 National Income, as the name suggests is the income of a nation, measured in terms of production, during the course of a financial year. Hence, when the production is represented in terms of final goods and services, it is called a National Product, whereas when it is represented in monetary terms, it is National Income. It tends to determine the quantum of economic activity carried out during the course of an accounting period.
National Income, as the name suggests is the income of a nation, measured in terms of production, during the course of a financial year. Hence, when the production is represented in terms of final goods and services, it is called a National Product, whereas when it is represented in monetary terms, it is National Income. It tends to determine the quantum of economic activity carried out during the course of an accounting period.
Contrarily, Domestic Income implies the summation of the factor incomes earned by all the production units, located within the territory of the country.
The post attempts to shed light on the differences between domestic income and national income.
Content: Domestic Income Vs National Income
- Comparison Chart
- Definition
- Key Differences
- Example
- Monetary National Income
- Real National Income
- Conclusion
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Domestic Income | National Income |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Domestic Income implies the income accrued to both residents and non-residents within the geographical boundaries of the country. | National Income is described as the income accrued to the ordinary residents of the country, irrespective of their geographical location (i.e. within and outside the country). |
| Does not matters | Who has generated the income? | Where the income is generated? |
| Represented as | National Domestic Product at Factor Cost (NDPFC) | Net National Product at Factor Cost (NNPFC) |
| Concept | Territorial Concept | National Concept |
| NFIA | Not a part of Domestic Income | Part of Domestic Income |
Definition of Domestic Income
Domestic Income implies the total money value of the final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of the country, during a specified period, say a year. In this way, it covers factor income of both, residents and non-residents, who are generating income within the country.
Further, domestic product and domestic income are one and the same thing.
For example, Foreign banks and companies that operate and earn income in the country are taken into account while calculating the domestic income.
Formula of Domestic Income
Domestic Income = Rent + Wages + Interest + Mixed Income + Profit Tax + Dividend + Undistributed Profit + Surplus of Government Sector (if it is given separately of private sector)
Or
Domestic Income = Compensation of Employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income
What is meant by Domestic Territory?
In the simplest sense, the term ‘domestic territory’ refers to the political boundaries of the nation. Further, it also covers:
- Ships and aircraft, which are owned and run by the normal residents amidst two or more countries.
- Fishing vessels, oil and natural gas rigs, and floating platforms whose operation is undertaken by the country’s residents in international waters, with exclusive rights as to its operation.
- Embassies, consulates, and military establishments of a country located in a foreign country.
However, it does not cover:
- Embassies, consulates, and military establishments belonging to a foreign nation.
- International organizations such as ILO, WHO, UNO, etc. that are located within the political frontiers of a country.
Also Read: Difference Between Intermediate Goods and Final Goods
Definition of National Income
National Product takes into account the total value of all goods and services arising as a result of economic activity. National Income implies the total of all the incomes earned, within or outside the geographical territory of the country, by its ordinary residents.
Therefore, the two are one and the same thing. This is because, the production of goods and services due to the use of primary factors, which tends to generate income.
- It encompasses only factor incomes and excludes transfer income.
- Income of only normal residents of the country is included.
What is Factor Income?
Factor Incomes include monetary payment made to the owners of factors of production by the firm for the factor services used, such as rent for land, interest for capital, wages for labor, profit for entrepreneurs.
Also Read: Difference Between Factor Income and Transfer Income
Who are Normal Residents?
A Normal Resident or Ordinary Resident is the person who ordinarily resides in the country and his/her center of economic interest is present in that country.
Formula of National Income
National Income = Domestic Income + Net Factor Income From Abroad (NFIA)
Net Factor Income from Abroad = Factor Income from Abroad – Factor Income paid Abroad
National Income along with its Related Totals, helps in indicating the macroeconomic performance and forecasting future events. Here, the term ‘related totals’ mean and include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Net Domestic Product (NDP)
- Gross National Product (GNP)
- Net National Product (NNP) at factor cost and at market price
- Personal Income
- Disposable Personal Income.
Also Read: Difference Between GDP and GNP
Features of National Income
- Monetary Expression: Millions of goods and services are produced around the year in an economy, that can be measured in different units like meters, tonnes, liters, kilograms, etc. So, a common base is used to add them together, which is money. That is why it is expressed in monetary terms.
- Flow of final goods: It takes into account the total value of final products only so as to prevent the issue of duplication or double counting. Hence, intermediate goods are not taken into consideration.
- Considers the value of currently produced goods and services: Because national income is a flow concept, it takes into consideration only those goods and services which are produced during such period for which the national income is calculated.
- Reflects only the production of normal residents: It indicates the production of normal residents, working within and outside the country. That is to say, production must be carried out by the owned factors of production only.
- Takes into account only those items which are traded in an organized market: In national income, only those goods are considered which are traded in the organized market while unorganized marketed production is excluded from it.
National Income can be calculated at current prices as well as constant prices.
National income at the current price does not accurately reflect the economic status of the nation, as it is the monetary income and not real income. An increase in such income may occur due to a rise in the prices of goods and services, while there is no real increase in the number of goods and services produced.
National Income at a constant price is the true indicator of economic growth which is reflected in the standard of living of its citizens, as it is the real national income. An increase in such income occurs due to a real increase in the output.
Methods of Calculating National Income
You can calculate the national income of a country, using the following methods:
- Value-added method or product method
- Income method
- Expenditure method
Also Read: Difference Between GDP and GNI
Key Differences Between Domestic Income and National Income
As we have understood the basic concept and formula of these two, now we will talk about the difference between domestic income and national income:
- National Income refers to the aggregate of all factor incomes, accrued to the country’s ordinary residents, during the course of a financial year. On the other hand, Domestic Income implies the sum of all the factor incomes earned by various factors of production, operating within the geographical boundaries of the country, during the course of an accounting year.
- Domestic Income is a territorial concept because it is based on the income generated within the geographical territory. As against, national income is a national concept, because it is based on the residential status of the producers around the world.
- In the calculation of domestic income, it does not matter who generated the income, i.e. it includes all the producers working within the domestic territory of the country, whereas in the calculation of national income, it does not matter where the income is generated, i.e. it takes into account all the producers who are normal residents of the country.
- NDPFC i.e. National Domestic Product at Factor Cost represents domestic income. Conversely, NNPFC which is Net National Product at Factor Cost denotes National Income.
- While Net Factor Income from Abroad is not included in domestic income, the same is considered in the case of national income.
Example
In the above picture, you can see a country, some residents and non-residents who are earning income within and outside that country. So, in this case, let us calculate the domestic income and national income, but first of all, we will recall their definitions.
- Domestic Income: Total Income earned within the domestic territory.
- National Income: Total Income earned by residents.
Therefore,
Domestic Income = 1,50,000 + 80,000 + 60,000 + 1,00,000 + 1,20,000 + 80,000 + 20,000 + 90,000 + 70,000 + 2,00,000 + 60,000 = 10,30,000
National Income = 1,50,000 + 60,000 + 1,00,000 + 20,000 + 70,000 + 2,00,000 + 90,000 + 2,00,000 + 90,000 + 80,000 + 60,000 = 11,20,000
Monetary National Income
Monetary National Income is nothing but National Income at Current Prices. This means that goods and services produced during the period are valued at the prices prevailing in the market.
As a constant increase in the price of goods and services is quite common in the modern economy. Therefore, the monetary national income is higher in comparison to real national income. However, when there is a substantial fall in the prices and production of goods and services, then real national income is greater than monetary national income.
Real National Income
Real National Income indicates National Income at a constant price. Hence, the goods and services valued at the prices of the base year. Hence, the following formula is used to convert monetary income into real income:
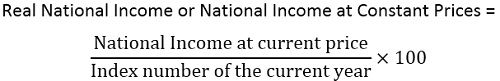
Conclusion
The difference between domestic income and national income is the net factor income from abroad. Further, being a macroeconomic component, it determines the economic growth of a country. It acts as a framework for economic appraisals and projections.





shah says
Nice