physical asset can either be an intangible asset like copyright, royalty, patent, trademark, etc. or it can be a monetary asset that includes trade receivables. Monetary assets are nothing but money-held assets which are yet to be received.
Also Read: Difference Between Copyright and Trademark - It is something, whose control is in the hands of the enterprise. There are instances when a firm does not own a resource but controls it, like in the case of financial lease, the lessee recognizes the asset taken on lease as an asset in his books, even when the ownership is in the hands of the lessor, and the lessor does not recognize it in his books of accounts. This is due to the fact that even when the ownership is in the hands of the lessor, he does not have the right to control it.
Also Read: Difference Between Finance Lease and Operating Lease - The resource is expected to generate economic benefit in the future so as to be considered an asset. Hence, when the benefit is going to be ended in the current accounting period, it is not termed as an asset.
- The resource must possess a certain cost or value, which is measurable reliably, to be called an asset.
- If the flow of economic benefit generated from the resource extends to more than one accounting period, it is considered improbable, the expenditure incurred is regarded as an expense and not an asset in that case.
What are Fictitious Assets?
Imaginary assets which do not possess any realizable value are called fictitious assets, such as deferred revenue expenditure.
Also Read: Difference Between Debit and Credit in Accounting
Definition of Liability
Liability refers to the debt or present financial obligation, arising from past events which require settlement at a future date and are expected to cause an outflow of the company’s financial resources. It indicates the amount of money owed by the firm to external parties like creditors, banks, debenture holders, etc. It is the amount due to outsiders for the benefits received in the past.
On buying goods on credit from the supplier, the obligation is created on the firm to pay the sum due to the supplier at an agreed future date. Also, when a firm takes a loan from a bank, debt is created on the firm to pay the principal along with interest.
For Example, Que limited takes a loan from a bank of ₹ 5 lakhs to pay to suppliers for inventory, for a period of three years, @ 10% interest.
Points to Note
- Liability indicates the present obligation of the firm, whose existence depends on the evidence available on the balance sheet date, that reasonably supports the conclusion.
Example: Suppose there is a suit filed against the enterprise, and if the firm loses, in that case, the firm has to pay compensation for the damages. when the suit is pending on the balance sheet date, the enterprise needs to recognize a liability for the damages payable. This can be done by creating a charge against profit when the probability of losing the suit is high and the amount of the damages payable can be accurately identified. - Provisions like provision for doubtful debts, provision for depreciation, etc indicate a decrease in the value of assets and not obligations of the company. Therefore, such provisions are not covered under AS- 29 i.e. Contingent liability. And so they are not treated as a liability for the company.
- Now, the question arises – when the liability should be recognized? Well, liability should be recognized when there is an anticipation of outflow of economic resources while settling present obligation and the amount of the outflow can be measured with reasonable accuracy.
Also Read: Difference Between Debtors and Creditors
Key Differences Between Assets and Liabilities
As we have discussed the meaning and important points of these two heads of the balance sheet. Now, we are going to talk about the difference between assets and liabilities:
- Assets refer to a firm’s resources that are being used or are going to be used in future operations of the enterprise, as well as adds value to the enterprise. On the other hand, liabilities refer to promises, obligations, or commitments in favor of different parties for money, goods, or services.
- Assets refer to all the property and estate which is owned by the firm. As against, liabilities implies the debt owed by the firm to others.
- Assets are meant to provide economic benefits in the future, whereas liabilities are meant to be settled in the future.
- Fixed Assets are subject to yearly depreciation, i.e. their value decreases with time, due to continuous use. As against, liabilities are non-depreciable in nature.
- When it comes to the nature of balance, every asset of the company has a debit balance, whereas every liability has a credit balance.
- In accounting, an increase in the asset is debited while a decrease in the asset is credited. Conversely, an increase in liability is credited, but a decrease in liability is debited.
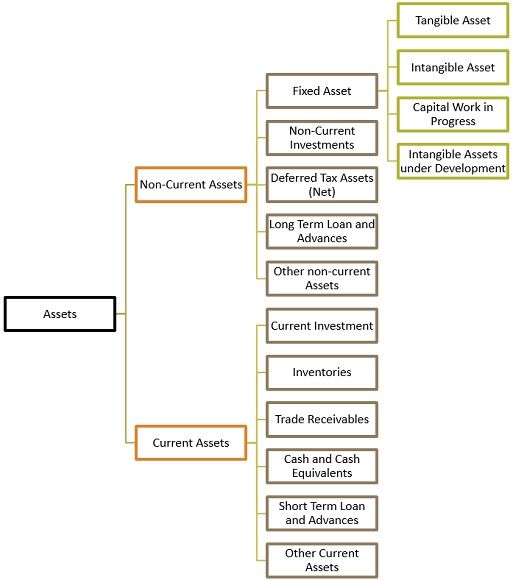
Classification of Assets
Assets are broadly classified into two categories:
Non-current Assets
An asset owned and controlled by the company, which is for the long term. Meaning that its benefit can be realized over a long period and cannot be converted into cash within one year.
Fixed Asset: Assets that are purchased by the firm, to use the same in business for a long duration and not for the purpose of resale or transforming them into another asset are fixed assets. They are of two types:
- Tangible Asset: Assets that exist in their material form, i.e. they can be seen or touched and they are bought for earning revenue. Example Land and Building, Plant and Machinery, Furniture and fixture, etc. These are further classified into:
- Wasting Asset: An asset with a limited life span, i.e. they are fully exhausted once they are used and they are not replaceable with a new asset, is a wasting asset. Example Mines, quarries, oil depositories, forests, etc.
- Non-Wasting Asset: Assets that are neither exhausted even with continuous usage nor lose value are called non-wasting assets. Example Freehold land.
- Intangible Assets: Assets that do not exist materially, as they cannot be seen or touch but they provide service and their existence can be felt are called intangible assets. Intangible assets are further subdivided into:
- Identifiable intangible fixed asset: Intangible assets which can be easily identified fall under this category. Example: License, Import Quotas, Trademark, Copyright, and Patents.
- Unidentifiable intangible fixed assets: Those intangible assets that are not easily identifiable, as they cannot be separated from their owner or the company is called an unidentified intangible fixed asset. Example: Goodwill.
- Capital Work in Progress: Those tangible assets which are under development process or construction and which can be converted into fixed assets once the development process is over is called capital work in progress.
- Intangible Assets under Development: Those intangible assets which are under the development phase and which are going to be converted into an intangible asset once the process is complete is called intangible assets under development.
Also Read: Difference Between Tangible and Intangible Assets
Non-Current Investments: Investments whose holding period is more than 12 months from the date on which the balance sheet is prepared are covered under this category.
Deferred Tax Assets (Net): It occurs when the company overpaid taxes or paid them in advance and thus these are refunded by the authorities.
Long Term Loan and Advances: Monetary sum lent by the firm to external parties which are going to be settled over a long span of time.
Other Non-current Assets: Non-current assets which are not covered under the above category are shown here.
Current Assets
Assets that change their form, during the course of their use and which are acquired for a short period so as to transform them into other forms is called current assets. Examples: Stock, account receivables, cash in hand, etc.
Current Investment: Any investment which is readily realizable, i.e. in the short term, within a period of 0-1 year.
Inventories: Stock of goods held by the firm for the purpose of resale, production, or further processing are called inventories.
Trade Receivables: Total amount that a company owes to its customers for goods and services provided, often reflected in the invoices issued by the company and the payment is still due.
Cash and Cash Equivalents: Assets that can be converted into cash in a very short period are called cash and cash equivalents.
Short Term Loan and Advances: Monetary sum lent by the firm to external parties which are going to be settled within a period of one year, from the date of the balance sheet.
Also Read: Difference Between Fixed Asset and Current Asset
Classification of Liabilities
Based on the holding period, liabilities are classified as: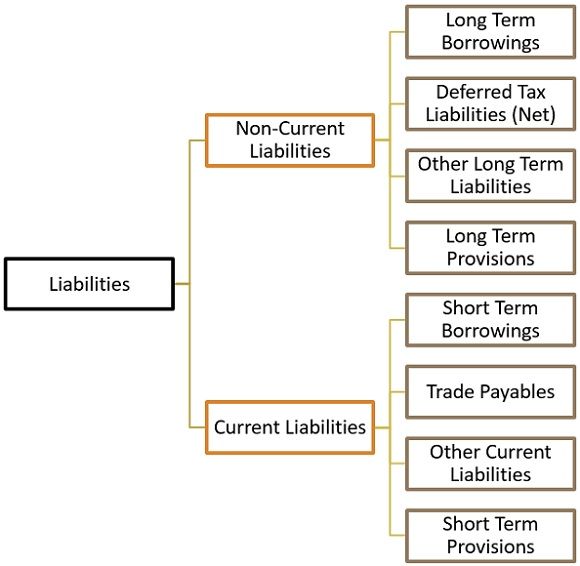
Non-Current Liabilities
These are long-term financial obligations of the firm whose settlement period is not within 12 months from the date on which the balance sheet is prepared.
Long Term Borrowings: Any outstanding debt of a certain amount held by the firm which has a maturity period of more than 12 months are long-term borrowings.
Deferred Tax Liabilities: Tax liability is due for the current financial year but not yet paid is a deferred tax liability.
Other Long term Liabilities: Long-term liabilities which are not covered under the above category are disclosed here.
Long Term Provisions: Provision for liability which is expected to be payable not within 12 months from the date on which the balance sheet is prepared.
Current Liabilities
Liabilities that are expected to be settled within the regular operating cycle or one year are called current liabilities. Creditors, Bills payable, etc fall under the category of current liabilities.
Short Term Borrowings: Financial borrowings of the company which are expected to be settled within one year are short-term borrowings.
Trade Payables: The sum due to be paid for the goods and services received from the suppliers in the ordinary course of business are called trade payables.
Other Current Liabilities: Current liabilities which are not covered under any of the above categories fall under this segment. Example: long-term debts, interest accrued but not due on borrowings, interest accrued and due on borrowings, interest received in advance, unpaid dividend, calls in advance, outstanding expenses, etc.
Short Term Provisions: Provision for liability which is expected to be payable within 12 months from the date on which the balance sheet is prepared is called a short term provision. Example: Provision for tax, provision for employee benefit, etc.
Also Read: Difference Between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable
Conclusion
So, we have understood that assets are property or rights which are owned and controlled by the enterprise, which may include cash, inventory, land, building, plant, and machinery, etc. On the other hand, liabilities refer to the debt, obligation, or commitment of the reporting enterprise which may include creditors, bank overdraft, loan, etc.






sakaria nahwiya says
thank you for sharing this well articulated information
shs strands says
Really an interesting blog I have gone through. There are excellent details you posted here. Thank you for sharing this blog.