 A private limited company is a closely held one and requires at least two or more persons, for its formation. On the other hand, a public limited company is owned and traded publicly. It requires seven persons for its setup.
A private limited company is a closely held one and requires at least two or more persons, for its formation. On the other hand, a public limited company is owned and traded publicly. It requires seven persons for its setup.
What is a Company?
The company refers to that voluntary association of persons which is established with an aim of achieving common objectives. It is a separate legal entity, i.e. one should not confuse between the company and its members as both are different personalities in the eyes of law. Also, it is characterized by perpetual succession, common seal, capacity to sue and be sued, and capital that is divided into transferable shares.
Also Read: Difference Between Partnership Firm and Company
This post will enlighten you with all the differences between Private Limited Company and a Public Limited Company.
Content: Private Limited Company Vs Public Limited Company
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Private Limited Company | Public Limited Company |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Private Limited Company refers to the company which is not listed on a stock exchange and the shares are held privately by the members concerned. | Public Limited Company implies a company that is listed on a recognized stock exchange and whose shares are traded openly by the public. |
| Minimum number of members | 2 | 7 |
| Maximum number of members | 200, except in case of one person company | Unlimited |
| Minimum number of directors | 2 | 3 |
| Articles of Association | It must frame its own articles of association. | It can frame its own articles of association or adopt Table F. |
| Transfer of Shares | The shares of a private company are not freely transferable, as there are restrictions in Articles of Association. | The shares of a public company are freely transferable, i.e. freely traded in an open market called a stock exchange. |
| Public Subscription | Issue of shares or debentures to the public is prohibited. | It can invite the public to subscribe to its shares or debentures. |
| Issue of prospectus | Prohibited from issuing a prospectus. | It can issue a prospectus or it can also opt for private placement. |
| Minimum amount of allotment | The company can allot shares, without obtaining minimum subscription. | The company cannot allot shares unless the minimum subscription stated in the prospectus is obtained. |
| Commencement of Business | It can start a business just after receiving a certificate of incorporation. | It requires a certificate of commencement of business after it is incorporated. |
| Appointment of Director | Two or more directors can be appointed by a single resolution. | One Director can be appointed by a single resolution. |
| Filing of Consent to act as Director | Directors need not require the filing of their consent to act as a director. | Directors must file their consent to act as a director, within 30 days of appointment with the Registrar. |
| Retirement of Directors by rotation | The directors are not required to retire by rotation. The directors can be permanent. | 2/3rd of the total number of directors must retire by rotation. |
| Place of Holding AGM | AGM can be held anywhere. | AGM is held at the registered office or any other place where the registered office is situated. |
| Statutory Meeting | Optional | Compulsory |
| Quorum | 2 members who are personally present at the meeting, constitute a quorum, irrespective of the number of members. | 5 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is 1000 or less. |
| 15 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is more than 1000 but less than 5000. | ||
| 30 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is more than 5000. | ||
| Exemptions | Enjoys many privileges and exemptions. | No such privileges and exemptions. |
Definition of Private Limited Company
A private limited company is a company that is created and incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013, or any other act being in force. It is a company that is not listed on a recognized stock exchange and whose shares are not traded publicly. It restricts the right to transfer shares the liability of the company is limited to the number of shares held by them
There is a limit on the maximum number of members, i.e. the number of members cannot be more than 200, excluding current employees and ex-employees who were members of the company when they were employed and continued to become members even after they left the company. Further, one should take note of the fact that joint holders of shares are treated as single members.
Further, in a private company, any sort of invitation to the public to subscribe for shares is prohibited.
Also Read: Difference Between Members and Shareholders
Registration Requirements
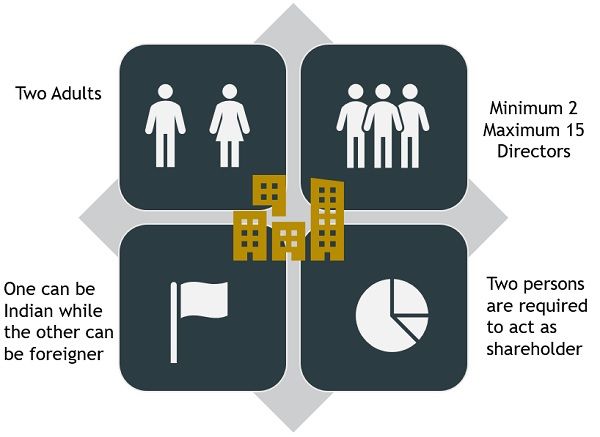
- At least two adults are required to act as the Director of the Company.
- It can have a maximum of 15 Directors
- At least one director has to be an Indian Citizen and Resident, while the others can be foreign nationals.
- Two persons must act as a shareholder.
Documents Required for Incorporation of Private Limited Company
- Proposed Directors who are Indian Nationals need to submit a copy of PAN as their ID proof and passport or Driving License or Voter ID or Adhar Card as their proof of address. They are also required to submit their bank statement or electricity/phone bill as their proof of residence.
- Proposed Directors who are Foreign Nationals need to submit a copy of their passport as their ID proof which can also act as a proof of address. They are also required to submit a copy of their bank statement or electricity/phone bill as their proof of residence.
- If the registered office is set up in a rented property, a rental agreement and no objection certificate by the landlord are required.
- If a registered office is set up in an owned property, ownership property documents are needed.
- Utility bills of the business place
Definition of Public Limited Company
A Public Limited Company or PLC is a joint-stock company that is created and incorporated under The Indian Companies Act, 2013 or any other act being in force previously. It is listed on a recognized stock exchange to raise capital from the general public.
It is a company with limited liability and is permitted to issue registered securities i.e. shares or debentures to the public, by inviting them to subscribe for its shares through IPO and is traded openly on at least one stock exchange. The liability of the shareholders is limited to the extent of the amount contributed by them.
Also Read: Difference Between IPO and FPO
Incorporation Requirements
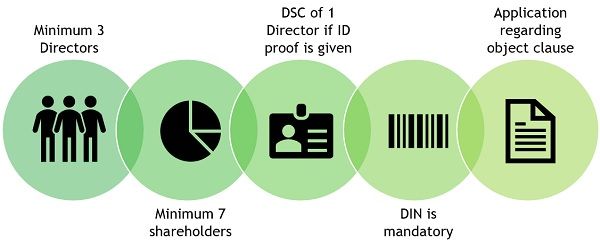
- Minimum number of 3 directors are required to form a public company.
- Minimum 7 shareholders are required to form a public company.
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) of any one director is required, in case self-attested copies of identity proof and address proof are submitted.
- Director Identification Number (DIN) is a must.
- An application containing the object clause of the company is to be made.
Also Read: Difference Between Executive and Non-Executive Director
Documents Required for Incorporation of Public Limited Company
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) and Directors Identification Number (DIN) of all Directors
- Copies of identity proofs such as Adhar Card, Voter ID, PAN Card or passport of all directors
- Passport size photograph of all Directors.
- If the registered office is set up in a rented property, a rental agreement and no objection certificate by the landlord are required.
- If a registered office is set up in an owned property, ownership property documents are needed.
- Utility bills of the business place
Points to be noted
- As per Section 185 of Companies (Amendment) Act, 2017, there is a complete ban on providing loans, guarantees, or advances to the Directors or its holding company, or any partner of the Director or any firm wherein the Director or relative is a partner.
- The maximum number of Directors that a company can appoint is 15. However, a company can appoint more than 15 Directors by passing a special resolution at the general meeting.
Key Differences Between Private and Public Limited Company
After learning about the meaning of the two types of companies, let us understand the difference between a private limited company and a public limited company:
- The public limited company refers to a company that is listed on a recognized stock exchange and its securities traded publicly in an open market. On the other hand, a private limited company is one that is not listed on a stock exchange, as its stock is held privately by the members.
- A private limited company has to frame its own articles of association, whereas a public limited company has two choices, i.e. either it can frame its own articles or it can adopt Table F.
- When it comes to the transfer of shares, there are restrictions in the articles of association regarding the transferability of the shares of a private company. Further approval of the Board of Directors is needed for such transfer. In contrast, there is no restriction on the transfer of shares in the case of a public limited company i.e. freely traded in an open market called a stock exchange.
Also Read: Difference Between Bombay Stock Exchange and National Stock Exchange - A private limited company is strictly prohibited from inviting the public to subscribe for its shares or debentures, whereas a public limited company can go for a public subscription to raise capital, through an IPO.
- A private limited company cannot issue a prospectus. It may issue shares by way of private placement by following the procedure given in Part II of Chapter III. Conversely, a public limited company can issue a prospectus by following the procedure given in part I of Chapter III or it can also opt for private placement by following the procedure contained in Part II of Chapter III.
Also Read: Difference Between Private Placement and Preferential Allotment - A private company can allot shares, even when it has not received a minimum subscription. Oppositely, a public company is restricted from alloting shares to the public unless the minimum subscription stated in the prospectus is received.
- To form a private limited company minimum of two members are required, whereas in the case of a public limited company at least seven members must be there for its formation.
- A private limited company can have a maximum of 200 members, except in the case of one person company, where there is one member. In contrast, in a public limited company, there can be unlimited members.
- At least two adults who act as a director are required at the time of incorporation of a private limited company. As against, a minimum of three directors is required in the case of a public limited company for its incorporation.
- A private limited company can start its business just after receiving the certificate of incorporation, whereas a public company needs a certificate of commencement of business after it has received a certificate of incorporation, to commence business.
- In a private limited company, two or more directors can be appointed by a single resolution, which is not in the case of a public limited company.
- In the case of a private company, directors need not require to file their consent to act as a director. On the other side, in the case of a public company, directors must file their consent with the registrar to act as a director within 30 days of their appointment as a director.
- 2/3rd of the total number of directors of a public limited company must retire by rotation. Conversely, the directors of a private company are not required to retire by rotation, they can be permanent.
- In the case of a private company, 2 members who are present physically at the general meeting, constitute a quorum, irrespective of the number of members. On the other hand, in the case of a public company, to form a quorum:
- 5 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is 1000 or less
- 15 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is more than 1000 but less than 5000
- 30 members are required to present in person when the number of members as on the date of the meeting is more than 5000.
- Talking about the place of holding Annual General Meeting (AGM), in case of a private company AGM can be held anywhere, whereas in the case of a public company AGM can be held at the registered office of the company or any other place within the city, village or town where the registered office is situated.
Also Read: Difference Between AGM and EGM - While a private company is not required to organize a statutory meeting, a public must organize a statutory meeting and deliver the report of such meetings to the shareholders and file the same with Registrar.
- Private Limited Company has greater operational flexibility, as compared to Public Limited Company in carrying out affairs of the company. There are a number of requirements and restrictions from which a private company is exempted that apply to a public company.
Video: Private Limited Company Vs Public Limited Company
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is it compulsory for companies to follow the SPICe+ process for incorporation of the company?
W.e.f. 23rd Feb 2020, every company must make an application for name reservation and incorporation of the company by way of web service SPICe+. One can reserve the unique name of the company in Part A of the SPICe+ form. It has the facility to apply for name, incorporation, and various integrated services at the same time by filling in the required details in Part A and Part B.
After filling the form in full, it has to be converted into pdf form, for affixing digital signatures. Once it is done, the digital applications can be uploaded with the linked forms i.e. eMOA, eAOA, etc.
Also Read: Difference Between MOA and AOA
What is Part A of web form SPICe+?
It is a section of the SPICe+ form, which contains details relating to name reservations for a new company. It can be submitted individually or combinedly with Part B. Part B offers services like incorporation, allotment of Directors Identification Number (DIN), mandatory issue of PAN, TAN, EPFO registration, etc.
What is SPICe+ form?
It is a unified form and a part of government initiative towards Ease of Doing Business (EODB).
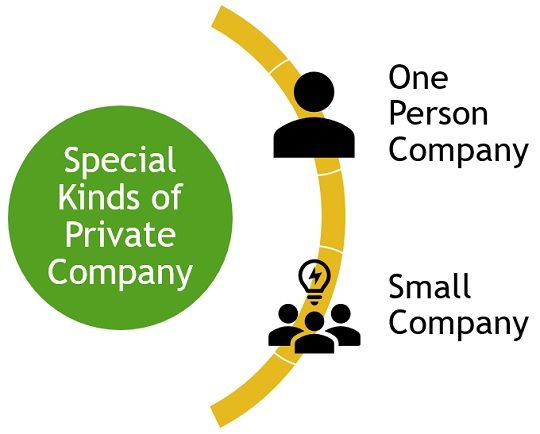
Special Kinds of Private Limited Company
There are two special kinds of Private Limited Company, these are:
One Person Company
A company with just one person as a member is a one-person company and so the name of that person is entered in the company’s memorandum who acts as a director as well. Such a company can be formed for any lawful purpose by one person. He has to be a natural person who is a resident of the country. Further, the company can be formed under a company limited by shares or a company limited by guarantee.
Also Read: Difference Between Authorized Capital and Issued Capital
Small Company
A company can be regarded as a small company when:
- Its paid-up capital does not exceed Rs. 50 lakh, and
- Its turnover as per the previous income statement should not be more than 20 crores.
Both the clauses must be satisfied i.e. if the company’s paid-up capital is 38 lakhs but the turnover is more than Rs. 2 crores, then the company won’t fall in the category of a small company for the year in which it crosses the limits specified and all the exemptions given to that company will not apply.
It is to be noted that the hitherto clause is not applicable to holding companies or subsidiary companies, companies registered under section 8 (charitable institutions), company governed by any special activities such as banking or insurance companies.
Conclusion
While a private company needs to add the words ‘Private Limited (Pvt. Ltd.)” at the end of its name, as a suffix, a public limited company needs to add the words ‘Limited’ at the end of its name.



MUSTAPHA ADAM says
THIS SITE HAS BEEN SO HELPFUL IN COMPLETING MY ASSIGNMENTS. THANKS SO MUCH.
Jessica Thomas says
Sure it’s very easy and simple to understand.
sebi says
This is a proper definition of both companies,thanx for helping us
Samuel v says
Nice, It also helped me in my assignments in school.
Can you put comparison of different forms of business organizations?, not everything, like
Sole proprietorship
Partnership
Co-operative society&
Company- Pvt. & Public…
Surbhi S says
Thanks and we will soon update the difference on the site, keep viewing.
Also me ur fan says
I am even studying this for exams thank u very much
indhu pavul says
Perfect article.
Ramanuj Prasad says
Very important difference of this website for preparation of exams
Rakesh Sharma says
Great , I Am fully satisfied.
Vishal Gupta says
This is a very clear and cut difference. I am fully satisfied with this meaningful data.
Achal says
Thanks for writing in such a way that it is so easy to understand.
ANAND says
Nice article.
Peter Morris says
I am fully satisfied with this meaningful data.This is a very clear and cut difference.
Surbhi S says
To all the readers,
Thank you all for appreciating the articles, it means a lot to us. Keep liking, sharing and reading. 🙂
Stuart Mutebi says
Thanks a lot it has fully introduced me to the business world
Sajal says
Nice article.very easy to understand.
Aann says
Jindal comes in which category…??
Surbhi S says
It is a public company.
Likhit says
Just out of curiosity looked at this post. Thank you for your clear and simple explanation.
hassan duale says
wow this is a nice article
Radha says
It’s easy to understand Thankyou🥰🤗🤗
Viyan says
Thank you for sharing this valuable information. It is most appreciated.
Ranjana pradhan says
It’s really a complete package
kirtan kumar says
very good information thanks for knowledge nice blog
VENUS POWER says
VERY INFORMATIVE FOR THE STARTUPS TO UNDER STAND THE PROCEDURE OF INCORPORATION