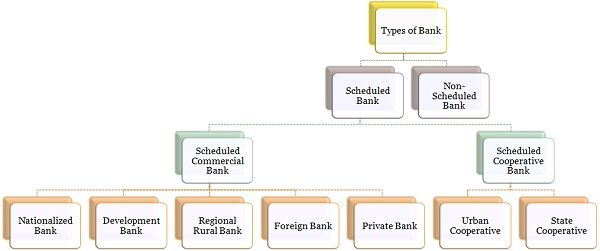
 Banks implies the financial institution that takes public deposits and extends credit to those who need it. They are a substantial part of the financial system, which assists in the overall economic development. These are broadly classified as scheduled and non-scheduled banks in India regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, wherein scheduled banks include all the commercial banks like nationalised, foreign, development, cooperative and regional rural banks.
Banks implies the financial institution that takes public deposits and extends credit to those who need it. They are a substantial part of the financial system, which assists in the overall economic development. These are broadly classified as scheduled and non-scheduled banks in India regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, wherein scheduled banks include all the commercial banks like nationalised, foreign, development, cooperative and regional rural banks.
On the other extreme, non-scheduled banks are the banks that do not adhere to the norms prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). In this article excerpt, you can find out all the relevant differences between scheduled and non-scheduled banks in India.
Content: Scheduled Bank Vs Non-Scheduled Bank
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Scheduled Banks | Non-Scheduled Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Scheduled banks is a banking corporation whose minimum paid up capital is Rs. 5 lakhs and does not harm the interest of the depositors. | Non-scheduled banks are the banks which do not comply with the rules specified by the Reserve Bank of India, or say the banks which do not come under the category of scheduled banks. |
| Second Schedule | Listed in the second schedule. | Not-listed in the second schedule. |
| Cash Reserve Ratio | Maintained with RBI. | Maintained with themselves. |
| Borrowing | Scheduled banks are allowed to borrow money from RBI for regular banking purposes. | Non-Scheduled banks are not allowed to borrow money from RBI for regular banking purposes. |
| Returns | To be submitted periodically. | No such provision of submitting periodic returns. |
| Members of clearing house | It can become a member of clearing house. | It cannot become member of clearing house. |
Definition of Scheduled Bank
Scheduled Banks as the name suggest are the banks, which are accounted in the Second Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Act, 1934. To qualify as a scheduled bank, the bank should conform to the following conditions:
- The total minimum value of paid up capital and reserve must be of Rs. 5 lacs.
- The bank requires to satisfy the central bank that its affairs are not carried out in a way that causes harm to the interest of the depositors.
- The bank needs to be a corporation rather than a sole-proprietorship or partnership firm.
Scheduled banks enjoy certain rights such as:
- Right to receive refinance facility from the apex bank
- Entitled for currency chest facility.
- Right to become members of clearing house
However, they are required to fulfil certain obligations like maintenance of an average daily balance of CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) with the central bank at the rates specified by it. Add to that; these banks need to submit returns at regular intervals, to the central bank subject to the rules of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Definition of Non-Scheduled Bank
Non-Scheduled Bank refers to the banks which are not listed in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India.
In finer terms, the banks which do not comply with the provisions specified by the central bank, within the meaning of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, or as per specific functions, etc. or as per the judgement of the RBI, are not able to serve and protect the depositor’s interest, are known as non-scheduled banks.
Non-Scheduled Banks are also required to maintain the cash reserve requirement, not with the RBI, but with themselves. These are local area banks.
Key Differences Between Scheduled and Non-Scheduled Bank
The difference between scheduled and non-scheduled banks can be drawn clearly on the following premises:
- A banking corporation whose paid up capital is Rs. 5 lacs or more and does not harm the interest of the depositors, is called as Scheduled bank. Unlike, non-scheduled banks are the banks which are not capable of complying with the provision of RBI, for scheduled banks.
- Scheduled banks are the ones covered in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank, whereas non-scheduled banks are the banks that are not covered in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank.
- Scheduled Banks need to maintain cash reserves with RBI, at the rates prescribed by it. On the other hand, Non-Scheduled Bank also needs to keep cash reserves, but with themselves only.
- Scheduled banks are entitled to borrow money from the central bank for regular banking purposes. Conversely, non-scheduled banks are not entitled to borrow money from the central bank for regular banking purposes. Nevertheless, under abnormal conditions, they can request the central bank for accommodation.
- Scheduled banks must submit the periodic returns to the Reserve bank of India. As against, there is no such requirement of submission of periodic returns to the central bank, in case of non-scheduled banks.
- Scheduled banks have the right to become the member in clearing house, while no such facility is allowed to non-scheduled banks.
Conclusion
When it comes to privileges, scheduled banks is ahead of non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks get remittances through the offices of the Reserve Bank of India and its agents, for free or at concessional rates. Moreover, borrowing facilities by Central Bank on the submission of the documents. Such facilities are not provided to the non-scheduled banks.





Kiran sonawane says
Very good information is provided in easy language
But I want much more information related to pathapedhi
What is the difference between pathapedhi and bank
Jaywant Javle says
Whether Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) mandatory for non scheduled Banks. How RBI regulates/supervises non scheduled Banks. If not, who regulates non scheduled Banks
DINESH KUMAR says
GOOD
vikas sinha says
very good article, rest of the information found on googling was so bad
Maria says
Thank you for sharing with us