 In horizontal power-sharing, no organ has unlimited or absolute powers, whereas, in the case of vertical power-sharing, the power of the central government is the highest and local government is lowest.
In horizontal power-sharing, no organ has unlimited or absolute powers, whereas, in the case of vertical power-sharing, the power of the central government is the highest and local government is lowest.
Democracy is based on the notion that – the source of all political power is people, i.e. citizens of the country. An ideal democracy is one where due respect is given to all the groups and views which are prevalent in society.
And that is why it is believed that political power should be distributed among the maximum possible citizens. Therefore, the concept of power-sharing emerged.
What is Power Sharing?
Power-sharing is an arrangement wherein powers and responsibilities are divided among different organs, levels and social groups. It can take many forms. Of which two most popular forms are – Horizontal Power Sharing and Vertical Power Sharing.
Content: Horizontal Vs Vertical Power Sharing
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Horizontal Power Sharing | Vertical Power Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The horizontal power-sharing is a division of power amidst various organs of the government, which are equally placed. | The vertical power-sharing is a division of power amidst different levels of the government. |
| Power | Government organs work at the same levels to exercise varied powers. | Constitution states the powers of different levels of the government. |
| Checks and balances | Each organ is independent of other organs and thus keeps the other organs under check. | Each unit is the sub-unit of the parent central body. The central body keeps a check on the sub-units. |
| Promotes the concept of | Expansion of Democracy | Deepening of Democracy |
| Purpose | All the organs work at the same level but for different purpose. | All the units work at different level but for the same purpose. |
Definition of Horizontal Power Sharing
In a democratic government, power is divided among different bodies, i.e. legislative, executive and judiciary, wherein legislative body makes laws, executive body implements or enforces them, while it is the judiciary who interprets them.
Such a division of power is called horizontal power-sharing, in which the different government organs are placed at the same rank/position to exercise their power. So, a demarcation is maintained between the organs, which ensures that no government body exercise the absolute power.
In this manner, checks and balances of power are maintained, as each organ checks the other, resulting in the balance of power among various bodies.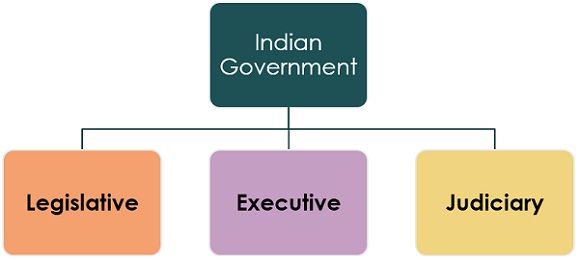
In India, the Legislative organ comprises of the Parliament or Legislative Assembly, Executive organ comprises of the Prime Minister and Cabinet Ministers, while the Supreme Court comes under the Judiciary organ.
Definition of Vertical Power Sharing
In vertical power-sharing, the power is shared among the government working at different levels, i.e. the higher and lower levels. The constitution explicitly describes the powers of each level of government and the lower organ works under the higher one. This is known as the Federal Division of Power.
In this power-sharing arrangement, there is a common government for the whole country and government at the provincial and regional level.
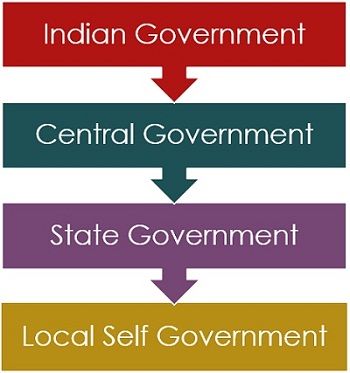 In India, the common government is called the Central Government, while the government working at the provincial and regional level is the State government and Local Self government respectively.
In India, the common government is called the Central Government, while the government working at the provincial and regional level is the State government and Local Self government respectively.
So, there are a number of matters of issues on which the Union government has the exclusive power to make decisions, while there are some matters on which the power is assigned to the State government to take a decision on a matter, which concerns their State.
In general, the Central government looks after the development of the entire country, while it is the responsibility of the State Government to develop the State.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Power Sharing
The points given below are noteworthy, so far as the difference between horizontal and vertical power-sharing is concerned:
- In the horizontal power-sharing method, there is a sharing of power by different organs of the government, which work at the same rank or position. Contrastingly, in vertical power-sharing method, the power is divided among different levels of the government from highest to lowest, by the constitution.
- In the horizontal division of power, there is a demarcation which ensures that no government organ has unlimited powers. On the contrary, in vertical division of power, the different levels of the government have varied degree of powers assigned to them by the constitution.
- In a horizontal power-sharing arrangement the government organs placed at the same level to exercise varied powers. As against, in a vertical power-sharing arrangement the constitution describes the powers of different levels of the government.
- The best thing about horizontal power sharing is that each organ checks the working of other organs, whereas, in the case of vertical power-sharing, the lower organ works under the higher one, so the higher one keeps a check on it.
- The horizontal division of power advocates the concept of expansion of democracy. Conversely, the vertical division of power tends to promote the deepening of democracy.
- In horizontal power-sharing all the government organs work at the same level, to serve different purposes. In contrast, in a vertical power-sharing arrangement, all the units and subunits at different level work for a common goal.
Conclusion
Initially, there is an undivided political power because it is believed that if power is distributed then decision making will be delayed. But, with the introduction of democracy, such beliefs are changed.
The power-sharing arrangements give more power to the general public, from choosing their representatives to having a voice in deciding the public policies.




Leave a Reply