 Motivation implies the process of encouraging people to act in order to attain the desired objectives. It is something that stimulates an individual to keep doing the act already initiated. In this context, Abraham Maslow, a renowned psychologist, highlighted the elements of the theory of motivation, in a classic paper released in 1943. His theory is based on human needs and its fulfilment.
Motivation implies the process of encouraging people to act in order to attain the desired objectives. It is something that stimulates an individual to keep doing the act already initiated. In this context, Abraham Maslow, a renowned psychologist, highlighted the elements of the theory of motivation, in a classic paper released in 1943. His theory is based on human needs and its fulfilment.
On the other hand, Frederick Herzberg is an American psychologist, who coined out the concept of job enrichment and two-factor theory on motivation based on rewards and incentives. He attempted to shed more light on the concept of work motivation.
Check out this article to know the differences between Maslow and Herzberg’s theory on motivation.
Content: Maslow’s Theory Vs Herzberg’s Theory
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory | Herzberg’s Two-factor Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Maslow's Theory is a general theory on motivation which states that the urge to satisfy needs is the most important factor in motivation. | Herzberg's Theory on motivation says that there are various factors existing at the workplace that causes job satisfaction or dissatisfaction. |
| Nature | Descriptive | Prescriptive |
| Relies on | Needs and their satisfaction | Reward and Recognition |
| Order of needs | Hierarchical | No sequence |
| Core concept | Unsatisfied needs stimulate individuals. | Gratified needs regulate behavior and performance. |
| Division | Growth and deficiency needs. | Hygiene and motivator factors. |
| Motivator | Unsatisfied needs | Only higher order needs |
Definition of Maslow’s Theory
Abraham Maslow was an Americal psychologist, who introduced the popular ‘Need hierarchy theory’ on motivation. The theory emphasizes the urge to satisfy needs of people working in the organization.
The theory is divided into two categories, i.e. growth needs and deficiency needs, which are further sub-classified into five needs, within each individual, represented in the shape of a pyramid. The theory is based on the premise that human needs are in proper sequence, wherein psychological need is at the bottom, and self-actualisation needs are at the top level. Other needs, i.e. safety needs, social needs and esteem needs are in the middle.
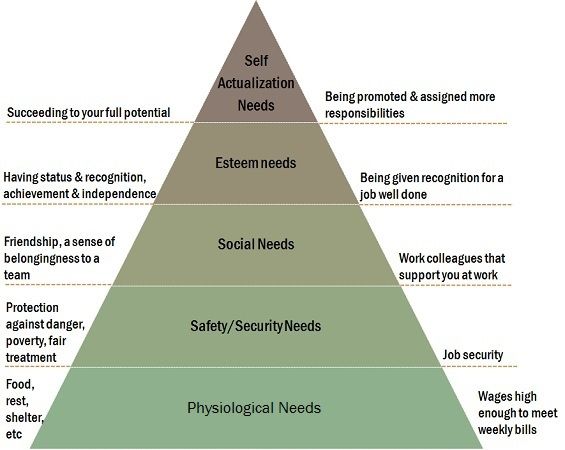 It infers that higher level needs cannot evolve until the lower level needs are satisfied. As the needs of human beings are unlimited, whenever one need is satisfied, another need take its place. Moreover, an unsatisfied need is the motivator which governs the behaviour of the individual.
It infers that higher level needs cannot evolve until the lower level needs are satisfied. As the needs of human beings are unlimited, whenever one need is satisfied, another need take its place. Moreover, an unsatisfied need is the motivator which governs the behaviour of the individual.
Definition of Herzberg’s Theory
Frederick Herzberg was a behavioural scientist, who developed a theory in the year 1959 called ‘The two-factor theory on Motivation or Motivation-Hygiene Theory’.
Herzberg and his associates carried out interviews of 200 persons including engineers and accountants. In that survey, they were asked about the components of a job that make them happy or unhappy, and their answers made it clear that it was the working environment that causes unhappiness or dissatisfaction.
As per the theory, hygiene factors, are essential to keep a reasonable level of satisfaction among employees. Such factors do not actually result in satisfaction, but their absence causes dissatisfaction, that is why, they are known as dissatisfiers. Secondly, motivational factors are inherent to the job, and so the increase in these factors will lead to the rise in the satisfaction level, while the decrease does not cause dissatisfaction in employees.
Key Difference Between Maslow and Herzberg’s Theory of Motivation
The basic points of difference between Maslow and Herzberg’s theory of motivation can be summed up as follows:
- Maslow’s Theory is a general theory of motivation which expresses that the urge to satisfy needs is the principle variable in motivation. In contrast, Herzberg’s Theory on motivation reveals that there are some variables existing at the workplace that results in job satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
- Maslow’s theory is descriptive, whereas the theory propounded by Herzberg is simple and prescriptive.
- The basis of Maslow’s theory is human needs and their satisfaction. On the other hand, the Herzberg’s theory relies on reward and recognition.
- In Maslow’s theory, there is a proper sequence of needs from lower to higher. Conversely, no such sequence exists in the case of Herzberg’s theory.
- Maslow’s theory states that unsatisfied needs of an individual act as the stimulator. As against, Herberg’s theory reveals that gratified needs govern the behaviour and performance of an individual.
- The needs of an individual are divided into two categories i.e. survival/deficiency needs and growth needs as per Maslow. On the contrary, in Herzberg’s model, the needs of an individual are classified into Hygiene and motivator factors.
- In Maslow’s theory, any unsatisfied need of an individual serves as the motivator. Unlike in the case of Herzberg, only higher level needs are counted as the motivator.
Conclusion
The two models developed by the two experts aims at simplifying the motivational process which proved that motivation is an important factor to improve the performance level of employees. Herzberg’s theory is an addition to the Maslow’s theory. These are not contradictory but complementary to one another.





abeer says
I really appreciate this article. very useful.
thanks
abeer
GOWER says
solid website bro
wid recommend to a pal
love
RobbERTO Findlay
maushooq says
useful
K. T. C. Samaraweera says
I am a Psychology under graduate. Thank you for the valuable help that you give us. I request you to mention the name of author clearly. Thank you again.
Maggie says
Very useful information
Pranish Shakya says
Needed this for my MBS Exam. Thank You for pointing light to it.