 Depreciation and amortisation are both meant to reduce the value of the asset year by year, but they are not one and the same thing. Writing off tangible assets for the reporting period is termed depreciation, whereas the process of writing off intangible fixed assets is amortization.
Depreciation and amortisation are both meant to reduce the value of the asset year by year, but they are not one and the same thing. Writing off tangible assets for the reporting period is termed depreciation, whereas the process of writing off intangible fixed assets is amortization.
Long-term fixed assets refer to the assets whose benefit is enjoyed for more than one accounting period. Fixed assets can be tangible fixed assets or intangible fixed assets. The value of fixed assets tends to decrease over time.
As per the matching concept, the part of the asset used for generating revenue needs to be recovered during the financial year so as to match the expenses for the period. And for this purpose, the concepts of depreciation and amortization apply to fixed assets.
In this post, you are going to find the differences between depreciation and amortization in detail.
Content: Depreciation Vs Amortization
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Depreciation | Amortization |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Depreciation is a technique used to measure the decrease in the value of the asset due to age, wear and tear or any other technical reason. | Amortization is an accounting method for periodically lowering the book value of an intangible asset over a period of time. |
| Governing Standard | IAS 16 deals with depreciation | IAS 38 deals with amortization. |
| Applies to | Tangible Assets | Intangible Assets |
| Recognized as | Accelerated basis in general. | Straight line basis in general. |
| Salvage value | Deducted from Cost of Asset while calculating depreciation. | Not deducted from the cost of the asset while calculating depreciation. |
| Objective | Allocating the cost of assets over their expected useful life. | Capitalizing the amount of the cost of an asset over its useful life. |
What is Depreciation?
With time, the value of an asset reduces gradually, and this reduction in its value is called depreciation. The reason for depreciation includes physical wear and tear, obsolescence or passage of time and the utility of using the asset. In simple words, a technique used to determine the loss in the value of the long-term fixed tangible asset due to usage, wear and tear, age or change in market conditions is known as depreciation.
The depreciation is charged as a capital expenditure against the revenue generated from the asset during the year, i.e., the matching concept.
Methods of Depreciation
There are four methods of Depreciation as per GAAP
- Straight-line
- Declining balance or Written down value method
- Sum-of-the-years’ digits, and
- Units of production
An organization may opt for any method of depreciation, but it should be applied consistently in every financial year. If an organization wants to change the method of depreciation, then the retrospective effect is to be given. Any surplus or deficit arising on account of such change in the method of depreciation shall be debited or credited to the profit & loss account as the case may be.
Formula for Depreciation
For calculating depreciation as per the straight-line method, you can use this formula:
(Cost of Asset – Salvage or Scrap Value) / Economic Life
Meaning of Salvage Value
Salvage Value means the value obtained when the asset is resold at the end of its lifetime.
Meaning of Economic Life
Economic Life is the estimated number of life years.
Characteristics of Depreciation
- It is a gradual and permanent fall in the value of fixed assets.
- The process of spreading the cost of an asset over its useful life is not a process of asset valuation.
- It is a charge against profit.
- We use the term ‘depreciation’ for tangible fixed assets only. However, it is not used for wasting assets such as mines, oil wells, etc.
- It is calculated in a systematic manner.
- Factors responsible for depreciation include physical deterioration and obsolescence.
- It is a non-cash expense.
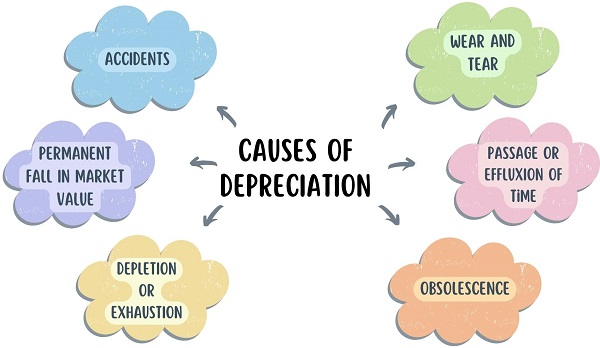
Causes of Depreciation
- Wear and Tear: On the continuous use of the asset in business year after year, its value keeps on decreasing every year due to wear and tear.
- Passage or Effluxion of Time: Some assets lose their value over time, no matter if they are used or not.
- Obsolescence: When the asset gets out of date, we call it obsolescence. This is an era of technology, and technology updates every day. So, machines become obsolete faster than ever before.
- Depletion or Exhaustion: Reduction in the value of wasting assets like minerals, mines, etc. When more and more extraction from mines took place, its value decreased.
- Permanent fall in market value: When the market value of some assets decreases, then it depreciates.
- Accidents: There are instances when an asset met an accident. In such a case, the asset becomes worthless or useless.
Objectives of Providing Depreciation
- Identifying the exact cost of production.
- Ascertaining the exact profit and loss
- Depict correct financial position
- Providing for asset replacement
- Adhering to the statutory requirement
- Availing tax relief
Also Read: Difference Between SLM and WDV
What is Amortization?
Amortization means periodically writing off the book value of a loan or any intangible asset over the expected period in which the asset will provide value. It is a method of incrementally charging the asset cost to expense over its useful life.
In this way, the asset moves from the balance sheet to the income statement. It gives an illusion that the intangible asset is consumed over its life years.
In other words, amortization is a method of measuring the loss in the value of long-term fixed intangible assets due to the passage of time. So, the process of determining their decreased worth is known as amortization.
Long-term fixed intangible assets are the assets which have been owned by the entity for more than three years but do not exist in their material form. For Example: Computer software, licenses, trademarks, copyrights, patents, franchises, etc. Further, we also amortize discounts on notes receivable and deferred charges.
It is a non-cash expense, so it does not need cash outflow. However, it does not diminish the value of the asset. Hence, because the expense is already incurred, amortization does not affect the liquidity of the company.
Formula for Calculating Amortization
You can use this formula for calculating amortization:
Amortization = Cost of Asset / Economic Life
Accounting Treatment
Amortization expense is recorded in the income statement. It results in a decrease in EBIT, and as a result, the tax to be paid by the company is reduced by that amount. Just like depreciation, the amount of amortization is also shown on the assets side of the Balance Sheet as a reduction in the intangible asset.
Also Read: Difference Between Book Value and Market Value
Key Differences Between Depreciation and Amortization
- Depreciation is a method of calculating how use, obsolescence, accident and wear and tear reduces the value of tangible asset. Amortization is an accounting method that evens out the cost of intangible assets used by the company.
- Depreciation applies to tangible assets, i.e. the assets which exist in physical form like plant and machinery, vehicles, computers, furniture, etc. Conversely, Amortization applies to intangible assets, i.e. the assets which exist in their non-physical form like royalty, copyright, computer software, import quotas, etc.
- Generally, the straight-line method is used for amortization so that the same amount is charged to expenses in every financial year. In contrast, companies often use a written-down value method for charging depreciation. The reason is the recognition of depreciation on an accelerated basis.
- The primary objective of depreciation is to allocate the cost of assets over their expected useful life. Unlike amortization, which focuses on capitalizing the amount of the cost of an asset over its useful life.
- Tangible assets possess salvage value; that is, the owner gets resale value, which is commonly included in the calculation of depreciation. Conversely, salvage value is not a part of amortization because intangible assets have no resale value after the expiration of their useful life.
- While IAS 16 deals with depreciation, IAS 38 deals with amortization.
- Depreciation is charged to rationally spread the cost of fixed assets over their useful life. Conversely, the use of amortization is to match the cost of using an intangible asset and the revenue which the asset generates in the normal course of business.
Conclusion
The only difference is that depreciation applies to tangibles while amortization applies to intangibles. Both are non-monetary capital expenditures. Hence, they are shown on the assets side of the Balance Sheet as a reduction in the value of the asset concerned. However, these two terms are governed by different accounting standards.





Esther Ifeoluwa says
Thanks for this.
well detailed and explained