 In a business, purchases are made by the firm to keep a stock of goods for the purpose of reselling it to customers and also for producing other products. When the purchases are made, they are recorded in the purchase day book first which indicates the name of the supplier and other details as to the product bought. Thereafter, the total is transferred to the Purchases account every month from the Purchases Book.
In a business, purchases are made by the firm to keep a stock of goods for the purpose of reselling it to customers and also for producing other products. When the purchases are made, they are recorded in the purchase day book first which indicates the name of the supplier and other details as to the product bought. Thereafter, the total is transferred to the Purchases account every month from the Purchases Book.
Purchase Book is a book of original entry, just like Journal. In fact, it is a subdivision of the Journal that keeps a record of credit purchases only. Contrarily, Purchase Account is a summary of the total purchases made throughout the year, for trading or producing activity.
What are Cash Purchases?
When the payment of goods purchased from the seller, is made immediately by the buyer, using cash, card, cheque or via any online mode, it is called cash purchases.
What are Credit Purchases?
When the payment of goods purchased from the seller is made at a future date by the seller, i.e. the seller allows a credit period to the buyer for making the payment is called Credit Purchases.
In this content, we are going to clear all your doubts regarding the difference between Purchase Book and Purchase Account.
Content: Purchase Book Vs Purchase Account
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Purchase Book | Purchase Account |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Purchase Book is a special purpose journal which is used to keep a systematic record of the goods bought on credit. | Purchase Account is a part of ledger, which balance of the purchase book is posted at the end of each month. |
| What is it? | Subsidiary Book | Ledger Account |
| Records | Only credit purchases | Both cash and credit purchases |
| Transfer | Total amount of Purchases book is posted in ledger at periodic intervals. | Balance of Purchase Account is transferred to Trading Account. |
| Debit and Credit side | No | Yes |
| System of Recording | Chronological recording of credit purchases. | Periodical total of the purchase book is taken to Purchase Account. |
| Contains | All information related to credit purchase of the goods. | Concerned Account to be debited or credited with their respective amount. |
| Basis of Entry | Source Document i.e. Invoice or Bill | Purchase Book and Cash Book |
| Is it considered at the time of preparing final accounts? | No | Yes |
Definition of Purchase Book
Purchase Book is a book of original entry, which keeps a record of credit purchases on a day-to-day basis, which is either used as raw material for production, or as stock for resale to customers. While entering the transactions in the purchase book, one must ensure that the credit purchases are of the items in which the firm is dealing. It is also called Purchase Journal.
The recording of transactions in the purchase book is made on the basis of purchase invoices, which are received by the entity from the supplier, that bear the net amount, after deducting the trade discount.
Advantages of Purchase Book
- It is useful for those entities with more credit purchases.
- Lessens the overall work, needed to pass journal entry.
- Ledger posting becomes easy as all the entries for credit purchases are recorded in a single book.
- Every single credit purchase is not required to be debited from the purchase account. Instead, the periodical total of the purchase day book is debited.
- One can get the required information relating to credit purchases.
- Any error committed at the time of entering the purchases can be identified at the time of posting.
What is Stock?
The term ‘stock’ represents the merchandise in which the trader trades, i.e. those items which are bought from the supplier for the purpose of regular sales. Hence, the cloth is a stock for a cloth merchant, diamond is the stock for a diamond merchant.
Points to Remember
- Only items related to the core business operations are recorded in the Purchases Book.
- Recording of cash purchases of goods and assets are recorded in Cash Book.
- Purchases of assets on credit bought for the purposes of running the business are not recorded in the purchase book. These are recorded separately in Journal Proper.
What is an Invoice
An invoice is a source document which the seller prepares and issues to the customer, which states the goods sold along with its details as to the quantity, price, discount, and tax. It includes additional charges for freight and transport. It indicates the total amount owed by the customer.
Also Read: Difference Between Voucher and Invoice
Definition of Purchase Account
Purchase Account is a ledger account that accumulates transactions concerned with purchases of merchandise be it cash or credit. In other words, all the transactions related to the purchase of goods are recorded in the ledger by opening a purchase account. In this way, the owner can get all the relevant information as to the purchase of goods, in one place.
- Like all other ledger accounts, the purchase account is also divided into two sides, i.e. Debit and Credit.
- It only records the value of purchases of stock made during a particular period.
- It is maintained under General Ledger.
- Purchase Account is a Nominal Account and the Creditors (Supplier’s) Account is a Personal Account.
- Purchases account always reflect debit balance, which is taken to the debit side of the Trading Account, at the end of the period.
As the purchase book only keeps the record of credit purchases, cash purchases are recorded in the cash book. So, it is necessary to refer to both while posting the transactions in the purchase account. It indicates the status of total purchases.
Posting from Purchase Book, in Purchase Account
Posting in Personal Account
Individual amounts are posted to the credit of the supplier’s account on a daily basis, as ‘By Purchases Account’ in the particulars column, and the respective amount is entered in the Amount column on the credit side, of the account.
Posting of Periodical Total
Periodical Total is entered in the debit side of the Purchases Account as ‘To Sundries as per Purchases Book’ in the particulars column, of the purchase account and the total amount is entered in the Amount column of the debit side.
Also Read: Difference Between Cash Book and Cash Account
Key Differences Between Purchase Book and Purchase Account
As we have compared the two and also discussed their meanings. Let us understand the difference between Purchase Book and Purchase Account:
- Purchase Book is a daybook in which non-cash purchase transactions are recorded in chronological order. Conversely, a Purchase account is a ledger account wherein all the entries related to purchasing merchandise for the business are recorded, be it cash or credit.
- Purchase Book and Purchase Account, represent two steps of the accounting cycle, wherein first of all the entry of the transaction is recorded in the purchase book, thereafter it is posted in the purchase account.
- A purchase book is a subsidiary book in which the merchandise purchased on credit is recorded. As against, the Purchase account is a part of the chart of accounts, wherein both cash and credit purchases are posted.
- The total amount of the Purchase book, at the end of each month, is taken to the Purchase ledger. Oppositely, the balance of the Purchase Account is transferred to Trading Account, usually at the end of the financial year.
- There are no debit and credit sides in Purchase Book, whereas Purchase Account has a debit side and a credit side.
- In a purchase book, each item is recorded in the order in which it took place, whereas, in the purchase account, the total of the purchase journal is posted at the end of every month.
- The purchase book contains all the relevant information related to the credit purchase of the goods, such as the name of the vendor, quantity, and rate of the goods and total amount. As against, In purchase account, we only mention the concerned account which is to be credited or debited and the respective amount.
- Source Document i.e. Invoice or Bill received from the supplier, acts as a basis of an entry in case of Purchase Book. On the Contrary, Purchase Book for credit purchases and Cashbook for cash purchases acts as a basis of an entry in the Purchase Account.
- At the time of preparing final accounts, the purchase account is generally referred, to transfer the balance in the trading account at the end of the financial year. As against, purchase book is not referred for such purposes.
Format of Purchase Book
- Date Column: In this column, the date of receipts/invoices of goods are entered.
- Particulars Column: The name of the supplier is entered first. Thereafter a brief description of the goods received is entered.
- Purchase Invoice Number Column: In this column, you need to enter the unique number of the purchase invoice of goods received.
- Ledger Folio Column: The page number of the ledger, wherein the respective transaction can be found, is entered here. This is for checking and reference of the records.
- Details Column: It is used to write the individual total of the items purchased from a supplier when more than one item has been bought. Apart from that, when a trade discount is allowed by the supplier, then the amount of discount can be deducted from the total amount of purchase.
- Amount Column: The net amount payable to the supplier with respect to the goods bought from the supplier is entered here.
Format of Purchase Account
- Date Column: In this column, we add the transaction date and not the date of posting from journal to ledger.
- Particulars Column: In this column, we either debit or credit the concerned account, considering the context of the transaction, as well as narration, can be added to describe the transaction in short.
- Journal Folio Column: In this column, we give page reference of the journal, on which the transaction is entered first and then posted in the concerned ledger account,
- Amount Column: In this column, the amount of the transaction is entered.
Example
01 July 2021, Purchased Cloth from Zed Corporation
1000 metres silk @ ₹ 20 per metre
200 metres cotton @ ₹ 12 per metre
15 July 2021, Purchased Cloth from Dee Textiles
300 metres Georgette @ ₹ 15 per metre
400 metres Cotton @ ₹ 10 per metre
25 July 2021, Purchased cloth from EL Limited
150 metres Chiffon @ ₹ 10 per metre
29 July 2021, Purchased cloth in cash from Vee Enterprises
200 metres Rayon @ ₹ 12 per metres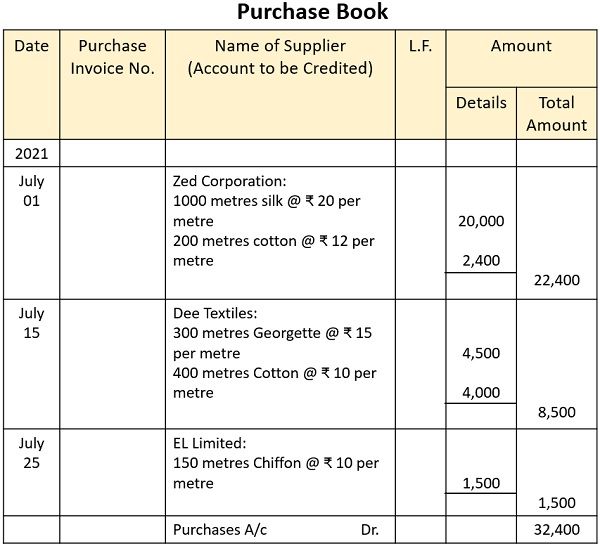
The purchase account will be created as follows: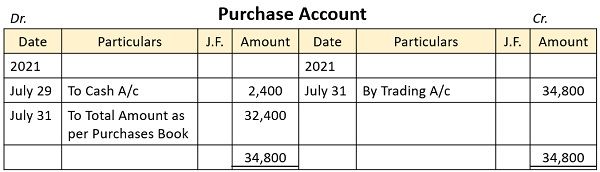
Conclusion
If the entries are correctly made in the purchase book, and then posted in the purchase account, the degree of occurrence of error will be zero. While the purchase book gives the required details about the purchases, the purchase account provides total purchases made by the firm every month.




Leave a Reply