 In olden times, in the absence of any medium of communication and technology, people used to store data in the form of written records. During that time, people used to write on palm leaves or bark of a tree and that handwritten sheet is popularly known as a manuscript. A script is a form of writing, which over a period of time evolved as language and then it is developed as literature.
In olden times, in the absence of any medium of communication and technology, people used to store data in the form of written records. During that time, people used to write on palm leaves or bark of a tree and that handwritten sheet is popularly known as a manuscript. A script is a form of writing, which over a period of time evolved as language and then it is developed as literature.
At that time, important messages and memories are engraved on rocks, pillars, clay tablets, and copper plates, by the rulers, which are called inscriptions. These help in reconstructing the history of the country.
This post describes the main differences between manuscripts and inscriptions, along with interesting facts and some practical details about them.
Content: Manuscripts Vs Inscriptions
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Manuscript | Inscription |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A manuscript is one such document, book, or piece of something, from the past which is handwritten and used to record history. | Inscriptions are meant to record historical events, which are carved with the use of words and symbols, to keep a permanent record. |
| Type of Source | Literary Source | Literary and Archaeological Source |
| Material used | These are written on palm leaves, the bark of trees, or on papers such as vellum, papyrus, and parchment. | These are engraved on stones, marbles, rocks, and metals. |
| Nature of Information | One or two-liner information | Bulky historical information |
| Preservation | Difficult as they are written on such surfaces which are prone to decomposition over time. | Easy, because they are written on such surfaces which are non-perishable. |
| Modification | Not possible | Easy to modify |
Definition of Manuscripts
A manuscript is a primitive and handwritten composition which records events, information, and memories of the past. For the purpose of keeping records:
- Dried leaves of palm trees, dried skin of sheep and goat, cloth, and bark of birch trees are often found in the Himalayas, or another plain surface is used.
- Writing is done with a brush reed or pen or some colored fluid.
- Plam leaves were cut to make pages and then these pages are fastened together, to create a booklet.
As the manuscript is written on perishable material due to which they have a very short life and so some of them get either partially or fully destroyed by insects, infected by fungus, or decompose over time while some survived. They are preserved in temples, monasteries, and archives.
These are ancient books of that time. The manuscript contains contemporary events which tell us about our past and inform us about the customs, religious beliefs practices, cultures and lifestyle (both social and economical) of the people and the traditions followed by people during that time.
Must Know
- Manuscripts can be found in numerous languages and scripts, many of these are not anymore read. A particular language can be written in a variety of scripts.
- They contain knowledge-based content.
- They are available in various types of repositories, such as museums, temples, learning institutions, etc
- They have long been neglected and are not in good physical condition. They are faded, brittle, fungus-infected, and insect-ridden.
Also Read: Difference Between Literature and Language
Definition of Inscriptions
Inscriptions are written records that are carved on the seals, stones, pillars, clay, caves, walls, wells, and copper and metallic plates of religious places, wooden tablets, stone pillars, rock surfaces, tombs, palaces, Stupas, slabs, bricks, images, and monuments. They are of official nature and designed for public observation.
They are an authentic source of information that tells the history of a country, as they bring forth the name of the king or ruler, years they ruled administration, the extent of their era, and dynasty as well. Also, they tell the language and lifestyle of the people, military achievements, social and religious conditions.
Interesting Facts
- Harappan script of c. 2500 BCE is the oldest inscription which is not yet deciphered.
- Ashokan inscriptions are the earliest deciphered script that existed on rock surfaces and stone pillars and found in every part of the subcontinent. These are mainly in the Brahmi script.
- Inscriptions were generally engraved on copper plates, called Tamrapatra, Danapatra, or Shasanapatra.
The subject in which we study inscriptions is known as Epigraphy. These are premier and copious sources of the political, social, commercial, and economic history of the country. Hence, for historians, inscriptions are an amazing tool that provides information about contemporary events and common people of that time. These are available in languages like Sanskrit, Tamil, Prakrit, Telegu, and so forth.
There are a number of inscriptions that carry relevant information about genealogy, dynastic details, the extent of empire, and names of those kings whose name has not been referred in ancestry.
Additionally, the inscriptions written in various Indic scripts, which are used for different purposes.
Types of Inscriptions
There are mainly nine types of inscriptions, depicted hereunder: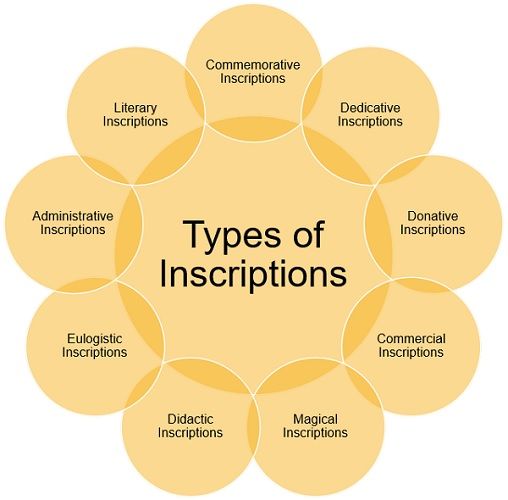
Let us discuss each of them, one by one:
| Commemorative Inscriptions | It keeps a record of births, deaths, spectacular achievement, or visits of kings or famous people and victory of a king, or protagonist or warrior. |
| Dedicative Inscriptions | Otherwise called as votive inscriptions. It is concerned with the construction of temples and the installation of statues, by the kings or rulers or any other person. It contains the name of the ruler who initiated it. |
| Donative Inscriptions | It contains donations made by the kings for different purposes. It also includes endowments made and grants given to Brahmin priests for the maintenance of temples by the kings or any official or a person. In these inscriptions the details of the grant is also furnished along with the name of person who made the donation. |
| Commercial Inscriptions | It includes coins and seals, which are used for writing for commercial purposes. |
| Magical Inscriptions | It contains the name of invocations of the God or Goddess represented by the animals unique to their group. The seals contain a magical formula. |
| Didactic Inscriptions | It include religious ethics and morals, and worldly advice.It is concerned with the statements, and the preaching of religion or morality. These are also known as religious inscriptions. |
| Eulogistic Inscriptions | These are to praise the activities of the kings and gives references to the military, administrative and literary achievements and qualities of kings. It may be a sheer eulogy or mixed with other types. |
| Administrative Inscriptions | It covers political and administrative aspects of rulers. They were engraved with the purpose of announcing the orders issued by the king among the people. |
| Literary Inscriptions | It includes pieces of poetic compositions, prose, dramas, etc. |
There are also a number of inscriptions that contain long panegyrics, that praise the kings and boasts their administrative powers.
Also Read: Difference Between Prose and Poetry
Key Differences Between Manuscripts and Inscriptions
As we have discussed the meaning and importance of these two literary sources of ancient times. Now we will talk about the difference between manuscript and inscription:
- Manuscript refers to the prehistoric handwritten record, in the form of a booklet, and contains information about the past culture, society, life, and traditions. On the other hand, inscriptions are the writings on hard and long-lasting material that are used to commemorate the victory, announce grants of land, or proclaim administrative degrees, record historical events, which are carved with the use of words and symbols, to keep a permanent record.
- While the manuscript is a literary source, the inscription is both a literary and archaeological source. It includes fossil remains, coins, monuments, written records, etc. which assist in the reconstruction of the past.
- The manuscript is written on dried leaves of a palm tree, dried skin of sheep, or bark of birch tree, whereas inscriptions are found on the stones, pillars, tombs, and caves. Inscriptions are engraved by the rulers or kings.
- While the manuscript consists of one or two liner information, the inscription consists of bulky historical information.
- Preservation of manuscripts is quite difficult as they are written on such material which is prone to decomposition over time, or they may be destroyed by insects. In contrast, preservation of inscriptions is very easy, as they are engraved on such material which is non-perishable in nature.
- Modifications cannot be made in the manuscript, whereas inscriptions are relatively easy to modify.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What did the manuscript contain?
Manuscripts contain information related to religious beliefs and practices followed by the people, the lifestyle of kings and rulers, medicines to cure certain diseases, and scientific information. Many manuscripts also contain poems, plays, and epics written in languages like Sanskrit, Prakrit, and Tamil.
How do scholars know what information is written in the inscription?
Inscriptions were carved more than a hundred years ago and with the passage of time the script, as well as the language, have changed. Therefore, a process called Decipherment is used by scholars to understand the matter written on the inscription.
What is a Script?
The script is a system or style of writing a language. When the sounds of a particular language are represented symbolically, it is termed as a script.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, both manuscripts and inscriptions are important as they contain the past of the country, its society, culture, achievements, events, etc. Hence, they need to be preserved with care and caution.





Leave a Reply