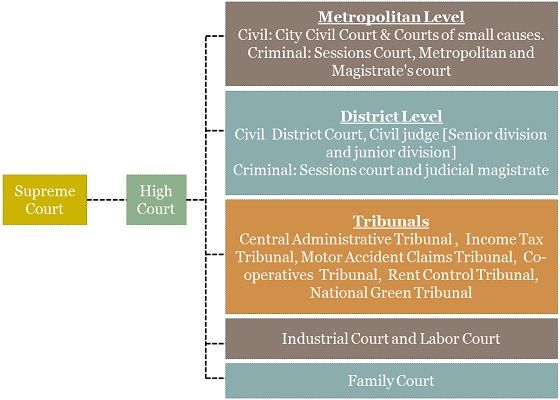
 The judiciary wing of the constitution performs a range of functions like dispute resolution, judicial review, enforcing fundamental rights and upholding law. It regulates the common law system of the country. In India, there are various levels of the judiciary which include the Supreme Court, the High Courts and the subordinate courts. The subordinate courts include district courts and tribunals. The first and foremost difference between court and tribunal is that tribunals are subordinate to courts.
The judiciary wing of the constitution performs a range of functions like dispute resolution, judicial review, enforcing fundamental rights and upholding law. It regulates the common law system of the country. In India, there are various levels of the judiciary which include the Supreme Court, the High Courts and the subordinate courts. The subordinate courts include district courts and tribunals. The first and foremost difference between court and tribunal is that tribunals are subordinate to courts.
Courts are established to maintain law and order in the respective jurisdiction. On the contrary, tribunals are a part of judicial set up that deals with direct taxes, labour, cooperatives, claims for accidents, etc. Check out this article for more differences.
Content: Tribunal Vs Court
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Tribunal | Court |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Tribunals can be described as minor courts, that adjudicates disputes arising in special cases. | Court refers to a part of legal system which are established to give their decisions on civil and criminal cases. |
| Decision | Awards | Judgement, decree, conviction or acquittal |
| Deals with | Specific cases | Variety of cases |
| Party | A tribunal may be a party to the dispute. | Court judges are impartial arbitrator and not a party. |
| Headed by | Chairperson and other judicial members | Judge, panel of judges or magistrate |
| Code of Procedure | No such code of procedure. | It has to follow the code of procedure strictly. |
Definition of Tribunal
Tribunal is a quasi-judicial institution that is set up to deal with the problems such as resolving administrative or tax related disputes. It performs a number of functions like adjudicating disputes, determining rights between contesting parties, making an administrative decision, reviewing an existing administrative decision and so forth. The different types of tribunals are:
- Central Administrative Tribunal: The tribunal is set up to resolve the disputes related to the recruitment and service conditions for selected personnel in public services, as well as posts as regards the union affairs or other local authorities.
- Income Tax Appellate Tribunal: The tribunal is set up to deal with appeals under the direct tax acts, wherein the decision made by the tribunal is considered as final. However, if a material question of law arises for determination, then the appeal goes to the High Court.
- Industrial Tribunal/Labor Court: It is a judiciary body which is established to adjudicate industrial disputes concerning any matter. The tribunal consists of one person who is designated as the presiding officer of a Tribunal.
- Motor Accidents Claim Tribunal: The tribunal is formed to deal with the matters and disputes concerning the motor accidents claims provided by the Motor Vehicle Act, 1988. According to the Act, a compulsory third party insurance has to be done and proper procedure to be adopted by the tribunal to settle the claims under dispute.
Definition of Court
The court can be described as the judiciary body set up by the government to adjudicate disputes between the competing parties through a formal legal process. It aims at giving justice in civil, criminal and administrative matters, as per the rule of law. In short, a court is a government institution where the decision on legal matters is taken by the judge or panel of judges or magistrate. The various types of courts are described as under:
- Supreme Court: The Supreme Court is an apex body, which is a court of record. All the courts in the country are bounded by the law made by the Supreme Court. It entertains appeals with respect to civil and criminal cases from the High Court and certain tribunals. It is the protector and guarantor of fundamental rights of the citizens.
- High Court: The chief judiciary at the state level is the High Court which enjoys civil and criminal, general and special jurisdiction. It has supervisory power over the subordinate courts and tribunals.
- Subordinate Courts: There are several civil and criminal courts, both original and appellate, that functions in their respective jurisdiction. These courts have same functions all around the country, with slight variations.
Key Differences Between Tribunal and Court
The points presented below explain the differences between tribunal and court:
- Tribunals mean the body of members who are elected to settle the controversies arising under certain special matters. On the other extreme court is understood as the judicial institution which is established by the constitution to administer justice, by legislation.
- The decision given by the tribunals on a particular matter is known as the award. As against this, the court’s decision is known as judgement, decree, conviction or acquittal.
- While tribunals are formed to deal with specific matters, courts deal with all types of cases.
- The tribunal can be a party to the dispute, whereas a court cannot be a party to the dispute. A court is impartial in the sense that it acts as an arbitrator between the defendant and prosecutor.
- The court is presided over by the judge, panel of judges, i.e. jury, or magistrate. Unlike, tribunals are headed by a chairman and other judicial members, elected by the appropriate authority.
- There is no code of procedure in a tribunal, but a court has a proper code of procedure, which must be followed strictly.
Conclusion
Both courts and tribunals are established by the Government, which possess judicial powers and have a perpetual succession. By and large, tribunals deal with special cases for which they are formed, while the rest of the cases are dealt in the courts, on which the judge gives his/her verdict.






konda prathap says
great work of difference
Ragini says
Really helpful …..thank u so much😊
minoo says
I am a paralegal student.
English is my second language so I have some difficulties to understand the differences between some subjects.
Since I found this site, I am able to study more deeply and understanding much better.
I appreciate the people who created this site.
swapan says
Really helpful
Ashik Reza Chowdhury says
Very good
Namatiti sofie says
Nice
Namwanje Shakirah says
Of much help
Brenda joey says
Great work❤️
iparked says
Very helpful
thank you
Phu Pham says
Thanks for the detailed explanations. They are truly helpful to me.